Abstract
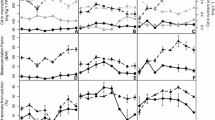
Suaeda salsa (L.) Pall., a typical halophyte plant in the Yellow River estuary, has high enrichment capacity for heavy metals. However, few studies have investigated the Cd absorption characteristics of S. salsa under different sediment burial and exogenous Cd input conditions, especially following the water-sediment regulation scheme (WSRS), which brought sediment burial and exogenous substances to the estuary. So, we established a greenhouse pot culture experiment with four sediment burial depths (0 cm, 3 cm, 6 cm, and 12 cm) and exogenous Cd input levels (0 mg·kg−1, 0.5 mg·kg−1, 1.0 mg·kg−1, and 1.5 mg·kg−1) and analyzed the leaf, stem, root, and total biomass; leaf, stem, and root Cd content; and storage, sediment Cd content, accumulation factor, root/leaf (R/L), root/stem (R/S), and stem/leaf (S/L) ratios to study the Cd absorption characteristics of S. salsa under the different sediment burial and exogenous Cd input. Results showed that high Cd content in roots, stems, and leaves was harmful to S. salsa growth, and then led to a decrease in biomass (characterized by stem, leaf, and total biomass). Suaeda salsa exhibited a survival strategy to deal with Cd toxicity, which involved the roots absorbing Cd from the sediment and storing it in stems and leaves (stem and leaf Cd content peaked at 0.5 mg·kg−1 Cd input) at low Cd input, whereas roots stored more Cd and reduced Cd transport to stems and leaves at high Cd input. Therefore, we observed the maximum value of leaf (500.63 ± 19.15 g·m−2), stem (648.22 ± 50.08 g·m−2), and total biomass (1246.92 ± 55.49 g·m−2) in the treatment with 1.5 mg·kg−1 Cd input and 3-cm sediment depth due to the Cd content in leaves and stems being relatively low. The accumulation factors of leaves, stems, and roots varied (0.39–0.99, 0.19–2.58, and 0.80–20.45, respectively), and most of the accumulation factors for roots and leaves and the R/L and R/S ratios were >1, which indicated that S. salsa had high enrichment levels of Cd, which mostly accumulated in the roots. Shallow or moderate burial depth was beneficial to S. salsa growth, but sediment burial was not beneficial to Cd absorption because the sum of leaf, stem, and root Cd storage was higher at 0-cm depth compared with the other depths. Variance analysis showed that the influence of Cd input on leaf, stem, root, and sediment Cd content and stem and root Cd storage was significant (P < 0.05), whereas sediment burial, interaction of sediment burial and Cd input on Cd content, storage, and biomass were not significant (P > 0.05). Therefore, we concluded that more attention should be paid to the control of sediment burial and heavy metal input, especially during the WSRS, in the Yellow River estuary.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abrahim G, Parker R (2002) Heavy-metal contaminants in Tamaki estuary: impact of city development and growth, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Geol 42:883–890
Azizollahi Z, Ghaderian SM, Ghotbi-Ravandi AA (2019) Cadmium accumulation and its effects on physiological and biochemical characters of summer savory (Satureja hortensis L.). Int J Phytorem 21:1241–1253
Bai JH, Huang LB, Yan DH, Wang QG, Gao HF, Xiao R, Huang C (2011) Contamination characteristics of heavy metals in wetland soils along a tidal ditch of the yellow river estuary, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 25:671–676
Bai J, Xiao R, Zhang K, Gao H (2012) Arsenic and heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from tidal freshwater and salt marshes before and after the flow-sediment regulation regime in the Yellow River delta, China. J Hydrol 450:244–253
Baldantoni D, Alfani AD, Tommasi P, Bartoli G, Virzo D, Santo A (2004) Assessment of macro and microelement accumulation capability of two aquatic plants. Environ Pollut 130:149–156
Çikili Y, Samet H, Dursun S (2016) Cadmium toxicity and its effects on growth and metal nutrient ion accumulation in Solanaceae plants. J Agric Sci 22:576–587
Cong M, Lv JS, Liu XL, Zhao JM, Wu HF (2013) Gene expression responses in Suaeda salsa after cadmium exposure. SpringerPlus 2:232–239
Cui BS, Yang QC, Yang ZF, Zhang KJ (2009) Evaluating the ecological performance of wetland restoration in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol Eng 35(7):1090–1103
Deng H, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2004) Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ Pollut 132:29–40
Deng ZF, An SQ, Zhao CJ, Chen L, Zhou CF, Zhi YB, Li HL (2008) Sediment burial stimulates the growth and propagule production of Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 76:818–826
Dias MC, Monteiro C, Moutinho-Pereira J, Correia C, Gonçalves B, Santos C (2013) Cadmium toxicity affects photosynthesis and plant growth at different levels. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1281–1289
Duman F, Cicek M, Sezen G (2007) Seasonal changes of metal accumulation and distribution in common club rush (Schoenoplectus lacustris) and common reed (Phragmites australis). Ecotoxicology 16:457–463
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2016) Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycinebetaine. S Afr J Bot 104:61–68
Fernandez RM, Fernandezfuego D, Bertrand A, Gonzalez AR (2014) Strategies for Cd accumulation in Dittrichia viscosa (L.) Greuter: role of the cell wall, non-protein thiols and organic acids. Plant Physiol Biochem 78:63–70
Gan Y, Huang X, Li S, Liu N, Li YC, Freidenreich A, Wang W, Wang R, Dai J (2019) Source quantification and potential risk of mercury, cadmium, arsenic, lead, and chromium in farmland soils of Yellow River Delta. J Clean Prod 221:98–107
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sediment logical approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
He J, Chen X, Wang X, Liu C, Zou Y (2012) The absorption and accumulation of heavy metals Cu and Pb in tidal wetland sediments by plant Suaeda heteroptera Kitag. J Dalian Ocean Univ 27(6):539–545 (in Chinese)
He SY, Yang XE, He ZL, Baligar VC (2017) Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: a review. Pedosphere 27:421–438
Hernandez LE, Carpena-Ruiz R, Garate A (1996) Alterations in the mineral nutrition of pea seedlings exposed to cadmium. J Plant Nutr 19:1581–1598
Jackson LJ (1998) Paradigms of metal accumulation in rooted aquatic vascular plants. Sci Total Environ 219:223–231
Jarvis JC, Moore KA (2015) Effects of seed source, sediment type, and burial depth on mixed-annual and perennial Zostera marina L. seed germination and seedling establishment. Estuar Coasts 38(3):964–978
Li LZ, Liu XL, Peijnenburg WJGM, Zhao JM, Chen XB, Yu JB, Wu HF (2012) Pathways of cadmium fluxes in the root of the halophyte Suaeda salsa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 75:1–7
Li YP, Sun MJ, He W, Wang H, Pan H, Yang QG, Lou YH, Zhuge YP (2021) Effect of phosphorus supplementation on growth, nutrient uptake, physiological responses, and cadmium absorption by tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 213:112021
Lima MW, Santos MLS, Faial KCF, Freitas ES, Lima MO, Pereira JAR, Cunha IPRT (2017) Heavy metals in the bottom sediments of the Furo of Laura estuary, Eastern Amazon, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 118(1-2):403–406
Lin RZ, Wang XR, Luo Y, Su WC, Guo HY, Yin DQ (2007) Effects of soil cadmium on growth, oxidative stress and antioxidant system in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Chemosphere 69:89–98
Liu HQ, Liu GJ, Wang J, Yuan ZJ, Da CN (2016) Fractional distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments collected from the Yellow River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11076–11084
Liu SM, Li LW, Zhang GL, Liu Z, Yu ZG, Ren JL (2012a) Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) estuary. J Hydrol 430-431:103–110
Liu SJ, Yang CY, Xie WJ, Xie CH, Fan P (2012b) The effects of cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Suaeda salsa. Procedia Environ Sci 16:293–298
Liu ZL, He XY, Chen W, Xu S, Ding WH (2009) Growth responses and cadmium accumulation of Lonicera japonica under cadmium stress. Chin J Ecol 28(8):1579–1583 (in Chinese)
Maun MA (1994) Adaptation enhancing survival and establishment of seedling on coastal dune systems. Vegetatio 111:59–70
Maun MA (1998) Adaptations of plants to burial in coastal sand dunes. Can J Bot 76(5):713–738
Meng GY, Jiang DS, Bai LY, Liu J, Wu LM, Zhou J (2012) Growth response, accumulation and transfer characteristics of ramie (Boehmeria nivea) under cadmium stress. Ecol Sci 31(2):192–196 (in Chinese)
Morina F, Küpper H (2020) Direct inhibition of photosynthesis by Cd dominates over inhibition caused by micronutrient deficiency in the Cd/Zn hyper accumulator Arabidopsis helleri. Plant Physiol Biochem 155:252–261
Mou XJ (2010) Study on the nitrogen biological cycling characteristics and cycling model of tidal wetland ecosystem in Yellow River estuary. Yantai institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yantai (in Chinese)
Mou XJ, Sun ZG (2011) Effects of sediment burial disturbance on seedling emergence and growth of Suaeda salsa in the tidal wetlands of the Yellow River estuary. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 409(1):99–106
Nyquist J, Greger M (2009) Response of two wetland plant species to Cd exposure at low and neutral pH. Environ Exp Bot 65:417–424
Pu G, Zeng D, Mo L, Liao J, Xu G, Huang Y, Zhang C (2018) Cadmium accumulation and its effects on physiological characteristics of Arundo donax L. in a simulated wetland. Global Nest J 20:1–7
Rao QH, Sun ZG, Tian LP, Li J, Sun WL, Sun WG (2018) Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in inshore sediments of the Yellow River estuary, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 32:2889–2902
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soil and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Song HL, Sun ZG (2014) Temporal variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in different Suaeda salsa marshes of the Yellow River estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:14174–14187
Song HL, Wang LZ, Yu WN, Wu XY (2018) Effects of sediment burial and exogenous Cd input on biomass allocation and antioxidative enzyme activities of Suaeda salsa in the coastal wetland of the Yellow River delta. Environ Sci 39(8):3910–3916
State Oceanic Administration of China (2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014) Ocean environmental quality communique of China in 2009, 2010, 2011,2012, 2013. (http://www.coi.gov.cn/gongbao/huanjing/201107/t20110729_17486.html)
Su FL, Wang TL, Zhang HZ, Song Z, Feng X, Zhang K (2018) The distribution and enrichment characteristics of copper in soil and Phragmites australis of Liao River estuary wetland. Environ Monit Assess 190:364–373
Sun ZG, Song HL, Sun WG, Sun JK (2014) Effects of continual burial by sediment on morphological traits and dry mass allocation of Suaeda salsa seedlings in the Yellow River estuary: an experimental study. Ecol Eng 68:176–183
Sun ZG, Mou XJ, Tong C, Wang CY, Xie ZL, Song HL, Sun WG, Lv YC (2015) Spatial variations and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in intertidal zone of the Yellow River estuary, China. Catena 126:43–52
Wang JJ, Bai JH, Gao ZQ, Lu QQ, Zhao QQ (2015) Soil as levels and bioaccumulation in Suaeda salsa and Phragmites australis wetlands of the yellow river estuary, China. Biomed Res Int 2015:301898 1-7
Wang X, Li Y, Liu C, Zhang Z, Shi G (2012) Effects of cadmium and salicylic acid on growth, Cd accumulation and photosynthesis of an energy crop, castor bean. Third International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation. IEEE.
Wang Y, Liu Z, Liu X, Song X, Cui D (2019) Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the topsoil of the Yellow River delta. J Soil Water Conserv 33(3):305–319
Xie ZL, Zhao GS, Sun ZG, Liu JY (2014) Comparison of arsenic and heavy metals contamination between existing wetlands and wetlands created by river diversion in the Yellow River estuary, China. Environ Earth Sci 72:1667–1681
vXu B, Xia D, Burnett WC, Dimova NT, Wang H, Zhang L, Gao M, Jiang X, Yu Z (2014) Natural 222Rn and 220Rn indicate the impact of the water–sediment regulation scheme (WSRS) on submarine groundwater discharge in the Yellow River estuary, China. Appl Geochem 51:79–85
Yu JB, Dong HF, Wang HB, Chen XB, Xie WJ, Mao PL, Gao YJ, Shan K, Chen JC, Ma XM (2011) Spatial distribution characteristics of metals in new-born coastal wetlands in the Yellow River delta. Wetland Sci 9(4):297–304
Zhang H, Zhao X, Du Z, Xiang L (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and wetland management in a newly created coastal natural reserve, China. J Coast Res 32(2):374–386
Zhang HG, Cui BS, Zhang KJ (2012) Surficial and vertical distribution of heavy metals in different estuary wetlands in the Pearl River, south China. Clean Soil, Air, Water 40(10):1174–1184
Zhang J, Zhao XX, Wang X, Lu WX (2015) Effects of cadmium stress on the growth and physiological property of Oenanthe javanica. Plant Physiol J 51(11):1969–1974
Zhang P, Huang H, Liu WR, Zhang CL (2017) Physiological mechanisms of a wetland plant (Echinodorus Osiris Rataj) to cadmium detoxification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21859–21866
Zhang S, Bai JH, Wang W, Huang LB, Zhang GL, Wang DW (2018) Heavy metal contents and transfer capacities of Phragmites australis and Suaeda salsa in the Yellow River Delta, China. Phys Chem Earth 104:3–8
Zheng G, Lv HP, Gao S, Wang SR (2010) Effects of cadmium on growth and antioxidant responses in Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings. Plant Soil Environ 56(11):508–515
Zhu GX, Xiao HY, Guo QJ, Zhang ZY, Zhao JJ, Yang D (2018) Effects of cadmium stress on growth and amino acid metabolism in two Compositae plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:300–308
Zhu MH, Ding YS, Zheng DC, Tao P, Ji YX, Cui Y, Gong WM, Ding DW (2005) Accumulation and tolerance of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd in plant Suaeda heteroptera Kitag in tideland. Mar Environ Sci 24(2):13–16
Zourarah B, Maanan M, Robin M, Carruesco C (2009) Sedimentary records of anthropogenic contribution to heavy metal content in Oum Er Bia Estuary (Morocco). Environ Chem Lett 7:67–78
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41601086; 41977067) and Project of Introducing and Cultivating Young Talent in the Universities of Shandong Province (No. QC2019YY144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Hongli Song, Juan An, Qianjin Liu, and Xiang Jin. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hongli Song, and the multi-way ANOVA analysis was performed by Yan Yan. Yuanzhi Wu and Xiyuan Wu commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., An, J., Liu, Q. et al. Cd absorption characteristics of Suaeda salsa under different sediment burial and exogenous Cd input conditions in the Yellow River estuary, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 62368–62377 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14066-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14066-3