Abstract
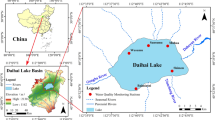
Honghu Lake, the largest shallow lake in Jianghan Plain of China, is essential for maintaining ecosystem functioning in this region. However, water pollution and high disturbance are seriously threatening the ecological security of this lake. To explore the causes of water quality fluctuations in Honghu Lake, the water quality index method (CCME-WQI), multivariate statistical, and source apportionment techniques were adopted to characterize temporal trends in lake water quality (2004–2017), identify the main driving factors of water quality indicators, and quantify the contribution of various pollution sources. Besides, the water periods of the lake have been reclassified due to the seasonal variation of rainfall in the study area. The results of CCME-WQI showed that the water quality in Honghu Lake initially improved over 2004–2011, with better water quality in the wet period than in the dry periods, while the results over 2012–2017 were found to be opposite. Correlation analysis identified untreated industrial wastewater (UIW) as the main pollution source affecting CODMn concentrations in Honghu Lake, while untreated domestic sewage discharge (UDS) was identified as the main pollution source affecting BOD and F. coli concentrations. The main pollution sources affecting nutrient indicators were rainfall and enclosure aquaculture (EA). Principal component analysis (PCA) combined with absolute principal component score-multiple linear regression model (APCS-MLR) further appointed the source contribution of each pollution source to water quality indicators. The results showed that EA in 2012 was reduced by 81% compared with 2004, resulting in the contribution of EA to NH3-N, TP, and TN decreased by 0.2 mg L−1, 0.039 mg L−1, and 0.37 mg L−1, respectively. Compared with 2012, UIW was reduced by 65% in 2016, resulting in the contribution of UIW to CODMn decreased by 1.17 mg L−1. In addition, compared with 2004, UDS decreased by 85% in 2016, and the contribution of UDS to BOD and F. coli decreased by 0.7 mg L−1 and 887 cfu L−1, respectively. Based on the results of APCS-MLR, it was predicted that the concentrations of COD and TP in Honghu Lake would meet the water quality requirements after 2017. However, the rainfall non-point source pollution must be further controlled to achieve the desired level of TN concentration. This study provided an accurate method for analyzing lake water pollution, and the results can provide a valuable reference for optimizing water quality management and pollution control strategies within Honghu Lake.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin DS, Mitchell AM (2000) The effects of drying and reflooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river-floodplain systems: a synthesis. Regul Rivers Res Manag 16(5):457–467
Baldwin DS, Gigney H, Wilson JS, Watson G (2008) Drivers of water quality in a large water storage reservoir during a period of extreme drawdown. Water Res 42(2008):4711–4724
Bian W, Wang LG, Zhang HZ, Wang JF, Tian ZF, Chen XY (2012) Study on phosphorus pollution load of aquaculture in Baiyangdian Lake. Adv Mater Res 518–523:1406–1411
Cai SM, Yi ZL (1991) Sedimentary features and the evolution of Lake Honghu, Central China. Hydrobiologia 214:341–345
Chang NB (2005) Sustainable water resources management under uncertainty. Stoch Env Res Risk A 19(2):97–98
Chang B, Li R, Zhu C, Liu K (2015) Quantitative impacts of climate change and human activities on water-surface area variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China. Water 7(12):2881–2899
Chen H, Teng Y, Wang J (2013) Load estimation and source apportionment of nonpoint source nitrogen and phosphorus based on integrated application of SLURP model, ECM, and RUSLE: a case study in the Jinjiang River. China Environ Monit Assess 185(2):2009–2021
Chen RR, Chen HY, Song LT, Teng YG (2019) Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Chemosphere 694(2019):133819
Chen S, Lin BW, Li YQ, Zhou SN (2020) Spatial and temporal changes of soil properties and soil fertility evaluation in a large grain-production area of subtropical plain, China. Geoderma 357(2020):113937
Dai YH, Feng L, Hou XB, Choi CY (2019) Policy-driven changes in enclosure fisheries of large lakes in the Yangtze Plain: evidence from satellite imagery. Sci Total Environ 688:1286–1297
Dede OT, Telci IT, Aral MM (2013) The use of water quality index models for the evaluation of surface water quality: a case study for Kirmir Basin, Ankara, Turkey. Water Qual Expo Health 5(1):41–56
Duan W, He B, Nover D, Yang G, Liu C (2016) Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the eastern Poyang Lake Basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability 8(2):133
Dugga P, Pervez S, Tripathi M, Siddiqui MN (2020) Spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment of the ionic components of groundwater of a mineral-rich tribal belt in Bastar, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100356
Elhatip H, Hinis MA, Gulgahar N (2007) Evaluation of the water quality at Tahtali dam watershed in Izmir, Turkey by means of statistical methodology. Stoch Env Res Risk A 22(3):391–400
Farnham IM, Singh AK, Stetzenbach KJ, Johannesson KH (2002) Treatment of nondetects in multivariate analysis of groundwater geochemistry data. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 60(1):265–281
Fitch, K., Kemker, C., 2014. Algae, Phytoplankton and Chlorophyll. Fundamentals of Environmental Measurements (WWW Document) Fondriest Environ. Inc.
Fu BJ, Wu BF, Lu YH, Xu ZH, Cao JH, Niu D, Yang GS, Zhou YM (2010) Three Gorges project: efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog Phys Geogr 34(6):741–754
Fuge R (2019) Fluorine in the environment, a review of its sources and geochemistry. Appl Geochem 100:393–406
Gao Q, Li Y, Cheng QY, Yu MX (2016) Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res 92:262–274
Gholizadeh MH, Melesse AM, Reddi L (2016) Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci Total Environ 566-567:1552–1567
Gui F, Yu G (2008) Numerical simulations of nutrient transport changes in Honghu Lake Basin, Jianghan Plain. Sci Bull 53(15):2353–2363
Gurjar SK, Tare V (2019) Spatial-temporal assessment of water quality and assimilative capacity of river Ramganga, a tributary of Ganga using multivariate analysis and QUEL2K. J Clean Prod 222:550–564
Han Q, Tong RZ, Sun WC, Wang GQ (2020) Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade. Sci Total Environ 701:134929
Huang F, Wang X, Lou L, Zhou Z, Wu J (2010) Spatial variation and source apportionment of water Pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Res 44(5):1562–1572
Hülya B, Hayal B (2008) Water pollution sources assessment by multivariate statistical methods in the Tahtali Basin, Turkey. Environ Geol 54(2):275–282
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China. J Hazard Mater 181(1-3):1051–1058
Li P, Zhang TL, Wang XX, Yu DS (2013) Development of biological soil quality indicator system for subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res 126:112–118
Li K, Wang L, Li ZH, Zhu P (2015) Spatial variability characteristics of water quality and its driving forces in Honghu Lake during high water-level period. Huan jing ke xue= Huanjing kexue 36(4):1285
Li K, Wang L, Li ZH, Wang XR, Fang Q (2017a) Exploring the spatial-seasonal dynamics of water quality, submerged aquatic plants and their influencing factors in different areas of a lake. Water 9(9):707
Li F, Qiu Z, Zhang J, Liu C, Cai Y, Xiao M (2017b) Spatial distribution and fuzzy health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water from Honghu Lake. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(9):1011
Li F, Zhang JD, Liu CY, Xiao MS (2018) Distribution, bioavailability and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Honghu Lake. China Process Saf Environ 116:169–179
Li F, Qiu Z, Zhang J, Liu C, Cai Y, Xiao M, Zhu L (2019) Temporal variation of major nutrients and probabilistic eutrophication evaluation based on stochastic-fuzzy method in Honghu Lake, Middle China. SCIENCE CHINA Technol Sci 62:417–426
Lin J, Li J, Zuo L, Lin J, Cao J (2018) Processing system of rapid dehydration, solidification/stabilization and resource reuse for silt of river and lake. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 199:042042
Liu CY, Zhang JD, Li F, Yang J, Wu ZX (2018) Trace elements spatial distribution characteristics, risk assessment and potential source identification in surface water from Honghu Lake, China. J Cent South Univ 25(7):1598–1611
Liu M, Ran Y, Peng XX, He Q (2019) Sustainable modulation of anaerobic malodorous black water: The interactive effect of oxygen-loaded porous material and submerged macrophyte. Water Res 160(2019):70–80
Liu LL, Dong YC, Kong M, Wang ZP (2020) Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models. Chemosphere 242:125272
Ma YK, Hao S, Zhao H, Fang J, Zhao J, Li X (2018) Pollutant transport analysis and source apportionment of the entire non-point source pollution process in separate sewer systems. Chemosphere 211:557–565
Ma X, Zhu F, Jin Q (2019) Antibiotics and chemical disease-control agents reduce innate disease resistance in crayfish. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 86:169–178
Makokha VA, Qi Y, Shen Y, Wang J (2016) Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China. Exposure and Health 8(1):31–41
Mo MH, Wang XL, Wu HJ, Cai SM, Zhang XY, Wang HL (2009) Ecosystem health assessment of Honghu Lake Wetland of China using artificial neural network approach. Chin Geogr Sci 19:349–356
Najar IA, Khan AB (2012) Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of three lakes in Kashmir, India, using multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 66:2367–2378
Ouyang Y, Nkedi-Kizza P, Wu QT, Huang CH (2006) Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Res 40:3800–3810
Pettersson K (2001) Phosphorus characteristics of settling and suspended particles in Lake Erken. Sci Total Environ 266:79–86
Qin B, Xu P, Wu Q, Luo L, Zhang Y (2007) Environmental issues of lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581(1):3–14
Querijero BL, Mercurio AL (2016) Water quality in aquaculture and non-aquaculture sites in Taal lake, Batangas Philippines. J Exp Biol Agric Sci 4:109–115
Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Hron K, Garrett RG (2017) A new method for correlation analysis of compositional (environmental) data – a worked example. Sci Total Environ 607-608:965–971
Schallenberg M, de Winton MD, Verburg P, Kelly DJ, Hamill KD, Hamilton DP, Dymond JR (2013) Ecosystem services of lakes. In: Dymond JR (ed) Ecosystem Services in New Zealand. Manaaki Whenua Press, Lincoln, New Zealand, pp 203–225
SEPA (2001) Pollutant Discharge Standards for Livestock and Poultry Breeding, GB 18596-2001. In: State Environment Protection Administration (SEPA), General Administration for Quality Supervision. Inspection and Quarantine of PR China, Beijing, China in Chinese
SEPA (2002) Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (EQSSW), GB 3838–2002. In: State Environment Protection Administration (SEPA), General Administration for Quality Supervision. Inspection and Quarantine of PR China, Beijing, China in Chinese
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin. Japan Environ Modell Softw 22:464–475
Singaraju S, Pasupuleti S, Hernandez EA, Uddameri V (2018) Prioritizing groundwater monitoring in data sparse regions using Atanassov Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets (A-IFS). Water Resour Manag 32 (4):1483–1499
Singh KP, Malik A, Sinha S (2005a) Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques-a case study. Anal Chim Acta 538(1-2):355–374
Singh KP, Malik A, Singh VK, Mohan D, Sinha S (2005b) Chemometric analysis of groundwater quality data of alluvial aquifer of Gangetic Plain, North India. Anal Chim Acta 550:82–91
Su SL, Li D, Zhang Q, Wu JP (2011) Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in different functional zones of Qiantang River. China Water Res 45:1781–1795
Thurston GD, Spengler JD (1985) A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in Metropolitan Boston. Atmos Environ 19:9–25
Wan YS, Wan L, Li YC, Doering P (2017) Decadal and seasonal trends of nutrient concentration and export from highly managed coastal catchments. Water Res 115:180–194
Wang HL, Li XY, Xie Y (2011) Hydrochemical evaluation of surface water quality and pollution source apportionment in the Luan River basin, China. Water Sci Technol 64(10):2119–2125
Wang H, An J, Cheng M, Shen L, Zhu B, Li Y, Wang Y, Duan Q, Sullivan A, Xia L (2016) One year online measurements of water-soluble ions at the industrially polluted town of Nanjing, China: sources, seasonal and diurnal variations. Chemosphere 148:526–536
Wang Z, Du Y, Yang C, Liu X, Zhang JQ (2017) Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu. China Sci Total Environ 609:1423–1432
Wang GQ, Li JW, Sun WC, Xue BL, Yinglan A, Liu TX (2019) Non-point source pollution risks in a drinking water protection zone based on remote sensing data embedded within a nutrient budget model. Water Res 157:238–246
Xian G, Crane M, Junshan S (2007) An analysis of urban development and its environmental impact on the Tampa Bay watershed. J Environ Manag 85(4):965–976
Xiao M, Bao F, Wang S, Cui F (2016) Water quality assessment of the Huaihe River segment of Bengbu (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Water Res 43(1):166–176
Yan F, Qiao D, Qian B, Ma L, Wang X (2016) Improvement of CCME WQI using grey relational method. J Hydrol 543:316–323
Yang K, Yu ZY, Luo Y, Yang Y, Zhao L, Zhou XL (2017) Spatial and temporal variations in the relationship between lake water surface temperatures and water quality - a case study of Dianchi Lake. Sci Total Environ 624:859–871
Zhang T, Ban X, Wang XL, Cai XB, Li E, Lu XR (2017) Analysis of nutrient transport and ecological response in Honghu Lake. China by using a mathematical model Sci Total Environ 575:418–428
Zhang XK, Li BL, Xu H, Wells M (2019) Effect of micronutrients on algae in different regions of Taihu, a large, spatially diverse, hypereutrophic lake. Water Res 151:500–514
Zhang H, Li H, Yu H, Cheng S (2020) Water quality assessment and pollution source apportionment using multi-statistic and APCS-MLR modeling techniques in Min River Basin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:41987–42000
Zhou F, Huang G, Guo H, Zhang W, Hao Z (2007a) Spatio-temporal patterns and source apportionment of coastal water pollution in eastern Hong Kong. Water Res 41(15):3429–3439
Zhou F, Guo HC, Liu Y (2007b) Chemometrics data analysis of marine water quality and source identification in southern Hong Kong. Mar Pollut Bull 54:745–756
Zhou F, Guo HC, Liu L (2007c) Quantitative identification and source apportionment of anthropogenic heavy metals in marine sediment of Hong Kong. Environ Geol, in press 53:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0644-7
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful for some data support provided by the Environmental Monitoring Center of Honghu City, Jingzhou Ecology and Environment Bureau, and Jingzhou Agricultural and Rural Development Center.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Jingzhou Ecology and Environment Bureau, Environmental Monitoring Center of Honghu City, and Jingzhou Agricultural and Rural Development Center but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of these third parties.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2016YFC0502700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuai Chen is the main researcher of this work; Simeng Wang, Mingjun Dong, and Yanxi Yu conducted the field investigation and collected data; Yanqiang Li gave comments on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Wang, S., Yu, Y. et al. Temporal trends and source apportionment of water pollution in Honghu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 60130–60144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14828-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14828-z