Abstract
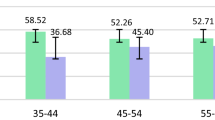
Heavy metals have been well documented to pose detrimental health effects. The current study aimed to measure the concentration of chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) in urinary samples of Iranian pregnant females and determine their potential correlations with different lifestyle variables. The study was conducted in 2019–2020 in Isfahan, Iran, and the urine samples were collected from 140 pregnant women. The concentrations of Cr and Ni in the urinary samples were measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). Data on socio-demographic characteristics, use of cleaning products, and lifestyle profiles was collected by validated questionnaires. Cr and Ni were detected in 100% of urinary samples with the mean concentration of 4.1±3.4 and 7.5±4.8 μg/g creatinine, respectively. Significant associations were found between the mean concentration of Cr and Ni with using cooking utensils made of copper, aluminum, Teflon, steel, and enameled, as well as with cosmetic use, and second-hand smoking exposure during pregnancy. The results also showed that the mean urinary Ni and Cr concentrations were significantly different among individuals who consumed seafood and canned food (p-value <0.05). Furthermore, the mean of urinary Cr and Ni concentrations at high levels of physical activity and scratched utensils used was significantly different from the other categories (p-value <0.05). According to our findings, the lifestyle determinants and cosmetic products had superiority to socio-demographic characteristics in predicting urinary heavy metals in Iranian pregnant women.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidadi H, Dehghan A, Zamand S, Mohammadi A, Taghavimanesh V, Akbari Sharak N (2019) Evaluation the amount of lead, cadmium, mercury, nickel and tin in canned tuna fish available in Neyshabur markets in 2017. J Neyshabur Univ Med Sci 7:48–57
Amadi CN, Igweze ZN, Orisakwe OE (2017) Heavy metals in miscarriages and stillbirths in developing nations. Middle East Fertil Soc J 22:91–100
Amin MM, Parastar S, Ebrahimpour K, Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Hashemi M, Mansourian M, Kelishadi R (2018b) Association of urinary phthalate metabolites concentrations with body mass index and waist circumference. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:11143–11151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1413-8
Amin MM, Ebrahim K, Hashemi M, Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Rafiei N, Mansourian M, Kelishadi R (2019a) Association of exposure to bisphenol A with obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Health Res 29:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2018.1515896
Berardi R, Pellei C, Valeri G, Pistelli M, Onofri A, Morgese F, Caramanti M, Mirza RM, Santoni M, De Lisa M (2015) Chromium exposure and germinal embryonal carcinoma: first two cases and review of the literature. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part A 78(1):1–6
Briffa J, Sinagra E, Blundell R (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 6(9):e04691
Castro-González M, Méndez-Armenta M (2008) Heavy metals: implications associated to fish consumption. E Toxicol Pharmacol 26:263–271
Chang CH, Liu CS, Liu HJ, Huang CP, Huang CY, Hsu HT, Liou SH, Chung CJ (2016) Association between levels of urinary heavy metals and increased risk of urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol 23:233–239
Chiba M, Masironi R (1992) Toxic and trace elements in tobacco and tobacco smoke. Bull World Health Organ 70:269
Cleland C, Ferguson S, Ellis G, Hunter RF (2018) Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) for assessing moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and sedentary behaviour of older adults in the United Kingdom. BMC Med Res Methodol 18:176
Corbin JC, Mensah AA, Pieber SM, Orasche J, Michalke B, Zanatta M, Czech H, Massabò D, Buatier de Mongeot F, Mennucci C (2018) Trace metals in soot and PM2. 5 from heavy-fuel-oil combustion in a marine engine. Environ. Sci. Technol 52:6714–6722
Dan EU, Ebong GA (2013) Impact of cooking utensils on trace metal levels of processed food items. Ann Food Sci Technol 14:350–355
Darvishmotevalli M, Bina B, Feizi A, Ebrahimpour K, Pourzamani H, Kelishadi R (2019) Monitoring of urinary phthalate metabolites among pregnant women in Isfahan Iran: the PERSIAN birth cohort. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17:969–978
Darvishmotevalli M, Moradnia M, Noorisepehr M, Fatehizadeh A, Fadaei S, Mohammadi H, Salari M, Jamali HA, Daniali SS (2019b) Evaluation of carcinogenic risks related to nitrate exposure in drinking water in Iran. MethodsX 6:1716–1727
Darvishmotevalli M, Moradnia M, Hosseini R, Bina B, Feizi A, Pour KE, Pourzamani HR, Kelishadi R (2021) Association between prenatal phthalate exposure and anthropometric measures of newborns in a sample of Iranian population. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int:1–11
DiBenedetto MK, Schunk DH (2018) Self-efficacy in education revisited through a sociocultural lens. Big Theories Revisited 2:117
Fadaei S, Noorisepehr M, Pourzamani H, Salari M, Moradnia M, Darvishmotevalli M, Mengelizadeh N (2021) Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for degradation of Reactive Black 5: batch and column study. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105414
Feng W, Cui X, Liu B, Liu C, Xiao Y, Lu W, Guo H, He M, Zhang X, Yuan J (2015) Association of urinary metal profiles with altered glucose levels and diabetes risk: a population-based study in China. PLoS One 10:e0123742
Fort M, Cosín-Tomás M, Grimalt JO, Querol X, Casas M, Sunyer J (2014) Assessment of exposure to trace metals in a cohort of pregnant women from an urban center by urine analysis in the first and third trimesters of pregnancy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:9234–9241
Fu Z, Xi S (2020) The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol Mech Methods 30:167–176
Gangwar C, Choudhari R, Chauhan A, Kumar A, Singh A, Tripathi A (2019) Assessment of air pollution caused by illegal e-waste burning to evaluate the human health risk. Environ Int 125:191–199
Ghaderpoori M, Kamarehie B, Jafari A, Alinejad AA, Hashempour Y, Saghi MH, Yousefi M, Conti GO, Mohammadi AA, Ghaderpoury A (2020) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in cosmetic products sold in Iran: the Monte Carlo simulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:7588–7595
Giimiistas MK (2003) Lipid peroxidation, erythrocyte superoxide-dismutase activity and trace metals in young male footballers. Yonsei Med J 44:979–986
Guo Y, Huo X, Li Y, Wu K, Liu J, Huang J, Zheng G, Xiao Q, Yang H, Wang Y (2010) Monitoring of lead, cadmium, chromium and nickel in placenta from an e-waste recycling town in China. Sci Total Environ 408:3113–3117
Hajizadeh Y, Feizabadi GK, Ebrahimpour K, Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Fadaei S, Darvishmotevalli M, Karimi H (2020) Urinary paraben concentrations and their implications for human exposure in Iranian pregnant women. Environ Health Sci Eng:1–12
Hajizadeh Y, Moradnia M, Feizabadi GK, Rafiei N, Tahmasbizadeh M, Darvishmotevalli M, Fadaei S, Karimi H (2021) The sex-specific association between maternal urinary paraben levels and offspring size at birth. Environ Health Sci Eng:1–10
Kohli NJV (2017) Here are other celebs who said no to endorsements on ethical grounds. SCOOPWHOOP, Sep 14:2017
Kuligowski J, Halperin KM (1992) Stainless steel cookware as a significant source of nickel, chromium, and iron. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 23:211–215
Kumar KM, Mukherjee A (2021) Impact of heavy metal exposure on newborn and pregnant women associated with leukocyte carcinoma. Adv Water Resour 131:311
Kumar A, Jigyasu DK, Subrahmanyam G, Mondal R, Shabnam AA, Cabral-Pinto M, Malyan SK, Chaturvedi AK, Gupta DK, Fagodiya RK (2021): Nickel in terrestrial biota: Comprehensive review on contamination, toxicity, tolerance and its remediation approaches. Chemosphere, 129996
Lauwerys RR, Bernard A (1987) Early detection of the nephrotoxic effects of industrial chemicals: state of the art and future prospects. Am J Ind Med 11:275–285
Li T, Wan Y, Ben Y, Fan S, Hu J (2017) Relative importance of different exposure routes of heavy metals for humans living near a municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ Pollut 226:385–393
Li H, Zheng J, Wang H, Huang G, Huang Q, Feng N, Xiao J (2019) Maternal cosmetics use during pregnancy and risks of adverse outcomes: a prospective cohort study. Sci Rep 9:1–8
Li K, Wang B, Yan L, Jin Y, Li Z, An H, Ren M, Pang Y, Lan C, Chen J (2021): Associations between blood heavy metal(loid)s and serum heme oxygenase-1 in pregnant women: do their distribution patterns matter? Environ. Pollut. 117249
Lin Z, Chen X, Xi Z, Lin S, Sun X, Jiang X, Tian H (2018) Individual heavy metal exposure and birth outcomes in Shenqiu county along the Huai River Basin in China. Toxicol Res 7:444–453
Magnusson C, Jugdaohsingh R, Hulthen L, Westerlund A, Powell JJ, Ransjö M (2019) Urinary excretion of silicon in men, non-pregnant women, and pregnant women: a cross-sectional study. Biol Trace Elem Res:1–7
McDermott S, Salzberg DC, Anderson AP, Shaw T, Lead J (2015) Systematic review of chromium and nickel exposure during pregnancy and impact on child outcomes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 78:1348–1368
Milnerowicz H, Nowak P, Wielogorska D, Wochynski Z, Sobiech K (2004) Effects of moderate physical exercise on blood and urine concentrations of cadmium and metallothionein in runners. Biol Sport 21:81–92
Mittal S (2019) Smoking and tobacco use: ill effects on Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child Health, and Adolescent (RMNCHA) program—a review. Ann Natl Acad Med Sci (India) 55:065–073
Mohammadi H, Alinejad A, Khajeh M, Darvishmotevalli M, Moradnia M, Mazaheri Tehrani A, Hosseindost GR, Zare MR, Mengelizadeh N(2019a) Optimization of the 3D electro‐Fenton process in removal of acid orange 10 from aqueous solutions by response surface methodology. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94 (10):3158–3171.
Mohammadi AA, Zarei A, Esmaeilzadeh M, Taghavi M, Yousefi M, Yousefi Z, Sedighi F, Javan S (2019b) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks assessment in soils around an industrial zone in Neyshabur. Iran Biol Trace Elem Res:1–10
Moradnia M (2019) The relation of cancer risk with nitrate exposure in drinking water in Iran. Iran J Public Health 48(2):362–364
Morais S, Costa FG, Pereira ML (2012) Heavy metals and human health. Environ Health 10:227–246
Ojezele OJ, Ojezele MO, Adeosun AM (2016) Cooking utensils as probable source of heavy metal toxicity. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24:2216–2220
Orisakwe OE, Otaraku JO (2013) Metal concentrations in cosmetics commonly used in Nigeria Sci World J:2013
Orisakwe OE, Nduka JK, Amadi CN, Dike DO, Bede O (2012) Heavy metals health risk assessment for population via consumption of food crops and fruits in Owerri, South Eastern, Nigeria. Chem Cent J 6:77
Pigłowski M (2018) Heavy metals in notifications of rapid alert system for food and feed. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:365
Pope R, Wu J, Boone C (2016) Spatial patterns of air pollutants and social groups: a distributive environmental justice study in the phoenix metropolitan region of USA. Environ Manag 58:753–766
Poustchi H, Eghtesad S, Kamangar F, Etemadi A, Keshtkar A-A, Hekmatdoost A, Mohammadi Z, Mahmoudi Z, Shayanrad A, Roozafzai F (2018) Prospective epidemiological research studies in Iran (the PERSIAN Cohort Study): rationale, objectives, and design. Am J Epidemiol 187:647–655
Quansah R, Armah FA, Essumang DK, Luginaah I, Clarke E, Marfoh K, Cobbina SJ, Nketiah-Amponsah E, Namujju PB, Obiri S (2015) Association of arsenic with adverse pregnancy outcomes/infant mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect 123:412–421
Rehman K, Fatima F, Waheed I, Akash MSH (2018) Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J Cell Biochem 119:157–184
Rocha G, Steinbach C, Munhoz J, Madia M, Faria J, Hoeltgebaum D, Barbosa F Jr, Batista B, Souza V, Nerilo S (2016) Trace metal levels in serum and urine of a population in southern Brazil. J Trace Elem Med Biol 35:61–65
Rzymski P, Tomczyk K, Poniedzialek B, Opala T, Wilczak M (2015) Impact of heavy metals on the female reproductive system. Ann Agric Environ Med 22:259–264
Said SA (2015) The impact of using the scratched utensil on food contamination with heavy metals. IOSR J Environ Sci I 9:2319–2399
Shams M, Tavakkoli Nezhad N, Dehghan A, Alidadi H, Paydar M, Mohammadi AA, Zarei A (2020) Heavy metals exposure, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risks assessment of groundwater around mines in Joghatai. Iran Int J Environ Anal Chem:1–16
Shokoohi R, Salari M, Shabanloo A, Shabanloo N, Marofi S, Faraji H, Vanaei Tabar H, Moradnia M (2020) Catalytic activation of persulphate with Mn3O4 nanoparticles for degradation of acid blue 113: process optimisation and degradation pathway. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1–20
Spencer PS, Palmer VS (2021) Direct and indirect neurotoxic potential of metal/metalloids in plants and fungi used for food, dietary supplements, and herbal medicine. Toxics 9:57
Tetens I, Sjödin AM (2014) Scientific opinion on health benefits of seafood (fish and shellfish) consumption in relation to health risks associated with exposure to methylmercury. EFSA J 12(7):3761
Wai KM, Mar O, Kosaka S, Umemura M, Watanabe C (2017) Prenatal heavy metal exposure and adverse birth outcomes in Myanmar: a birth-cohort study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1339
Weidenhamer JD, Kobunski PA, Kuepouo G, Corbin RW, Gottesfeld P (2014) Lead exposure from aluminum cookware in Cameroon. Sci Total Environ 496:339–347
Wenzel AG, Brock JW, Cruze L, Newman RB, Unal ER, Wolf BJ, Somerville SE, Kucklick JR (2018) Prevalence and predictors of phthalate exposure in pregnant women in Charleston, SC. Chemosphere 193:394–402
Yang Y, Liu H, X-h X, F-y L (2013) Outline of occupational chromium poisoning in China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:742–749
Yu X-D, Yan C-H, Shen X-M, Tian Y, Cao L-L, Yu X-G, Zhao L, Liu J-X (2011) Prenatal exposure to multiple toxic heavy metals and neonatal neurobehavioral development in Shanghai. China Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:437–443
Zaw YH, Taneepanichskul N (2019) Blood heavy metals and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the first trimester of pregnancy among migrant workers. PLoS One 14:e0218409
Zeng X, Xu X, Qin Q, Ye K, Wu W, Huo X (2019) Heavy metal exposure has adverse effects on the growth and development of preschool children. Environ Geochem Health 41:309–321
Zheng Li M, Serio T, Meiman J, He X, M DIRECT FROM ATSDR (n.d.) The biomonitoring of Great Lakes Populations-III Program: the Milwaukee Angler Project. J Environ Health 83:40–43
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Department of Environmental Health Engineering at Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (IUMS) for their assistance.
Data availability and material
The material and raw data are available upon request.
Code availability
None.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. This paper was extracted from a PhD thesis funded by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (IR.MUI.RESEARCH.REC.1399.065), and project number # 399025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Moradnia and H. Movahedian Attar surveyed the studies for data extraction and inclusion, assess the study quality, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; Z. Heidari performed the data-analysis; F. Mohammadi provided critical input for the manuscript; Roya Kelishadi did critical revision of the manuscript. All authors have contributed considerably, and all authors are in agreement with respect to the manuscript content. The authors read and confirmed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
All participants voluntarily agree to participate in this research study.
Consent for publication
The studied participants consented for the publication of their identifiable details.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moradnia, M., Attar, H.M., Heidari, Z. et al. Prenatal exposure to chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) in a sample of Iranian pregnant women: urinary levels and associated socio-demographic and lifestyle factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 63412–63421 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15201-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15201-w