Abstract
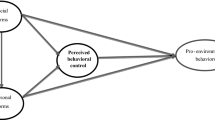
This study uses the theory of planned behavior to examine the individual’s intentions and zig-zag kiln technology adoption attitude in responding to carbon emissions in Pakistan. This study is based on cross-sectional data and a representative sample of 335 brick kilns owners from 11 districts of Punjab province of Pakistan is collected. Partial least squares structural equation modeling technique was used for the analysis. Results depicted that environmental concern and self-efficacy have a significant influence on attitude toward sustainable technology while subjective norms have a significant effect on intentions toward zig-zag kiln technology. A 1% increase in environmental concern and self-efficacy increases sustainable environmental technology by 24% and 58%, respectively. Furthermore, perceived behavioral control and intentions also significantly impact adoption attitude, and a 1% increase in perceived behavioral control and intentions increase the zig-zag kiln adoption attitude by 68% and 30%, respectively. Results depicted that adoption attitude is significantly determined by these explanatory variables. The study’s findings provided new evidence for the government to place more emphasis on enhancing kiln owners’ attitudes, social norms, and perceived behavioral control, which would lead towards the adoption of this new technique.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Research data can be provided upon serious request.
References
Abir AH, Sarker AH (2019) Role of laws to control brick manufacturing and kiln establishment in Bangladesh: scope of alternative bricks. VNU J Sci: Earth and Environmental Sciences 35(1)
Adnan N, Nordin SM, Rahman I, Rasli AM (2017) A new era of sustainable transport: an experimental examination on forecasting adoption behaviour of EVs among Malaysian consumer. Transp Res A Policy Pract 103:279–295
Adnan N, Nordin SM, Amini MH, Langove N (2018) What make consumer sign up to PHEVs? Predicting Malaysian consumer behaviour in adoption of PHEVs. Transp Res A Policy Pract 113:259–278
Afroz R, Masud MM, Akhtar R, Islam MA, Duasa JB (2015) Consumer purchase intention towards environmentally friendly vehicles: an empirical investigation in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):16153–16163
Ahmad M, Zhao ZY, Irfan M, Mukeshimana MC (2019) Empirics on influencing mechanisms among energy, finance, trade, environment, and economic growth: a heterogeneous dynamic panel data analysis of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14148–14170
Ajzen I (2002a) Residual effects of past on later behaviour: habituation and reasoned action perspectives. Personal Soc Psychol Rev 6(2):107–122
Ajzen I (2002b) Perceived behavioural control, self-efficacy, locus of control, and the theory of planned behaviour. J Appl Soc Psychol 32(4):665–683
Akinshipe, O., & Kornelius, G. (2017). Chemical and thermodynamic processes in clay brick firing technologies and assosciated atmospheric emissions metrics-a review.
Al Mamun A, Masud MM, Fazal SA, Muniady R (2019) Green vehicle adoption behaviour among low-income households: evidence from coastal Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27305–27318
Alam, S. (2019). A review of the existing policy instrument for transforming the brick kiln sector of Bangladesh.
Ali MR, Shafiq M, Andejany M (2021) Determinants of consumers’ intentions towards the purchase of energy efficient appliances in Pakistan: an extended model of the theory of planned behaviour. Sustainability 13(2):565
Aubert BA, Schroeder A, Grimaudo J (2012) IT as enabler of sustainable farming: an empirical analysis of farmers’ adoption decision of precision agriculture technology. Decis Support Syst 54(1):510–520
Babbie E, Wagner III WE, & Zaino J (2018). Adventures in social research: data analysis using IBM SPSS statistics. Sage Publications.
Bamberg S (2003) How does environmental concern influence specific environmentally related behaviours? A new answer to an old question. J Environ Psychol 23(1):21–32
Beck L, Ajzen I (1991) Predicting dishonest actions using the theory of planned behaviour. J Res Pers 25(3):285–301
Bobek DD, Hatfield RC (2003) An investigation of the theory of planned behaviour and the role of moral obligation in tax compliance. Behav Res Account 15(1):13–38
Borges JAR, Tauer LW, Lansink AGO (2016) Using the theory of planned behaviour to identify key beliefs underlying Brazilian cattle farmers’ intention to use improved natural grassland: a MIMIC modelling approach. Land Use Policy 55:193–203
Cavaliere A, Ventura V (2018) Mismatch between food sustainability and consumer acceptance toward innovation technologies among Millennial students: the case of Shelf Life Extension. J Clean Prod 175:641–650
Cheah, I., & Phau, I. (2011). Attitudes towards environmentally friendly products. Market Intelligence Plan.
Chen MF, Tung PJ (2014) Developing an extended theory of planned behaviour model to predict consumers’ intention to visit green hotels. Int J Hosp Manag 36:221–230
Chen H, Hao Y, Li J, Song X (2018) The impact of environmental regulation, shadow economy, and corruption on environmental quality: theory and empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 195:200–214
Cheung R, Lau MM, Lam AY (2015) Factors affecting consumer attitude towards organic food: an empirical study in Hong Kong. J Glob Scholars Market Sci 25(3):216–231
Das, S., Murad, S. I., Ulla, M. S. A., Ahamed, J. U., & Razzaq, M. A. (2019). Prospect and energy analysis of zigzag brickfields in Bangladesh.
David M, Afzal M, Shoaib M, Aman F, Cloete KJ, Turi N, Jahan S (2020) Study of occupational exposure to brick kiln emissions on heavy metal burden, biochemical profile, cortisol level and reproductive health risks among female workers at Rawat, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(35):44073–44088
Diamantopoulos A, Siguaw JA (2006) Formative versus reflective indicators in organizational measure development: a comparison and empirical illustration. Br J Manag 17(4):263–282
Fishbein M, Jaccard J, Davidson AR, Ajzen I, Loken B (1980) Predicting and understanding family planning behaviours. In Understanding attitudes and predicting social behaviour, Prentice Hall
Fornell C, Larcker DF (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res 18(1):39–50
Fu JR (2011) Understanding career commitment of IT professionals: perspectives of push–pull–mooring framework and investment model. Int J Inf Manag 31(3):279–293
Gallagher KS, Muehlegger E (2011) Giving green to get green? Incentives and consumer adoption of hybrid vehicle technology. J Environ Econ Manag 61(1):1–15
Gao L, Wang S, Li J, Li H (2017) Application of the extended theory of planned behaviour to understand individual’s energy saving behaviour in workplaces. Resour Conserv Recycl 127:107–113
Garson GD (2016) Partial least squares: regression and structural equation models. Statistical Associates Publishers, Asheboro
Giles M, Mcclenahan C, Cairns E, Mallet J (2004) An application of the theory of planned behaviour to blood donation: the importance of self-efficacy. Health Educ Res 19(4):380–391
Ha HY, Janda S (2012) Predicting consumer intentions to purchase energy-efficient products. J Consum Mark 29:461–469
Hair Jr JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, & Gudergan SP (2017). Advanced issues in partial least squares structural equation modeling. Sage Publications.
Hair JF, Gabriel M, Patel V (2014) AMOS covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM): guidelines on its application as a marketing research tool. Braz J Market 13(2):44–55
Hazen BT, Mollenkopf DA, Wang Y (2017) Remanufacturing for the circular economy: an examination of consumer switching behaviour. Bus Strateg Environ 26(4):451–464
Hsieh JK, Hsieh YC, Chiu HC, Feng YC (2012) Post-adoption switching behaviour for online service substitutes: a perspective of the push–pull–mooring framework. Comput Hum Behav 28(5):1912–1920
Hussan A (2020) The repercussions of development: brick kilns a boon (economy) or bane (environment). an observation made through analysis of some air parameters. Plant Arch 20(2):1945–1948
ILO (2017) World Employment and Social Outlook. International Labor Organization, Geneva
Irfan M, Hao Y, Ikram M, Wu H, Akram R, Rauf A (2021) Assessment of the public acceptance and utilization of renewable energy in Pakistan. Sustain Prod Consum 27:312–324
Jabeen G, Yan Q, Ahmad M, Fatima N, Qamar S (2019) Consumers’ intention-based influence factors of renewable power generation technology utilization: a structural equation modeling approach. J Clean Prod 237:117737
Janmaimool P (2017) Application of protection motivation theory to investigate sustainable waste management behaviours. Sustainability 9(7):1079
Judge M, Warren-Myers G, Paladino A (2019) Using the theory of planned behaviour to predict intentions to purchase sustainable housing. J Clean Prod 215:259–267
Jung J, Han H, Oh M (2017) Travelers’ switching behaviour in the airline industry from the perspective of the push-pull-mooring framework. Tour Manag 59:139–153
Khalid S (2019) An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J Geochem Explor 197:14–26
Khan MW, Ali Y, De Felice F, Salman A, Petrillo A (2019) Impact of brick kilns industry on environment and human health in Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 678:383–389
Khare A (2015). Antecedents to green buying behaviour: a study on consumers in an emerging economy. Market Intell Plann.
Kim Y, & Choi SM (2005). Antecedents of green purchase behaviour: an examination of collectivism, environmental concern, and PCE. ACR North Am Adv.
Kumar A (2019) Exploring young adults’e-waste recycling behaviour using an extended theory of planned behaviour model: a cross-cultural study. Resour Conserv Recycl 141:378–389
Lalani B, Dorward P, Holloway G, Wauters E (2016) Smallholder farmers’ motivations for using Conservation Agriculture and the roles of yield, labour and soil fertility in decision making. Agric Syst 146:80–90
Le Dang H, Li E, Nuberg I, Bruwer J (2014) Understanding farmers’ adaptation intention to climate change: a structural equation modelling study in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ Sci Pol 41:11–22
Linan, F., Rodríguez-Cohard, J. C., & Rueda-Cantuche, J. M. (2005). Factors affecting entrepreneurial intention levels. 4Sth Congress Eur Reg Sci Assoc.
Lopes JRN, de Araújo Kalid R, Rodríguez JLM, Ávila Filho S (2019) A new model for assessing industrial worker behaviour regarding energy saving considering the theory of planned behaviour, norm activation model and human reliability. Resour Conserv Recycl 145:268–278
Lundgren-Kownacki K, Kjellberg SM, Gooch P, Dabaieh M, Anandh L, Venugopal V (2018) Climate change-induced heat risks for migrant populations working at brick kilns in India: a transdisciplinary approach. Int J Biometeorol 62(3):347–358
Ma YJ, Gam HJ, Banning J (2017) Perceived ease of use and usefulness of sustainability labels on apparel products: application of the technology acceptance model. Fash Text 4(1):1–20
Maichum K, Parichatnon S, Peng KC (2016) Application of the extended theory of planned behaviour model to investigate purchase intention of green products among Thai consumers. Sustainability 8(10):1077
Marques CS, Ferreira JJ, Gomes DN, Rodrigues RG (2012) Entrepreneurship education: how psychological, demographic and behavioural factors predict the entrepreneurial intention. Educ Train 54(8-9):657–672
Mazumdar M, Goswami H, Debnath A (2018) Brick industry as a source of pollution-its causes and impacts on human rights: a case study of brick kilns of palasbari revenue circle. Int J Humanit Soc Sci 6(3):220–240
Moons I, De Pelsmacker P (2012) Emotions as determinants of electric car usage intention. J Mark Manag 28(3-4):195–237
Moser AK (2015) Thinking green, buying green? Drivers of pro-environmental purchasing behaviour. J Consum Mark 32:167–175
Nasim S, Sharif F (2020) To adopt, or not to adopt, ‘why’ is the question: a case for clean kiln technologies in developing countries. J Clean Prod 257:120553
Nasir M, Rehman FU, Kishwar S, Bashir S, & Adil M (2021). Air pollution and child health: the impact of brick kiln pollution on children’s cognitive abilities and physical health in Pakistan. Environ Dev Sustain 1-17.
Osman A, Md Isa F, Othman SN, Jaganathan M (2014) Attitude towards recycling among business undergraduate students in Malaysia. Am-Eurasian J Sustain Agric 8(13):6–12
Oteng-Peprah M, De Vries N, Acheampong MA (2020) Households’ willingness to adopt greywater treatment technologies in a developing country–exploring a modified theory of planned behaviour (TPB) model including personal norm. J Environ Manag 254:109807
Patra SHK (2021) STATUS OF BRICK KILN WORKERS IN SOUTH-EAST ASIA. J Nat Remedies 21(10):1
Petschnig M, Heidenreich S, Spieth P (2014) Innovative alternatives take action–investigating determinants of alternative fuel vehicle adoption. Transp Res A Policy Pract 61:68–83
Qader IKA, Zainuddin Y (2011) The influence of media exposure, safety and health concerns, and self-efficacy on environmental attitudes towards electronic green products. Asian Acad Manag J 16(2)
Rahman S, & Kazi SM (2019). Assessment of brick kiln technologies of Bangladesh.
Ramayah T, Lee JWC, Lim S (2012) Sustaining the environment through recycling: an empirical study. J Environ Manag 102:141–147
Ru X, Qin H, Wang S (2019) Young people’s behaviour intentions towards reducing PM2. 5 in China: extending the theory of planned behaviour. Resources. Conserv Recycl 141:99–108
Saikawa E, Panday A, Kang S, Gautam R, Zusman E, Cong Z, ... & Adhikary B (2019). Air pollution in the Hindu Kush Himalaya. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment, 339-387.
Sajjad A, Chu J, Anwar MA, Asmi F (2020) Between green and gray: smog risk and rationale behind vehicle switching. J Clean Prod 244:118674
Sánchez M, López-Mosquera N, Lera-López F (2016) Improving pro-environmental behaviours in Spain. The role of attitudes and socio-demographic and political factors. J Environ Policy Plan 18(1):47–66
Sandelowski M (1996) One is the liveliest number: the case orientation of qualitative research. Res Nurs Health 19(6):525–529
Sangroya D, Nayak JK (2017) Factors influencing buying behaviour of green energy consumer. J Clean Prod 151:393–405
Sanjel S, Thygerson SM, Khanal SN, Joshi SK (2016) Environmental and occupational pollutants and their effects on health among brick kiln workers. Open J Saf Sci Technol 6:81–98
Saud B, Paudel G (2018) The threat of ambient air pollution in Kathmandu. Nepal J Environ Public Health 2018
Saunders M, Lewis P, Thornhill A (2009) Research methods for business students. Financial Times/Prentice Hall, Essex
Shafqat D, & Shahid S (2020). Quarterly Issue 45 & 48.
Shi H, Wang S, Zhao D (2017) Exploring urban resident’s vehicular PM2. 5 reduction behaviour intention: an application of the extended theory of planned behaviour. J Clean Prod 147:603–613
Siegrist M, Hartmann C (2020) Consumer acceptance of novel food technologies. Nat Food 1(6):343–350
Sok J, Hogeveen H, Elbers ARW, Lansink AO (2016) Using farmers’ attitude and social pressures to design voluntary Bluetongue vaccination strategies. Prev Vet Med 133:114–119
Sun Y, Liu D, Chen S, Wu X, Shen XL, Zhang X (2017) Understanding users’ switching behaviour of mobile instant messaging applications: an empirical study from the perspective of push-pull-mooring framework. Comput Hum Behav 75:727–738
Tabernero C, Hernández B (2011) Self-efficacy and intrinsic motivation guiding environmental behaviour. Environ Behav 43(5):658–675
Tonglet M, Phillips PS, Read AD (2004) Using the theory of planned behaviour to investigate the determinants of recycling behaviour: a case study from Brixworth, UK. Resour Conserv Recycl 41(3):191–214
Tsarenko Y, Ferraro C, Sands S, McLeod C (2013) Environmentally conscious consumption: the role of retailers and peers as external influences. J Retail Consum Serv 20(3):302–310
Valdes H, Vilches J, Felmer G, Hurtado M, Figueroa J (2020) Artisan brick kilns: state-of-the-art and future trends. Sustainability 12(18):7724
van Dijk WF, Lokhorst AM, Berendse F, De Snoo GR (2016) Factors underlying farmers’ intentions to perform unsubsidised agri-environmental measures. Land Use Policy 59:207–216
Walton T, Austin DM (2011) Pro-environmental behaviour in an urban social structural context. Sociol Spectr 31(3):260–287
Wan C, Shen GQ, Choi S (2017) Experiential and instrumental attitudes: interaction effect of attitude and subjective norm on recycling intention. J Environ Psychol 50:69–79
Wang S, Fan J, Zhao D, Yang S, Fu Y (2016) Predicting consumers’ intention to adopt hybrid electric vehicles: using an extended version of the theory of planned behaviour model. Transportation 43(1):123–143
Wang C, Zhang J, Yu P, Hu H (2018) The theory of planned behaviour as a model for understanding tourists’ responsible environmental behaviours: the moderating role of environmental interpretations. J Clean Prod 194:425–434
Wang S, Wang J, Yang F, Li J, & Song J (2019). Determinants of consumers’ remanufactured products purchase intentions: evidence from China. International J Prod Res 1-16.
Wong KKK (2019). Mastering partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) with Smartpls in 38 hours. iUniverse
Wu SI, Chen JY (2014) A model of green consumption behaviour constructed by the theory of planned behaviour. Int J Market Stud 6(5):119
Xu Y, Zhang W, Bao H, Zhang S, Xiang Y (2019) A SEM–neural network approach to predict customers’ intention to purchase battery electric vehicles in China’s Zhejiang province. Sustainability 11(11):3164
Yanakittkul P, Aungvaravong C (2020) A model of farmers intentions towards organic farming: a case study on rice farming in Thailand. Heliyon 6(1):e03039
Yarimoglu E, & Gunay T (2019). The extended theory of planned behaviour in Turkish customers’ intentions to visit green hotels. Bus Strategy Environ.
Zavala, M., Molina, L. T., Maiz, P., Monsivais, I., Chow, J. C., Watson, J. G., ... & Roscioli, J. R. (2018). Black carbon, organic carbon, and co-pollutant emissions and energy efficiency from artisanal brick production in Mexico. Atmos Chem Physics, 18(8), 6023, 6037.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to all those who provided help during the process of making this study and especially to anonymous reviewers who gave their precious time to review our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAA Naqvi and S Anwar: supervision, conceptualization, and formal analysis; B Hussain: writing-original draft; RHU Hassan: data collection and processing; SAR Shah and AA Shah: interpretation of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors have considered all research ethics to conduct this research.
Consent to participate
Verbal consent of all the respondents was taken. Participants were clearly briefed that their data would only be used for the study purpose and they agreed to give the required information.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publication in the journal.
Competing interests
The author declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 555 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, B., Naqvi, S.A.A., Anwar, S. et al. Zig-zag technology adoption behavior among brick kiln owners in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 45168–45182 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13837-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13837-2