Abstract
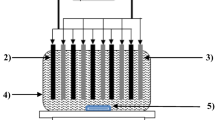
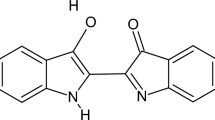
Indigo carmine removal from aqueous solutions was investigated by the electrocoagulation process and biochemical responses of Gammarus pulex to solutions before and after treatment were studied. Electrocoagulation experiments in the first stage were carried out with central composite design (CCD) using response surface methodology (RSM). Optimization of process variables that maximize indigo carmine removal by electrocoagulation process was carried out by using a second-order model within the studied test range of various process variables. According to the optimization results, optimum conditions for obtaining 82.55% maximum indigo carmine removal were pH 5.86, a current density of 13.31 mA/cm2, an indigo carmine concentration of 20.01 mg/L, and a time period of 115.80 min. Under optimum conditions for indigo carmine removal, the amount of sludge formed was 0.928 kg/m3, electrode consumption was 0.0305 kg/m3, and energy consumption was 7.461 kWh/m3. The operating cost was calculated as 0.79 US$/m3 under treatment conditions where optimum indigo carmine removal was achieved. In the second stage, G. pulex was exposed to treated and untreated synthetic indigo carmine solutions obtained from experiments according to optimum conditions in order to investigate the biochemical response for 24 and 96 h. Treatment efficiency was evaluated with superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) biomarkers. Results clearly showed that the electrocoagulation process was a simple and effective treatment method for the decolorization of wastewaters containing indigo carmine dye. The bioassays used in the present study provided good credibility for checking the detoxification of treated and untreated indigo carmine solutions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript.
References
Aksu O, Yildirim NC, Yildirim N, Danabas D, Danabas S (2014) Biochemical response of crayfish (Astacus leptodactylus) exposed to textile wastewater treated by indigenous white rot fungus Coriolus versicolor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):2987–2993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3550-z
Aksu O, Yildirim NC, Danabas D, Yildirim N (2017) Biochemical impacts of the textile dyes Remazol Brilliant Blue R and Congo red on the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus (Decapoda, Astacidae). Crustaceana 90(13):1563–1574. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685403-00003738
Aleboyeh A, Daneshvar N, Kasiri MB (2008) Optimization of C.I. Acid Red 14 azo dye removal by electrocoagulation batch process with response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process 47(5):827–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2007.01.033
Arshad R, Bokhari TH, Javed T, Bhatti IA, Rasheed S, Iqbal M, Nazir A, Naz S, Khan MI, Khosa MKK, Iqbal M, Zia-ur-Rehman M (2020a) Degradation product distribution of Reactive Red-147 dye treated by UV/H2O2/TiO2 advanced oxidation process. J Mater Res Technol 9(3):3168–3178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.062
Arshad R, Bokhari TH, Khosa KK, Bhatti IA, Munir M, Iqbal M, Iqbal DN, Khan MI, Iqbal M, Nazir A (2020b) Gamma radiation induced degradation of anthraquinone Reactive Blue-19 dye using hydrogen peroxide as oxidizing agent. Radiat Phys Chem 168:108637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108637
Arthur J (1980) Review of freshwater bioassay procedures for selected amphipods. Aquatic Invertebrate Bioassays. In: Buikema A, Cairns J (eds) West Conshohocken. PA, ASTM International, pp 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP33410S
Asaithambi P, Aziz ARA, Daud WMAW (2016) Integrated ozone electrocoagulation process for the removal of pollutant from industrial effluent: optimization through response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process 105:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2016.03.013
Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: a review. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00113-7
Behbahani M, Alavi Moghaddam MR, Arami M (2011) Techno-economical evaluation of fluoride removal by electrocoagulation process: optimization through response surface methodology. Desalination 271:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.12.033
Bharath M, Krishna BM, Manoj Kumar B (2018) A review of electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment. Int J ChemTech Res 11(3):289–302. https://doi.org/10.20902/IJCTR.2018.110333
Bilal N, Ali S, Iqbal M (2014) Application of advanced oxidations processes for the treatments of textile effluents. Asian J Chem 26(7):1882–1886 https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2014.14885
Brzezicki JM, Andersen ME, Cranmer BK, Tessari JD (2003) Quantitative identification of atrazine and its chlorinated metabolites in plasma. J Anal Toxicol 27:569–557. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/27.8.569
Camcioglu S, Ozyurt B, Hapoglu H (2017) Effect of process control on optimization of pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation. Process Saf Environ Prot 111:300–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.07.014
Chelikani P, Fita I, Loewen PC (2004) Diversity of structures and properties among catalases. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:192–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3206-5
De Lange HJ, Noordoven W, Murk AJ, Lürling M, Peeters ETHM (2006) Behavioural responses of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea, Amphipoda) to low concentrations of pharmaceuticals. Aquat Toxicol 78:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.03.002
Demirci O, Asma DH (2013) Antioxidant responses in Phanerochaete chrysosporium exposed to Astrazone Red FBL textile dye. Cell Biochem Funct 31:86–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.2865
Diaz JM, Plummer S (2018) Production of extracellular reactive oxygen species by phytoplankton: past and future directions. J Plankton Res 40(6):655–666. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fby039
El-Taweel YA, Nassef EM, Elkheriany I, Sayed D (2015) Removal of Cr(VI) ions from waste water by electrocoagulation using iron electrode. Egypt J Pet 24:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.05.011
Fajardo AS, Martins RC, Silva DR, Quinta-Ferreira CA, Martinez-Huitle RM (2017) Dye wastewaters treatment using batch and recirculation flow electrocoagulation systems. J Electroanal Chem 801:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.07.015
Gaetani GF, Galiano S, Canepa L, Ferraris AM, Kirkman HN (1989) Catalase and glutathione peroxidase are equally active in detoxification of hydrogen peroxide in human erythrocytes. Blood 73:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V73.1.334.334
Gautam K, Kumar S, Kamsonlian S (2019) Decolourization of reactive dye from aqueous solution using electrocoagulation: kinetics and isothermal study. Z Phys Chem 233(10):1447–1468. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2017-1044
Geffard A, Queau H, Dedourge O, Biagianti-Risboug S, Geffard O (2007) Influence of biotic and abiotic factors on metallothio-nein level in Gammarus pulex. Comp Biochem Physiol–Part C 145:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.02.012
Gilhotra V, Das L, Sharma A, Kang TS, Singh P, Dhuria RS, Bhatti MS (2018) Electrocoagulation technology for high strength arsenic wastewater: process optimization and mechanistic study. J Clean Prod 198(6):93–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.023
Goksoyr A, Forlin L (1995) The cytochrome P-450 system in fish, aquatic toxicology and environmental monitoring. Aquat Toxicol 22:287–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(92)90046-P
Haghshenas HF, Khodaii A, Khedmati M, Tapkin S (2015) A mathematical model for predicting stripping potential of hot mix asphalt. Constr Build Mater 75:88–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.11.041
Hashim KS, Al Khaddar R, Jasim N, Shaw A, Phipps D, Kot P, Pedrola MO, Alattabi AW, Abdulredha M, Alawsh R (2019) Electrocoagulation as a green technology for phosphate removal from river water. Sep Purif Technol 210:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.056
Iqbal M, Bhatti IA (2015) Gamma radiation/H2O2 treatment of a nonylphenol ethoxylates: degradation, cytotoxicity, and mutagenicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 299:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.045
Iqbal M, Ahmad MZ, Bhatti IA, Qureshi K, Khan A (2015) Cytotoxicity reduction of wastewater treated by advanced oxidation process. Chem Int 1(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1469792
Isa MH, Ezechi EH, Ahmed Z, Magram SF, Kutty SRM (2014) Boron removal by electrocoagulation and recovery. Water Res 51:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.12.024
Jamil A, Bokhari TH, Iqbal M, Bhatti IA, Zuber M, Nisar J, Masood N (2019) Gamma radiation and hydrogen peroxide based advanced oxidation process for the degradation of disperse dye in aqueous medium. Z Phys Chem 234(2):279–294. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2019-1384
Jamil A, Bokhari TH, Iqbal M, Zuber M, Bukhari IH (2020) ZnO/UV/H2O2 based advanced oxidation of disperse red dye. Z Phys Chem 234(1):129–143. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2019-0006
Kacan E (2016) Optimum BET surface areas for activated carbon produced from textile sewage sludges and its application as dye removal. J Environ Manag 166:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.044
Katheresan V, Kansedo J, Lau SY (2018) Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):4679–4697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Kaur S, Kaur A (2015) Variability in antioxidant/detoxification enzymes of Labeo rohita exposed to an azo dye, acid black (AB). Comp Biochem Physiol C 167:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2014.06.009
Kaur S, Kaur K, Kaur A (2018) Responses of the antioxidant defences of Labeo rohita exposed to Basic violet-1 (BV-1). J Appl Nat Sci 10(4):1248–1253. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v10i4.1911
Khan SU, Islam DT, Farooqi IH, Ayub S, Basheer F (2019) Hexavalent chromium removal in an electrocoagulation column reactor: process optimization using CCD, adsorption kinetics and pH modulated sludge formation. Process Saf Environ Prot 122:118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.11.024
Khandegar V, Saroha AK (2013) Electrocoagulation for the treatment of textile industry effluent - a review. J Environ Manag 128C:949–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.06.043
Khorram AG, Fallah N (2018) Treatment of textile dyeing factory wastewater by electrocoagulation with low sludge settling time: optimization of operating parameters by RSM. J Environ Chem Eng 6:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.054
Kobya M, Gengec E, Demirbas E (2016) Operating parameters and costs assessments of a real dyehouse wastewater effluent treated by a continuous electrocoagulation process. Chem Eng Process 101:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.11.012
Kothai A, Sathishkumar C, Muthupriya R, Siva Sankar K, Dharchana R (2020) Experimental investigation of textile dyeing wastewater treatment using aluminium in electro coagulation process and Fenton’s reagent in advanced oxidation process. Mater Today 45:1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.094
Lewis DFV (2001) Guide to cytochromes P450 structure and function. Taylor & Francis Inc., CRC Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1093/annhyg/meg068
Lopes PA, Pinheiro T, Santos MC, da Luz MM, Collares-Pereira MJ, Viegas-Crespo AM (2001) Response of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater fish populations (Leuciscus alburnoides complex) to inorganic pollutants exposure. Sci Total Environ 280(1-3):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00822-1
Mariah GK, Pak KS (2020) Removal of brilliant green dye from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. Mater Today 20(4):488–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.175
McCord JM (1996) Effects of positive iron status at a cellular level. Nutr Rev 54:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.1996.tb03876.x
Murthy ZVP, Parmar S (2011) Removal of strontium by electrocoagulation using stainless steel and aluminum electrodes. Desalination 282:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.08.058
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. Fourth Edition. John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 856 p.
Pouet MF, Grasmick A (1995) Urban wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation and flotation. Water Sci Technol 31:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1223(95)00230-K
Schlezinger JJ, Stegeman JJ (2001) Induction and suppression of cyto-chrome P450 1A by 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl and its relation-ship to oxidative stress in the marine fish scup (Stenotomus chrysops). Aquat Toxicol 52:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-445x(00)00141-7
Scott M, Zuo L, Lubin BH, Chiu DTY (1991) NADPH, not glutathione, status modulates oxidant sensitivity in normal and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient erythrocytes. Blood 77:2059–2064. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V77.9.2059.2059
Secula MS, Cretescu I, Petrescu S (2011) An experimental study of indigo carmine removal from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation. Desalination 277:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.031
Sefatjoo P, Moghaddam MRA, Mehrabadi AR (2020) Evaluating electrocoagulation pretreatment prior to reverse osmosis system for simultaneous scaling and colloidal fouling mitigation: application of RSM in performance and cost optimization. J Water Process Eng 35:101201:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101201, 101201
Song S, He Z, Qiu J, Xu L, Chen J (2007) Ozone assisted electrocoagulation for decolorization of C.I. Reactive Black 5 in aqueous solution: an investigation of the effect of operational parameters. Sep Purif Technol 55:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.12.013
Stegeman JJ, Woodin BR, Singh H, Oleksiak MF, Celander M (1997) Cytochromes P450 (CYP) in tropical fishes: catalytic activities,expression of multiple CYP proteins and high levels of microsomal P450 in liver of fishes from Bermuda. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 116:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0742-8413(96)00128-4
Tatar S, Yildirim NC, Serdar O, Yildirim N, Ogedey A (2018) The using of Gammarus pulex as a biomonitor in ecological risk assessment of secondary effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plant in Tunceli, Turkey. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24(3):819–829. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1400374
Tatar S, Serdar O, Yildirim NC (2019) Changes in antioxidant and detoxification systems of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex exposed to congo red. J Anatol Environ Animal Sci 4(2):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2019.1579199
Tompkins LM, Wallace AD (2007) Mechanisms of cytochrome P450 induction. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 21:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.20180
Tripathi R, Gupta A, Thakur IS (2019) An integrated approach for phycoremediation of wastewater and sustainable biodiesel production by green microalgae, Scenedesmus sp. ISTGA1. Renew Energy 135:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.056
Wirgin II, Theodorakis CV (2002) Molecular biomarkers in aquatic organisms. In: ADAMS SM (ed) Biological indicators of aquatic ecosystem stress. Bethesda, AFS, pp 73–82
Yildirim NC, Yaman M (2019) The usability of oxidative stress and detoxification biomarkers in Gammarus pulex for ecological risk assessment of textile dye methyl orange. Chem Ecol 35(4):319–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2019.1579199
Yildirim NC, Tanyol M, Yildirim N, Serdar O, Tatar S (2018) Biochemical responses of Gammarus pulex to malachite green solutions decolorized by Coriolus versicolor as a biosorbent under batch adsorption conditions optimized with response surface methodology. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.059
Yildirim NC, Tanyol M, Serdar O, Yildirim N (2019) Gammarus pulex as a model organism to assess the residual toxicity of slaughterhouse wastewater treated by electrocoagulation process. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02666-2
Zhang C, Zhang S, Diao H, Zhao H, Zhu X, Lu F (2013) Purification and characterization of a temperature- and pH- stable laccase from the spores of Bacillus vallismortis fmb-103 and its application in the degradation of malachite green. J Agric Food Chem 61:5468–5473. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4010498
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Projects Department of Munzur University (Project No.: YLMUB017-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.T. and N.C.Y. designed and conceptualized the experiments. D.A., M.T., and N.C.Y. applied the experiments. M.T. and N.C.Y analyzed the data and made tables and figures. M.T. and N.C.Y wrote the paper. All the authors read and contributed to the submitted version of the manuscript. M.T. and N.C.Y acquired the funding and were responsible for resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in the work.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanyol, M., Yildirim, N.C. & Alparslan, D. Electrocoagulation induced treatment of indigo carmine textile dye in an aqueous medium: the effect of process variables on efficiency evaluated using biochemical response of Gammarus pulex. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 55315–55329 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14819-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14819-0