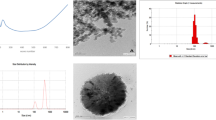
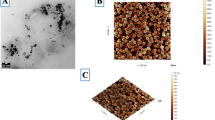
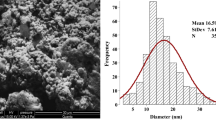
Abstract
Drainage of treated wastewater to surface water is a severe threat to the health of aquatic organisms. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of 0.5 and 1% water-soluble fractions of crude oil (WSFO), WSFO treated with magnetic nanoparticles of Fe3O4 (TWSFO-Fe3O4) and with the gravity separation method (TWSFO-GSM) on Cirrhinus cirrhosis for 21 days. The rate of erythrocyte hemolysis in fish exposed to untreated 0.5 and 1% WSFO were significantly high. The activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were significantly increased in the groups exposed to TWSFO-GSM compared to the control group, while lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was reduced. No significant differences in LDH, ALT, ALP, and GGT activities were observed in the fish treated with TWSFO-Fe3O4. The aspartate aminotransferase activity was significantly increased after exposure to TWSFO-Fe3O4 (1%) and TWSFO-GSM. The levels of triglyceride were decreased, whereas glucose, cholesterol, and cholinesterase activity increased in fish after both treatments. The total protein and albumin contents significantly decreased in fish under exposure to both doses of TWSFO-Fe3O4 and TWSFO-GSM. The globulin level decreased in fish exposed to TWSFO-Fe3O4 (1%) and TWSFO-GSM. Glutathione peroxidase, catalase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activities, and total antioxidant levels were significantly reduced in the hepatocytes of fish exposed to TWSFO-Fe3O4, TWSFO-GSM, and WSFO, while superoxide dismutase activity and malondialdehyde content were increased. This study showed that despite removing oil drips from the WSFO, the xenobiotics present in the effluent treated by gravitational or nano-magnetite methods caused changes in biochemical parameters and induced oxidative stress. Therefore, it is recommended to prevent the discharge of treated effluent from the oil and petrochemical industries to aquatic ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology. However, restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. However, data are available from the authors upon reasonable request and permission of the Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology.
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Hamed HS (2020) Antagonistic effects of dietary guava (Psidium guajava) leaves extract on growth, hemato-biochemical, and immunity response of cypermethrin-intoxicated Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, fingerlings. Aquaculture 529:735668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735668
Abdel-Wahhab MA, Aljawish A, Kenawy AM, El-Nekeety AA, Hamed HS, Abdel-Aziem SH (2016) Grafting of gallic acid onto chitosan nano particles enhances antioxidant activities in vitro and protects against ochratoxin A toxicity in catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 41:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.12.005
Aberare OL, Okuonghae P, Mukoro N, Dirisu JO, Osazuwa F, Odigie E, Omoregie R (2011) Triglycerides, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol in rats exposed to premium motor spirit fumes. N Am J Med Sci 3(6):277–280. https://doi.org/10.4297/najms.2011.3277
Alak G, Ucar A, Parlak V, Yeltekin AÇ, Taş IH, Ölmez D, Kocaman EM, Yılgın M, Atamanalp M, Yanık T (2017) Assessment of 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine activity, gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activity on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) tissues exposed to biopesticide. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 203:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.10.007
Alves-Bezerra M, Cohen DE (2018) Triglyceride metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol 8(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c170012
Andersen Ø, Frantzen M, Rosland M, Timmerhaus G, Skugor A, Krasnov A (2015) Effects of crude oil exposure and elevated temperature on the liver transcriptome of polar cod (Boreogadus saida). Aquat Toxicol 165:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.04.023
Ansari ZA, Desilva C, Badesab S (2012) Total petroleum hydrocarbon in the tissues of some commercially important fishes of the Bay of Bengal. Mar Pollut Bull 64(11):2564–2568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.029
Atta AM, Al-Lohedan HA, Al-Hussain SA (2015) Functionalization of Magnetite Nanoparticles as Oil Spill Collector. Int J Mol Sci 16(4):6911–6931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16046911
Banaee M, Mirvagefei AR, Rafei GR, Majazi Amiri B (2008) Effect of sub-lethal Diazinon Concentrations on Blood Plasma Biochemistry. Int J Environ Res 2(2):189–198
Banaee M, Soltanian S, Sureda A, Gholamhosseini A, Nematdoost Haghi B, Akhlaghi M, Derikvandy A (2019a) Evaluation of single and combined effects of cadmium and micro-plastic particles on biochemical and immunological parameters of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chemosphere 236:124335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.066
Banaee M, Sureda A, Taheri S, Hedayatzadeh F (2019b) Sub-lethal effects of dimethoate alone and in combination with cadmium on biochemical parameters in freshwater snail, Galba truncatula. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 220:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.03.002
Banaee M, Akhlaghi M, Soltanian S, Sureda A, Gholamhosseini A, Rakhshaninejad M (2020) Combined effects of exposure to sub-lethal concentration of the insecticide chlorpyrifos and the herbicide glyphosate on the biochemical changes in the freshwater crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus. Ecotoxicology 29:1500–1515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02233-0
Barron MG, Carls MG, Heintz R, Rice SD (2004) Evaluation of fish early life-stage toxicity models of chronic embryonic exposures to complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. Toxicol Sci 78(1):60–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfh051
Baszanowska E, Otremba Z (2019) Detecting the presence of different types of oil in seawater using a fluorometric index. Sensors 19(17):3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173774
Baum G, Kegler P, Scholz-Böttcher BM, Alfiansah YR, Abrar M, Kunzmann A (2016) Metabolic performance of the coral reef fish Siganus guttatus exposed to combinations of water borne diesel, an anionic surfactant and elevated temperature in Indonesia. Mar Pollut Bull 110(2):735–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.078
Beg MU, Al-Subiai SN, Al-Jandal N, Butt SA, Beg KR, Al-Husaini M (2015) Seasonal effect on biomarkers of exposure to petroleum hydrocarbons in fish from Kuwait's marine area. Mar Pollut Bull 100(2):673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.017
Bender ML, Frantzen M, Vieweg I, Falk-Petersen IB, Johnsen HK, Rudolfsen G, Tollefsen KE, Duboug P, Nahrgang J (2016) Effects of chronic dietary petroleum exposure on reproductive development in polar cod (Boreogadus saida). Aqua Toxicol 180:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.10.005
Benzie I, Strain J (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”, the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239(1):70–76
Blahova J, Cocilovo C, Plhalova L, Svobodova Z, Faggio C (2020) Embryotoxicity of atrazine and its degradation products to early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 77:103370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103370
Burgos-Aceves MA, Cohen A, Smith Y, Faggio C (2018) MicroRNAs and their role on fish oxidative stress during xenobiotic environmental exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.001
Carvalho FM, Silvany Neto AM, Mendes JL, Cotrim HP, Nascimento AL, Lima Júnior AS, Cunha TO (2006) Liver enzyme abnormalities among oil refinery workers. Rev Saude Publica 40(1):92–98. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0034-89102006000100015
Couillard CM, Leighton FA (1993) In vitro red blood cell assay for oxidant toxicity of petroleum oil. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:839–845
Crupi R, Morabito R, Remigante A, Gugliandolo E, Britti D, Cuzzocrea S, Marino A (2019) Susceptibility of erythrocytes from different sources to xenobiotics-induced lysis. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 221:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.03.008
da Costa Cunha G, Pinho NC, Alves Silva IA, Santana Costa JA, da Silva CM, Romão LP (2019) Removal of heavy crude oil from water surfaces using a magnetic inorganic-organic hybrid powder and membrane system. J Environ Manage 247:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.050
Danion M, Le Floch S, Lamour F, Quentel C (2014) EROD activity and antioxidant defenses of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) after an in vivo chronic hydrocarbon pollution followed by a post-exposure period. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(24):13769–13778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2720-3
D'Costa A, Shyama SK, Praveen Kumar MK (2017) Bioaccumulation of trace metals and total petroleum and genotoxicity responses in an edible fish population as indicators of marine pollution. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.03.049
Derikvandy A, Pourkhabbaz HR, Banaee M, Sureda A, Nematdoost Haghi B, Pourkhabbaz AR (2020) Genotoxicity and oxidative damage in zebrafish (Danio rerio) after exposure to effluent from ethyl alcohol industry. Chemosphere 251:126609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126609
Duarte RM, Honda RT, Val AL (2010) Acute effects of chemically dispersed crude oil on gill ion regulation, plasma ion levels and haematological parameters in tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). Aquat Toxicol 97(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.12.020
Dzul-Caamal R, Salazar-Coria L, Olivares-Rubio HF, Rocha-Gómez MA, Girón-Pérez MI, Vega-López A (2016) Oxidative stress response in the skin mucus layer of Goodea gracilis (Hubbs and Turner, 1939) exposed to crude oil: A non-invasive approach. Com Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 200:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.05.008
El Hajam M, Plavan GI, Kandri NI, Dumitru G, Nicoara MN, Zerouale A, Faggio C (2020) Evaluation of softwood and hardwood sawmill wastes impact on the common carp "Cyprinus carpio" and its aquatic environment: An oxidative stress study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 75:103327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103327
Ellinger JJ, Lewis IA, Markley JL (2011) Role of aminotransferases in glutamate metabolism of human erythrocytes. J Biomol NMR 49(3):221–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-011-9481-9
Gagnon MM, Holdway DA (1999) Metabolic enzyme activities in fish gills as biomarkers of exposure to petroleum hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 44(1):92–99. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1999.1804
Garcia D, Lima D, da Silva DG, de Almeida EA (2020) Decreased malondialdehyde levels in fish (Astyanax altiparanae) exposed to diesel: Evidence of metabolism by aldehyde dehydrogenase in the liver and excretion in water. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110107
Gore A, Neufeld-Cohen A, Egoz I, Baranes S, Gez R, Grauer E, Chapman S, Lazar S (2020) Efficacy of retigabine in ameliorating the brain insult following sarin exposure in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 395:114963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.114963
Gorshkov A, Pavlova O, Khlystov O, Zemskaya T (2020) Fractioning of petroleum hydrocarbons from seeped oil as a factor of purity preservation of water in Lake Baikal (Russia). J Great Lakes Res 46(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2019.10.010
Góth LA (1991) Simple method for determination of serum catalase and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta 196:143–152
Gu X, Manautou GE (2012) Molecular mechanisms underlying chemical liver injury. Expert Rev Mol Med 14:e4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399411002110
Hamed HS, Abdel-Tawwab M (2017) Ameliorative effect of propolis supplementation on alleviating bisphenol-A toxicity: Growth performance, biochemical variables, and oxidative stress biomarkers of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 202:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.08.001
Hamed HS, Abdel-Tawwab M (2021) Dietary pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel mitigated the adverse effects of silver nanoparticles on the performance, haemato-biochemical, antioxidant, and immune responses of Nile tilapia fingerlings. Aquaculture 540:736742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736742
Hamed HS, Ismal SM, Faggio C (2021) Effect of allicin on antioxidant defense system, and immune response after carbofuran exposure in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 240:108919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108919
Hameed AM, Al-Azawi AJ (2016) Acute and Chronic Effects of Water Soluble Fraction WSF of Diesel Fuel on Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L. 1758). J. Int. Environ Appl & Sci 11(4):331–345
Hamidi S (2018) Impact of sewage from heavy oil removal by magnetite nanoparticle (Fe3O4) on Indian carp fish (Cirrhinus mrigala). Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology, Iran, Environmental Department, Faculty of Natural Resources and the Environment, Behbahan
Hansen BH, Parkerton T, Nordtug T, Størseth TR, Redman A (2019) Modeling the toxicity of dissolved crude oil exposures to characterize the sensitivity of cod (Gadus morhua) larvae and role of individual and unresolved hydrocarbons. Mar Pollut Bull 138:286–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.10.065
Hansen BH, Sørensen L, Carvalho PA, Meier S, Booth AM, Altin D, Farkas J, Nordtug T (2018) Adhesion of mechanically and chemically dispersed crude oil droplets to eggs of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Sci Total Environ 640-641:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.207
Hatami M, Banaee M, Nematdoost Haghi B (2019) Sub-lethal toxicity of chlorpyrifos alone and in combination with polyethylene glycol to common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chemosphere 219:981–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.077
Hoang SA, Sarkar B, Seshadri B, Lamb D, Wijesekara H, Vithanage M, Liyanage C, Bolan NS (2021) Mitigation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated hazardous soils using organic amendments: A review. J Hazardous Mater 416:125702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125702
Hook SE, Mondon J, Revill AT, Greenfield PA, Stephenson SA, Strzelecki J, Corbett P, Armstrong E, Song J, Doan H, Barrett S (2018) Monitoring sublethal changes in fish physiology following exposure to a light, unweathered crude oil. Aquat Toxicol 204:27–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.08.013
Ibrahim AT, Banaee M, Sureda A (2019) Selenium protection against mercury toxicity on the male reproductive system of Clarias gariepinus. Com Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 225:108583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.108583
Johann S, Nüßer L, Goßen M, Hollert H, Seiler TB (2020) Differences in biomarker and behavioral responses to native and chemically dispersed crude and refined fossil oils in zebrafish early life stages. Sci Total Environ 709:136174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136174
Johnson AM, Rohlfs EM, Silverman LM (1999) Proteins. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 477–540
Kaja S, Payne AJ, Naumchuk Y, Koulen P (2017) Quantification of lactate dehydrogenase for cell viability testing using cell lines and primary cultured astrocytes. Curr Protoc Toxicol 72:2261–22610. https://doi.org/10.1002/cptx.21
Kochhann D, Meyersieck Jardim M, Valdez Domingos FX, Val AL (2015) Biochemical and behavioral responses of the Amazonian fish Colossoma macropomum to crude oil: the effect of oil layer on water surface. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.09.016
Koenig G, Seneff S (2015) Gamma-Glutamyltransferase: A Predictive Biomarker of Cellular Antioxidant Inadequacy and Disease Risk. Dis Markers 818570:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/818570
Lari E, Abtahi B, Hashtroudi MS (2016) The effect of the water soluble fraction of crude oil on survival, physiology and behaviour of Caspian roach, Rutilus caspicus (Yakovlev, 1870). Aquat Toxicol 170:330–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.09.003
Lavoie JM (2016) Dynamics of hepatic and intestinal cholesterol and bile acid pathways: The impact of the animal model of estrogen deficiency and exercise training. World J Hepatol 8(23):961–975
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R, Maitra A, Deck LM, Royer RE, Jagt GL, Semenza V, Dang CV (2010) Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(5):2037–2042. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914433107
Lee DH, Jacobs DR (2009) Is serum γ-glutamyltransferase an exposure marker of xenobiotics? Empirical evidence with polycylic aromatic hydrocarbon. Clin Chem Lab Med 47(7):860–862. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm.2009.197
Li X, Ding G, Xiong Y, Ma X, Fan Y, Xiong D (2018) Toxicity of Water-Accommodated Fractions (WAF), Chemically Enhanced WAF (CEWAF) of Oman Crude Oil and Dispersant to Early-Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(3):314–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2413-6
Liu YJ, Fan XY, Wang AD, Xia YZ, Fu WR, Liu JY, Jiang FL, Yi L (2019) LDHA Suppression Altering Metabolism Inhibits Tumor Progress by an Organic Arsenical. Int J Mol Sci 20(24):6239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246239
Malakahmad AH, Law MX, Ng KW, Abd Manan TS (2016) The Fate and Toxicity Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Water Streams of Malaysia. Procedia Engineering 148:806–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.572
Matin A, Baig U, Gondal MA, Akhtarc S, Zubair SM (2018) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic microporous membranes by spray-coating ytterbium oxide particles for efficient oil-water separation. J Membr Sci 548:390–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.045
Mobasher M, Aramesh K, Aldavoud S, Ashrafganjooei N, Divsalar K, Phillips C, Larijani B (2008) Proposing a national ethical framework for animal research in Iran. Iran J Public Health 37(1):39–46
Moss DV, Henderson AR (1999) Clinical enzymology. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 617–721
Mu X, Liu J, Yang K, Huang Y, Li X, Yang W, Qi S, Tu W, Shen G, Li Y (2018) Diesel water-accommodated fraction induced lipid homeostasis alteration in zebrafish embryos. Environ Pollut 242:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.055
Muthuviveganandavel V, Hwang I, Anita V, Malarani PS, Selvam C, Hemalatha M, Pandurangan M (2013) Synthetic Pyrethroid effect on blood plasma biomarker enzymes and histological changes in Catla catla. Int J Exp Pathol 94(2):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/iep.12009
Muñoz-Peñuela M, Nostro FLL, Dal'Olio Gomes A, Tolussi CE, Branco GS, Pinheiro JPS, de Godoi FGA, Moreira RG (2021) Diclofenac and caffeine inhibit hepatic antioxidant enzymes in the freshwater fish Astyanax altiparanae (Teleostei: Characiformes). Com Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 240:108910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108910
Nahrgang J, Bender ML, Meier S, Nechev J, Berge J, Frantzen M (2019) Growth and metabolism of adult polar cod (Boreogadus saida) in response to dietary crude oil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.082
Nath S, Matozzo V, Bhandari D, Faggio C (2018) Growth and liver histology of Channa punctatus exposed to a common biofertilizer. Nat Prod Res 33(11):1591–1598. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1428586
Nogueira L, Rodrigues AC, Trídico CP, Fossa CE, de Almeida EA (2011) Oxidative stress in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and armored catfish (Pterygoplichthys anisitsi) exposed to diesel oil. Environ Monit Assess 180(1-4):243–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1785-9
Nozar SL, Pauzi MZ, Salarpouri A, Daghooghi B, Salimizadeh M (2015) Total petroleum hydrocarbons in edible marine biota from Northern Persian Gulf. Environ Monit Assess 187(4):214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4443-4
Olivares-Rubio HF, Espinosa-Aguirre JJ (2021) Acetylcholinesterase activity in fish species exposed to crude oil hydrocarbons: A review and new perspectives. Chemosphere 264(1):128401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128401
Oliveira HH, Liebel S, Rossi SC, Azevedo AC, Barrera EA, Garcia JR, GArcia E, Grötzner SR, Neto FF, Randi MAF, Ribeiro CA (2015) Mixtures of benzo(a)pyrene, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and tributyltin are more toxic to Neotropical fish Rhamdia quelen than isolated exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.07.023
Pagano M, Faggio C (2015) The use of erythrocyte fragility to assess xenobiotic cytotoxicity. Cell Biochem Funct 33:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3135
Page CA, Bonner JS, Sumner PL, Autenrieth RL (2000) Solubility of petroleum hydrocarbons in oil/water systems. Mar Chem 70(1-3):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4203(00)00016-5
Pereira AC, Gonçalves BB, da Silva Brito R, Vieira LG, de Oliveira Lima E, Rocha TL (2020) Comparative developmental toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles and ferric chloride to zebrafish (Danio rerio) after static and semi-static exposure. Chemosphere 254:126792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126792
Peter VS, Joshua EK, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Peter MC (2007) Metabolic and thyroidal response in air-breathing perch (Anabas testudineus) to water-borne kerosene. Gen Comp Endocrinol 152(2):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.05.015
Petrovici A, Strungaru SA, Nicoara M, Robea MA, Solcan C, Faggio C (2020) Toxicity of deltamethrin to zebrafish gonads revealed by cellular biomarkers. J Mar Sci Eng 8(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020073
Placer Z, Cushman L, Johnson B (1996) Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biochemical systems. Anal Biochem 16(2):359–364
Pllino CA, Holdway DA (2003) Hydrocarbon-induced changes to metabolic and detoxification enzymes of the Australian crimson-spotted rainbowfish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis). Environ Toxicol 18(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.10098
Pourfakhraei E, Badraghi J, Banaei A, Mamashli F, Ashkevarian S (2015) The use of magnetite iron oxide nanoparticles in water-oil separation. Nano Scale 2(2):41–55
Recabarren-Villalón T, Ronda AC, Arias AH (2019) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons levels and potential biomarkers in a native South American marine fish. Reg Stud Mar Sci 29:100695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100695
Rezaei Shadegan M, Banaee M (2018) Effects of dimethoate alone and in combination with Bacilar fertilizer on oxidative stress in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Chemosphere 208:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.177
Rifai N, Bachorik PS, Albers JJ (1999) Lipids, lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 809–861
Sacks DB (1999) Carbohydrates. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 766–785
Saeed T, Al-Mutairi M (1999) Chemical composition of the water-soluble fraction of the leaded gasolines in seawater. Environ Int 25(1):117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(98)00093-2
Salahi A, Noshadi I, Badrnezhad R, Kanjilal B, Mohammadi T (2013) Nano-porous membrane process for oily wastewater treatment: Optimization using response surface methodology. J Environ Chem Eng 1(3):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.04.021
Sayed AE, Hamed HS (2017) Induction of apoptosis and DNA damage by 4-nonylphenol in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and the antioxidant role of Cydonia oblonga. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.024
Sayed AE, Kataoka C, Oda S, Kashiwada S, Mitani H (2018) Sensitivity of medaka (Oryzias latipes) to 4-nonylphenol subacute exposure; erythrocyte alterations and apoptosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 58:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.12.023
Simonato JD, Fernandes MN, Martinez CB (2013) Physiological effects of gasoline on the freshwater fish Prochilodus lineatus (Characiformes: Prochilodontidae). Neotrop Ichthyol 11(3):683–691. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-62252013000300022
Simonsen G, Strand M, Øye G (2018) Potential applications of magnetic nanoparticles within separation in the petroleum industry. J Pet Sci Eng 165:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.02.048
Sinaei M (2013) Effect of 16 pure hydrocarbons on the stabilization and lysis of fish (mudskipper: Boleophthalmus dussumieri) erythrocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.018
Sørensen L, Hansen BH, Farkas J, Donald CE, Robson WJ, Tonkin A, Meier S, Rowland SJ (2019) Accumulation and toxicity of monoaromatic petroleum hydrocarbons in early life stages of cod and haddock. Environ Pollut 251:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.126
Thiendedsakul P, Boonsoongnern P, Jarad P, Tulayakul P (2020) Comparative liver metabolic enzyme activity of cytochrome P450 and glutathione-S-transferase in crocodile (Crocodylus siamensis) and livestock. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 235:108784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108784
Tian Y, Zeng Y, Li C, Wang X, Liu Q, Zhao Y (2020) Ecological risk assessment of petroleum hydrocarbons on aquatic organisms based on multisource data. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:110262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110262
Wang S, Meng F, Liu Y, Xia S, Wang R (2021) Exogenous inositol ameliorates the effects of acute ammonia toxicity on intestinal oxidative status, immune response, apoptosis, and tight junction barriers of great blue-spotted mudskippers (Boleophthalmus pectinirostris). Com Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 240:108911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108911
Wegwu MO, Omeodu SI (2010) Evaluation of Selected Biochemical Indices in Clarias gariepinus Exposed to Aqueous Extract of Nigerian Crude Oil (Bonny Light). J Appl Sci Environ Manag 14(1):77–81
Yu L, Han M, He F (2017) A review of treating oily wastewater. Arabian J Chem 10:S1913–S1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.020
Yuan J, Guo J, Wang H, Guo A, Lian Q, Gu Z (2019) Acute toxicity of cypermethrin on the juvenile of red claw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Chemosphere 237:124468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124468
Zhou K, Zhou X, Liu J, Huang Z (2020) Application of magnetic nanoparticles in petroleum industry: A review. J Pet Sci Eng 188:106943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2020.106943
Acknowledgement
The authors appreciate Maryam Banaie’s assistance for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology, Iran (3-2-5544 BKATU). A. Sureda was supported by by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CIBEROBN -CB12/03/30038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sakineh Hamidi: M.Sc Student (Environmental Science); Contribution: Investigation, Project administration
Mahdi Banaee; Assistance Professor (Aquaculture and Ecotoxicology); Contribution: Supervisor, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing - Original Draft
Hamid Reza Pourkhabbaz; Assistance Professor (Environmental Science); Contribution: Supervisor
Antoni Sureda: Associate Professor (Biochemistry); Contribution: Writing - Original Draft, Review and Editing
Saeid Khodadoust: Assistance Professor (Chemistry Science); Contribution: Adviser
Ali Reza Pourkhabbaz: Associate Professor (Environmental Science); Contribution: Adviser
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In this study, none of the authors used human beings as research subjects. International, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Experimental protocols were done following the Iranian animal ethics framework under the supervision of the Iranian Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals and Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology (BKATU-6/1/43819-1397).
Consent to publish
There was no person’s data in any form (including any individual details, images or videos).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamidi, S., Banaee, M., Pourkhabbaz, H.R. et al. Effect of petroleum wastewater treated with gravity separation and magnetite nanoparticles adsorption methods on the blood biochemical response of mrigal fish (Cirrhinus cirrhosus). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 3718–3732 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15106-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15106-8