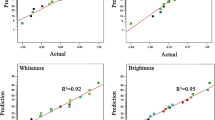
Abstract
Nowadays, the paper industry supplies its required fibers either from primary fibers, including wood and plants, or waste papers, called secondary fibers. One of the most challenging recycling processes is deinking of papers digitally printed with electrophotographic ink. In order to produce optically high-quality paper from recycled waste papers, deinking step is required at the desired levels. In this work, the environmentally friendly green enzymatic deinking of printed paper was modeled and optimized via an innovative approach called artificial intelligence method. The effect of treatment temperature, treatment time, and enzyme dosage on mechanical properties (tensile and burst strengths) as well as optical properties (whiteness and brightness) of handsheet was investigated. The developed code can appropriately learn the non-linear behavior of deinking process, and make decisions according to the pattern constructed intelligently. Finally, multi-objective optimization at the specified treatment temperature, treatment time, and enzyme dosage was performed to identify the best conditions for enzyme-deinked handsheet (maximized mechanical and optical properties).
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahn S, Rehan S, Moon DG, Eo YJ, Ahn SK, Yun JH, Cho A, Gwak J (2017) An amorphous Cu--In--S nanoparticle-based precursor ink with improved atom economy for CuInSe 2 solar cells with 10.85% efficiency. Green Chem 19:1268–1277
Andami F, Ataeefard M, Najafi F, Saeb MR (2016) From suspension toward emulsion and mini-emulsion polymerisation to control particle size, particle size distribution, and sphereness of printing toner. Pigment Resin Technol 45:363–370
Andami F, Ataeefard M, Najafi F, Saeb MR (2017) Understanding the interactive effects of material parameters governing the printer toner properties: a response surface study. J Polym Eng 37:587–597
Andersen J, Mack J (2018) Mechanochemistry and organic synthesis: from mystical to practical. Green Chem 20:1435–1443
Ataeefard M (2015) Production of black toner through emulsion aggregation of magnetite, carbon black, and styrene-acrylic co-polymer: investigation on the effect of variation in components. J Compos Mater 49:1553–1561
Ataeefard M, Nourmohammadian F (2015) Producing fluorescent digital printing ink: investigating the effect of type and amount of coumarin derivative dyes on the quality of ink. J Lumin 167:254–260
Ataeefard M, Saeb MR (2015) A multiple process optimization strategy for manufacturing environmentally friendly printing toners. J Clean Prod 108:121–130
Bazrafshan Z, Ataeefard M, Nourmohammadian F (2015) Modeling the effect of pigments and processing parameters in polymeric composite for printing ink application using the response surface methodology. Prog Org Coat 82:68–73
Casal-Campos A, Fu G, Butler D, Moore A (2015) An integrated environmental assessment of green and gray infrastructure strategies for robust decision making. Environ Sci Technol 49:8307–8314
Dienes D, Egyhazi A, Reczey K (2004) Treatment of recycled fiber with Trichoderma cellulases. Ind Crop Prod 20:11–21
Efrati Z, Talaeipour M, Khakifirouz A, Bazyar B (2013) Impact of cellulase enzyme treatment on strength, morphology and crystallinity of deinked pulp. Cellul Chem Technol 47:547–551
Him NRN, Apau C, Azmi NS (2016) Effect of temperature and pH on deinking of laser-jet waste paper using commercial lipase and esterase. J Life Sci Technol 4:79–84
Jeffries TW, Klungness JH, Sykes MS, Rutledge-Cropsey KR (1994) Comparison of enzyme-enhanced with conventional deinking of xerographic and laser-printed paper. TAPPI J 77:173–179
Kiatkamjornwong S, Kongsupapsiri C (2000) Control of monodisperse particle size of styrenic—acrylate copolymers in dispersion copolymerization. Polym Int 49:1395–1408
Kim K, Kim I, Oh Y, Lee D, Woo K, Jeong S, Moon J (2014) Influence of precursor type on non-toxic hybrid inks for high-efficiency Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 thin-film solar cells. Green Chem 16:4323–4332
Kipphan H (2001) Handbook of print media: technologies and production methods. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN: 978-3-540-29900-4
Leach R (2012) The printing ink manual. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN: 978-94-017-5148-3
Marshall G (1997) Recent Progress in Toner Technologies. IS&T Press, Springfield
Ni W, Wu S, Ren Q (2013) Silanized TiO2 nanoparticles and their application in toner as charge control agents: preparation and characterization. Chem Eng J 214:272–277
Pala H, Mota M, Gama FM (2004) Enzymatic versus chemical deinking of non-impact ink printed paper. J Biotechnol 108:79–89
Pathak P, Bhardwaj NK, Singh AK (2011) Optimization of chemical and enzymatic deinking of photocopier waste paper. BioResources 6:447–463
Rosen M, Ohta N (2006) Color desktop printer technology. CRC Press. eBook ISBN 9781315221458
Soni R, Nazir A, Chadha BS (2010) Optimization of cellulase production by a versatile Aspergillus fumigatus fresenius strain (AMA) capable of efficient deinking and enzymatic hydrolysis of Solka floc and bagasse. Ind Crop Prod 31:277–283
Steinmann ZJN, Schipper AM, Hauck M, Huijbregts MAJ (2016) How many environmental impact indicators are needed in the evaluation of product life cycles? Environ Sci Technol 50:3913–3919
Taheran M, Komtchou S, Lonappan L, Naji T, Brar SK, Cledon M, Drogui P (2017) Environmental issues of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1107–1142
Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, Huddleston M, Landis AE, Sherman J, Shrake SO, Copley-Woods N, Bilec MM (2015) Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol 49:1779–1786
Zhang J, Qiu H, Li X, Niu J, Nevers MB, Hu X, Phanikumar MS (2018) Real-time nowcasting of microbiological water quality at recreational beaches: a wavelet and artificial neural network-based hybrid modeling approach. Environ Sci Technol 52:8446–8455
Zou Y, Wang X, Khan A, Wang P, Liu Y, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2016) Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environ Sci Technol 50:7290–7304
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.G.H. performed the analyses. M.A. is the corresponding author and wrote the manuscript. S.M.S.T. performed the ANN and contributed to the writing of the manuscript. S.M.E. and S.M. performed the analyses. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ataeefard, M., Tilebon, S.M.S., Etezad, S.M. et al. Intelligent modeling and optimization of environmentally friendly green enzymatic deinking of printed paper. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 39486–39499 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15622-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15622-7