Abstract
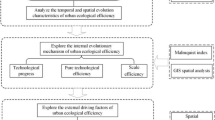
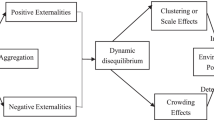
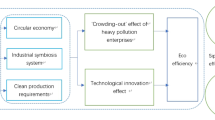
Nowadays, the development of green economy and the improvement of environmental efficiency have been a hotspot in both academia and industry. Especially, the effect of the collaborative agglomeration of manufacturing and productive services industries on environmental efficiency has drawn attention from Chinese policymakers, during a critical period of industrial transformation and upgrading and ecological civilization construction in China. However, few studies have explored whether and how industrial collaborative agglomeration affects environmental efficiency based on population structure perspective. To bridge this gap, using the methods of the stochastic frontier approach (SFA), the moderating effect of population structure, and the spatial effect, and employing the panel data of 66 cities in eastern China during 2009-2018, this paper studies the effect of industrial collaborative agglomeration on environmental efficiency and measure the fluctuates of influence including population structure. The results show that industrial collaborative agglomeration has the effect of improving environmental efficiency, and both of them have strong spatial spillover effect. Direct effect of the industrial collaborative agglomeration is more significant positive than indirect effect. It indicates that the environmental efficiency is affected by the industrial collaborative agglomeration in both the local region and neighboring regions. In addition, population density, aging and quality play a positive moderate role by strengthening the spillover effect of industrial collaborative agglomeration, while the moderating effect of population urbanization is not significant. Then, the recommendations and policy implications to improve environmental efficiency are put forward based on the research results: optimizing the coordinated governance system of regional ecological environment, accelerating the innovation of industrial value chain, and promoting the sustainable development of industry and ecology with the advantage of population structure.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amigues J, Moreaux M (2019) Competing land uses and fossil fuel, and optimal energy conversion rates during the transition toward a green economy under a pollution stock constraint. J Environ Econ Manag 97:92–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2019.03.006
Ben Arfi W, Hikkerova L, Sahut J (2018) External knowledge sources, green innovation and performance. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 129:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.017
BP (2019) Statistical review of world energy, London. https://www.nengapp.com/news/detail/2263237, Accessed 18 March 2021.
Burridge P (1981) Testing for a Common Factor in a Spatial Autoregression Model. Environ Plan A 13(7):795–9800. https://doi.org/10.1068/a130795
Chen L, Jia G (2017) Environmental efficiency analysis of China's regional industry: a data envelopment analysis (DEA) based approach. J Clean Prod 142:846–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.045
Chen D, Chen S, Jin H (2018a) Industrial agglomeration and CO2 emissions: Evidence from 187 Chinese prefecture-level cities over 2005–2013. J Clean Prod 172:993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.068
Chen H, Hao Y, Li J, Song X (2018b) The impact of environmental regulation, shadow economy, and corruption on environmental quality: theory and empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 195:200–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.206
Cheng Z (2016) The spatial correlation and interaction between manufacturing agglomeration and environmental pollution. Ecol Indic 61:1024–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.060
Ehrenfeld JR (2005) Eco-Efficiency-Philosophy, theory, and tools. J Ind Ecol 9(4):6–8. https://doi.org/10.1162/108819805775248070
Elhorst JP, Bao Y, Florax RJGM, Le Gallo J (2014) Matlab Software for Spatial Panels. Int Reg Sci Rev 37(3):389–405. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017612452429
Gan T, Yang H, Liang W, Liao X (2021) Do economic development and population agglomeration inevitably aggravate haze pollution in China? New evidence from spatial econometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5063–5079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10847-4
Gao JM, Li XH (2011) Theoretical and empirical study on the interactive mechanism between producer services and manufacturing. China Indust Econ 6:151–160 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2011.06.015
Golley J, Zheng W (2015) Population dynamics and economic growth in China. China Econ Rev 35:15–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2015.05.005
Han F, Xie R, Fang J (2018) Urban agglomeration economies and industrial energy efficiency. Energy 162:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.163
He Q, Han J, Guan D, Mi Z, Zhao H, Zhang Q (2018) The comprehensive environmental efficiency of socioeconomic sectors in China: An analysis based on a non-separable bad output SBM. J Clean Prod 176:1091–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.220
Huang C, Wang JW, Wang CM, Cheng JH, Dai J (2021) Does tourism industry agglomeration reduce carbon emissions? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:30278–30293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12706-2
Kilicoglu C, Cetin M, Aricak B, Sevik H (2020) Site selection by using the multi-criteria technique-a case study of bafra, turkey. Environ Monit Assess 192(9):608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08562-1
Kilicoglu C, Cetin M, Aricak B, Sevik H (2021) Integrating multicriteria decision-making analysis for a gis-based settlement area in the district of atakum, samsun, turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 143:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03439-2
Lan F, Sun L, Pu W (2021) Research on the influence of manufacturing agglomeration modes on regional carbon emission and spatial effect in China. Econ Model 96:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2020.03.016
Lee R, Mason A (2010) Some macroeconomic aspects of global population aging. Demography 47:151–172. https://doi.org/10.1353/dem.2010.0002
LeSage JP, Pace RK (2010) Spatial econometric models. In Handbook of applied spatial analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp 355–376
Li XG, Yang J, Liu XJ (2013) Analysis of Beijing's environmental efficiency and related factors using a DEA model that considers undesirable outputs. Math Comput Model 58(5):956–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2012.10.016
Li T, Han D, Feng S, Liang L (2019a) Can Industrial Co-Agglomeration between Producer Services and Manufacturing Reduce Carbon Intensity in China? Sustainability 11(15):4024. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11154024
Li Z, Zhou Y, Wan B, Chen Q, Huang B, Cui Y, Chung H (2019b) The impact of urbanization on air stagnation: Shenzhen as case study. Sci Total Environ 664:347–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.232
Li XH, Xu YY, Yao X (2021) Effects of industrial agglomeration on haze pollution: a Chinese city-level study. Energy Policy 148:111928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111928
Lin BQ, Tan RP (2019) Economic agglomeration and green economy efficiency in China. Econ Res J 54:119–132 (in Chinese)
Liu XP, Zhang XL (2021) Industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and carbon productivity: evidence from china. Resour Conserv Recycl 166(2):105330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105330
Liu J, Cheng Z, Zhang H (2017) Does industrial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? J Clean Prod 164:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.179
Liu W, Zhan J, Zhao F, Wei X, Zhang F (2020) Exploring the coupling relationship between urbanization and energy eco-efficiency: a case study of 281 prefecture-level cities in China. Sustain Cities Soc 64:102563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102563
Maddala GS, Wu S (2010) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):631–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1631
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China (MEE), 2018. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, http://english.mee.gov.cn/News_service/news_release/201812/P020181203536441502157.pdf. Accessed 18 March 2021.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, (2020). China Statistical Yearbook 2020. China Statistics Press, Beijing, China. https://www.chinayearbooks.com/china-statistical-yearbook-2020. html. Accessed 18 March 2021.
O'Neill BC, Dalton M, Fuchs R, Jiang L, Pachauri S, Zigova K (2010) Global demographic trends and future carbon emissions. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107(41):17521–17526. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1004581107
Ramanathan R (2005) An Analysis of Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Countries of the Middle East and North Africa. Energy 30:2831–2842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2005.01.010
Ren YH, Xu L, You WH (2010) A spatial econometric model and its application on the factors of financial industry agglomeration. J Quant Tech Econ 5:104–115 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2010.05.011
Shen L, Wang Y (2018) Supervision mechanism for pollution behavior of Chinese enterprises based on haze governance. J Clean Prod 197:571–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.160
Shi B, Shen KR (2013) The government intervention, the economic agglomeration and the energy efficiency. Manag World 10:6–18 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2013.10.002
Song M, Guan Y (2014) The environmental efficiency of Wanjiang demonstration area: a Bayesian estimation approach. Ecol Indic 36:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.007
Song M, Wang S, Zhang H (2020) Could environmental regulation and R&D tax incentives affect green product innovation? J Clean Prod 258:120849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120849
Su Y, Yu Y (2020) Spatial agglomeration of new energy industries on the performance of regional pollution control through spatial econometric analysis. Sci Total Environ 704:135261–135261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135261
Waiengnier M, Van Hamme G, Hendrikse R, Bassens D (2020) Metropolitan Geographies of Advanced Producer Services: Centrality and Concentration in Brussels. Tijdschr Econ Soc Geogr 111(4):585–600. https://doi.org/10.1111/tesg.12394
Wang Q, Yuan B (2018) Air pollution control intensity and ecological total-factor energy efficiency: the moderating effect of ownership structure. J Clean Prod 186:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.106
Wang ZW, Cui BS, Zhang QY (2017) Modern Models and Methods of Spatial Econometrics. Peking University Press, Peking, pp 7–8
Wang B, Sun YF, Wang ZH (2018) Agglomeration effect of CO2 emissions and emissions reduction effect of technology: a spatial econometric perspective based on china's province-level data. J Clean Prod 204:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.243
Wang K, Wu M, Sun Y, Shi X, Sun A, Zhang P (2019a) Resource abundance, industrial structure, and regional carbon emissions efficiency in China. Res Policy 60:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.01.001
Wang X, Klemeš JJ, Dong X, Fan W, Xu Z, Wang Y, Varbanov PS (2019b) Air pollution terrain nexus: A review considering energy generation and consumption. Renew Sust Energ Rev 105:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.01.049
Wierzbowski M, Filipiak I, Lyzwa W (2017) Polish energy policy 2050-An instrument to develop a diversified and sustainable electricity generation mix in coal-based energy system. Renew Sust Energ Rev 74:51–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.02.046
Woo C, Chung Y, Chun D, Seo H, Hong S (2015) The static and dynamic environmental efficiency of renewable energy: a Malmquist index analysis of OECD countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.070
Wu YM, Li JX (2008) Spatial econometric analysis of energy consumption of Chinese provinces. China Popul Resources Environ 3:93–98 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2008.03.017
Xi JP (2017) Full text of Xi Jinping's report at 19th CPC National Congress. http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/19thcpcnationalcongress/2017-11/04/content_34115212.htm, Accessed 18 March 2021.
Xie LY (2013) A spatial econometric analysis of impact of Chinese provinces' R&D investment on economic growth. China Soft Sci 9:37–47 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-9753.2013.09.004
Xie R, Yao S, Han F, Fang J (2019) Land Finance, Producer Services Agglomeration, and Green Total Factor Productivity. Int Reg Sci Rev 42(5-6):550–579. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017619836270
Xu LH, Deng YP (2012) Does foreign direct investment lead to environmental pollution in China? ——Spatial measurement based on Chinese provincial panel data. Manag World 2:30–43 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2012.02.004
Xu H, Zhao JW (2020) The green technology advancement effect of R&D investment: based on the perspective of technological progress at the city level. China Popul Resources Environ 30(02):121–128 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.12062/cpre.20191017
Yang T, Wang Q (2020) The nonlinear effect of population aging on carbon emission-empirical analysis of ten selected provinces in china. Sci Total Environ 740:140057. 740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140057
Yang ZB, Shao S, Zhang C (2015) Production Comparative Advantage, Ratchet Effect and Technical Capital Deviation of Chinese Industry. J Quant Tech Econ 32(09):39–55 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2015.09.003
Yang Z, Song T, Chahine T (2016) Spatial representations and policy implications of industrial co-agglomerations, a case study of Beijing. Habitat Int 55(3):32–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.02.007
Yang GQ, Li MQ, Meng X (2017a) The scale of migrants, fiscal autonomy and the allocation of public goods——the spatial econometric test of 286 cities' panel data. China Soft Sci 6:49–58 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-9753.2017.06.006
Yang Y, Liu J, Zhang Y (2017b) An analysis of the implications of China’s urbanization policy for economic growth and energy consumption. J Clean Prod 161:1251–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.207
Yang W, Yuan G, Han J (2019) Is China's air pollution control policy effective? Evidence from Yangtze River Delta cities. J Clean Prod 220:110–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.287
Yang H, Lu F, Zhang F (2020) Exploring the effect of producer services agglomeration on China’s energy efficiency under environmental constraints. J Clean Prod 263:121320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121320
Yuan YJ, Xie RH (2015) Empirical research on the relationship of industrial agglomeration, technological innovation and environmental pollution. Stud Sci Sci 33(9):1340–1347 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-2053.2015.09.007
Yuan H, Feng Y, Lee C, Cen Y (2020) How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ 92:104944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104944
Zeng W, Li L, Huang Y (2021) Industrial collaborative agglomeration, marketization, and green innovation: Evidence evidence from China’s provincial panel data. J Clean Prod 279:123598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123598
Zhang Y, Da Y (2013) Decomposing the changes of energy-related carbon emissions in China: evidence from the PDA approach. Nat Hazards 69(1):1109–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0752-5
Zhang H, Han AH, Yang QL (2017) Spatial Effect Analysis of Synergetic Agglomeration of Manufacturing and Producer Services in China. J Quant Tech Econ 34(2):3–20 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2017.02.001
Zhang Y, Shen L, Shuai C, Bian J, Zhu M, Tan Y, Ye G (2019) How is the environmental efficiency in the process of dramatic economic development in the Chinese cities? Ecol Indic 98:349–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.006
Zhou Y, Xing X, Fang K, Liang D, Xu C (2013) Environmental efficiency analysis of power industry in China based on an entropy SBM model. Energy Policy 57:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.09.060
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41571121); Innovation Research for the Postgraduates of Guangzhou University (Grant No.2020GDJC-D01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yue Zhu: Methodology, Software, Writing—Original draft preparation. Wenbo Du: Data curation, Validation, Visualization. Juntao Zhang: Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work does not require any ethical approval.
Consent to participate
The authors obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out.
Consent to publish
All authors agree with the content and give explicit consent to submit and publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, ., Du, W. & Zhang, J. Does industrial collaborative agglomeration improve environmental efficiency? Insights from China’s population structure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 5072–5091 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15618-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15618-3