Abstract
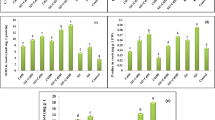
Neodymium (Nd) potentially threatens ecological equilibrium for its wide usage in industries. In this study, the accumulation and effect of Nd on roots were investigated in the rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) exposed to different concentrations of Nd (0, 1, 10, 100, and 1000 μM). The toxic effect of Nd on rice growth was observed at the higher concentration, but the positive effects were found at the lower concentration. The accumulation of Nd was present in six different chemical forms, and the insoluble phosphate and oxalate Nd were the major forms of Nd in the roots. In addition, Nd was accumulated in the soluble fractions, organelles, and cell walls of rice seedlings, and the root cell wall was a major Nd sink site. The result of Fourier transform infrared spectrometer spectral analysis indicated that the functional groups of -OH and C-OH were the major binding sites of Nd in the cell wall of roots. Moreover, the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the activity of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and peroxidase (POD) were significantly increased with the increase of Nd concentration. The enhanced antioxidant capacity also played an important role in Nd detoxification of rice seedlings. In all, the results indicated that forming of inactive oxalate or phosphate and efficient sequestration into the root cell wall was a key process in Nd accumulation and detoxification of rice seedlings.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data obtained during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adeel M, Lee JY, Zain M, Rizwan M, Nawab A, Ahmad MA, Shafiq M, Yi H, Jilani G, Javed R, Horton R, Rui Y, Tsang DCW, Xing B (2019) Cryptic footprints of rare earth elements on natural resources and living organisms. Environ Int 127:785–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.022
Agathokleous E, Kitao M, Calabrese EJ (2018) The rare earth element (REE) lanthanum (La) induces hormesis in plants. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 238:1044–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.068
Alonso-Simón A, García-Angulo P, Mélida H, Encina A, Álvarez JM, Acebes JL (2011) The use of FTIR spectroscopy to monitor modifications in plant cell wall architecture caused by cellulose biosynthesis inhibitors. Plant Signal Behav 6(8):1104–1110. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.8.15793
Berni R, Luyckx M, Xu X, Legay S, Sergeant K, Hausman J-F, Lutts S, Cai G, Guerriero G (2019) Reactive oxygen species and heavy metal stress in plants: Impact on the cell wall and secondary metabolism. Environ Exp Bot 161:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.10.017
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chen H, Chen Z (2019) Rare earth elements in paddy fields from eroded granite hilly land in a southern China watershed. PLoS One 14(9):e0222330. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222330
Chen SA, Zhao B, Wang X, Yuan X, Wang Y (2004) Promotion of the growth of Crocus sativus cells and the production of crocin by rare earth elements. Biotechnol Lett 26(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:bile.0000009455.31817.a5
Dhiman M, Singhal S (2019) Effect of doping of different rare earth (europium, gadolinium, dysprosium and neodymium) metal ions on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of LaFeO3 perovskites. J Rare Earths 37(12):1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.12.015
Diatloff E, Smith FW, Asher CJ (2008) Effects of lanthanum and cerium on the growth and mineral nutrition of corn and mungbean. Ann Bot 101(7):971–982. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcn021
Drazkiewicz M, Skorzynska-Polit E, Krupa Z (2007) The redox state and activity of superoxide dismutase classes in Arabidopsis thaliana under cadmium or copper stress. Chemosphere 67(1):188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.032
Fashui H (2002) Study on the mechanism of cerium nitrate effects on germination of aged rice seed. Biol Trace Elem Res 87(1-3):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:87:1-3:191
Freitas R, Costa S, DC CE, Morais T, Moleiro P, Matias AC, Pereira AF, Machado J, Correia B, Pinheiro D, Rodrigues A, Colónia J, Soares A, Pereira E (2020) Toxicological effects of the rare earth element neodymium in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chemosphere 244:125457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125457
Gao Y, Zeng F, Yi A, Ping S, Jing L (2003) Research of the entry of rare earth elements Eu3+ and La3+ into plant cell. Biol Trace Elem Res 91(3):253–265. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:91:3:253
Goth L (1991) A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta 196(2–3):143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(91)90067-m
Gurrappa I, Pandian S (2006) Corrosion characteristics of Nd–Fe–B permanent magnets in different environments. Corros Eng Sci Technol 41(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1179/174327806X94018
Gwenzi W, Mangori L, Danha C, Chaukura N, Dunjana N, Sanganyado E (2018) Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci Total Environ 636:299–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.235
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Ippolito MP, Fasciano C, d'Aquino L, Morgana M, Tommasi F (2010) Responses of antioxidant systems after exposition to rare earths and their role in chilling stress in common duckweed (Lemna minor L.): a defensive weapon or a boomerang? Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58(1):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9340-9
Jiachen W, Xiangsheng L, Jun Y, He Z, Ying L, Yubin F, Yanping W, Xuewei H (2006) Development and prospect of rare earth functional biomaterials for agriculture in China. J Rare Earths 24(1, Supplement 1):427–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(07)60419-0
Khan AM, Bakar NKA, Bakar AFA, Ashraf MA (2017) Chemical speciation and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in the ecosystem: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(29):22764–22789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7427-1
Krzesłowska M (2011) The cell wall in plant cell response to trace metals: polysaccharide remodeling and its role in defense strategy. Acta Physiol Plant 33(1):35–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0581-z
Kumari A, Sinha MK, Pramanik S, Sahu SK (2018) Recovery of rare earths from spent NdFeB magnets of wind turbine: leaching and kinetic aspects. Waste Manag (New York, NY) 75:486–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.033
Küpper H, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2000) Cellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Planta 212(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000366
Lai HY (2015) Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Impatiens walleriana in relation to its phytoextraction potential. Chemosphere 138:370–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.047
Lai Y, Wang Q, Yang L, Huang B (2006) Subcellular distribution of rare earth elements and characterization of their binding species in a newly discovered hyperaccumulator Pronephrium simplex. Talanta 70 (1):0-31 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.12.062, 26
Li D, Huang S, Peng A (2001) The absorbed rate and distribution rule of rare earth elements in wheat by 141Ce as tracer. Huan jing ke xue 22(2):74–77
Li L, Zhou D, Wang P, Peijnenburg WJ (2009) Kinetics of cadmium uptake and subcellular partitioning in the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to cadmium-contaminated soil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57(4):718–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9296-9
Li Z, Diaz LA, Yang Z, Jin H, Lister TE, Vahidi E, Zhao F (2019) Comparative life cycle analysis for value recovery of precious metals and rare earth elements from electronic waste. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.05.025
Liu WS, van der Ent A (2020) Spatially resolved localization of lanthanum and cerium in the rare earth element hyperaccumulator fern Dicranopteris linearis from China. Environ Sci Technol 54(4):2287–2294. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05728
Liu D, Zheng S, Wang X (2016) Lanthanum regulates the reactive oxygen species in the roots of rice seedlings. Sci Rep 6:31860. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31860
Lixandru A, Venkatesan P, Jönsson C, Poenaru I, Hall B, Yang Y, Walton A, Güth K, Gauß R, Gutfleisch O (2017) Identification and recovery of rare-earth permanent magnets from waste electrical and electronic equipment. Waste Manag 68:482–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.028
Ma Y, He X, Zhang P, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Zhang J, Wang G, Xie C, Luo W, Zhang J, Zheng L, Chai Z, Yang K (2017) Xylem and phloem based transport of CeO2 nanoparticles in hydroponic cucumber plants. Environ Sci Technol 51(9):5215–5221. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05998
Migaszewski ZM, Gałuszka A, Dołęgowska S (2016) Rare earth and trace element signatures for assessing an impact of rock mining and processing on the environment: Wiśniówka case study, south-central Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(24):24943–24959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7713-y
Nunes LAO, Souza AS, Carlos LD, Malta OL (2017) Neodymium doped fluoroindogallate glasses as highly-sensitive luminescent non-contact thermometers. Opt Mater 63:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.08.038
Oyanagui Y (1984) Reevaluation of assay methods and establishment of kit for superoxide dismutase activity. Anal Biochem 142(2):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(84)90467-6
Pagano G, Aliberti F, Guida M, Oral R, Siciliano A, Trifuoggi M, Tommasi F (2015) Rare earth elements in human and animal health: State of art and research priorities. Environ Res 142:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.06.039
Peng Q, Zhou Q (2009) Antioxidant capacity of flavonoid in soybean seedlings under the joint actions of rare earth element La(III) and ultraviolet-B stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 127(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8218-4
Pilon M, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Gogolin KA, Ye H (2006) Copper cofactor delivery in plant cells. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9(3):256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.007
Rauser WE (1999) Structure and function of metal chelators produced by plants: the case for organic acids, amino acids, phytin, and metallothioneins. Cell Biochem Biophys 31(1):19–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02738153
Salgado OGG, Teodoro JC, Alvarenga JP, de Oliveira C, de Carvalho TS, Domiciano D, Marchiori PER, Guilherme LRG (2020) Cerium alleviates drought-induced stress in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Rare Earths 38(3):324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.07.014
Schulze R, Buchert M (2016) Estimates of global REE recycling potentials from NdFeB magnet material. Resour Conserv Recycl 113:12–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.05.004
Shaikh S, Thomas K, Zuhair S (2020) An exploratory study of e-waste creation and disposal: upstream considerations. Resour Conserv Recycl 155:104662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104662
Sinha S, Gupta M, Chandra P (1996) Bioaccumulation and biochemical effects of mercury in the plant Bacopa monnieri (L). Environ Toxicol Water Qual 11(2):105–112
Siqueira-Silva AI, Rios CO, Pereira EG (2019) Iron toxicity resistance strategies in tropical grasses: the role of apoplastic radicular barriers. J Environ Sci 78:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.005
Smeets K, Cuypers A, Lambrechts A, Semane B, Hoet P, Van Laere A, Vangronsveld J (2005) Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidative mechanisms in Phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol Biochem 43(5):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.03.007
Stepka Z, Dror I, Berkowitz B (2018) The effect of nanoparticles and humic acid on technology critical element concentrations in aqueous solutions with soil and sand. Sci Total Environ 610-611:1083–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.170
Tai P, Zhao Q, Su D, Li P, Stagnitti F (2010) Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 80(9):1031–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.030
Wang X, Liu D (2017) Integration of cerium chemical forms and subcellular distribution to understand cerium tolerance mechanism in the rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(19):16336–16343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9274-0
Wang Z, Liu D, Lu P, Wang C (2001) Accumulation of rare earth elements in corn after agricultural application. J Environ Qual 30(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2001.30137x
Wang L, Huang X, Zhou Q (2009) Protective effect of rare earth against oxidative stress under ultraviolet-B radiation. Biol Trace Elem Res 128(1):82–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8250-4
Wang X, Lin Y, Liu D, Xu H, Liu T, Zhao F (2012) Cerium toxicity, uptake and translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. J Rare Earths 30(6):579–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60094-5
Wang J, Li D, Lu Q, Zhang Y, Xu H, Wang X, Li Y (2020) Effect of water-driven changes in rice rhizosphere on Cd lability in three soils with different pH. J Environ Sci 87:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.020
Weigel HJ, Jager HJ (1980) Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean plants. Plant Physiol 65(3):480–482. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.65.3.480
Weng B, Xie X, Weiss DJ, Liu J, Lu H, Yan C (2012) Kandelia obovata (S., L.) Yong tolerance mechanisms to Cadmium: subcellular distribution, chemical forms and thiol pools. Mar Pollut Bull 64(11):2453–2460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.047
Wu FB, Dong J, Qian QQ, Zhang GP (2005) Subcellular distribution and chemical form of Cd and Cd-Zn interaction in different barley genotypes. Chemosphere 60(10):1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.071
Xu T, Su C, Hu D, Li F, Lu Q, Zhang T, Xu Q (2016) Molecular distribution and toxicity assessment of praseodymium by Spirodela polyrrhiza. J Hazard Mater 312:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.040
Yuan D, X-q S, Huai Q, Wen B, Zhu X (2001) Uptake and distribution of rare earth elements in rice seeds cultured in fertilizer solution of rare earth elements. Chemosphere 43(3):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00142-9
Zakotnik M, Tudor CO, Peiró LT, Afiuny P, Skomski R, Hatch GP (2016) Analysis of energy usage in Nd–Fe–B magnet to magnet recycling. Environ Technol Innov 5:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2016.01.002
Zhan J, Huang H, Yu H, Zhang X, Zheng Z, Wang Y, Liu T, Li T (2020) The combined effects of Cd and Pb enhanced metal binding by root cell walls of the phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (Hook.). Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 258:113663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113663
Zhang W, Lin K, Zhou J, Zhang W, Liu L, Zhang Q (2014) Cadmium accumulation, sub-cellular distribution and chemical forms in rice seedling in the presence of sulfur. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(1):348–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.12.006
Zicari MA, d'Aquino L, Paradiso A, Mastrolitti S, Tommasi F (2018) Effect of cerium on growth and antioxidant metabolism of Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:536–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.113
Funding
This study was supported by the Major Basic Research Program of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020ZD19), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30900071), and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2014DM010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X Wang: conceptualization and supervision; KL Shi and KL Lyu: methodology; DW Liu: writing—original draft preparation; KL Shi, J Chen, and CK Liu: investigation; X Wang: writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable. Animals were not used in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, K., Liu, C., Liu, D. et al. The accumulation and effect of rare earth element neodymium on the root of rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 48656–48665 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14072-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14072-5