Abstract
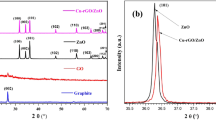
Novel tri-phase CuO–MgO–ZnO nanocomposite was prepared using the co-precipitation technique and investigated its physical properties using characterization techniques including XRD, FTIR, Raman, IV, UV-vis, PL, and SEM. The application of grown CuO–MgO–ZnO nanocomposite for the degradation of various dyes under sunlight and antibacterial activity against different bacteria were studied. The XRD confirmed the existence of diffraction peaks related to CuO (monoclinic), MgO (cubic), and ZnO (hexagonal) with CuO phase 40%, MgO 24%, and ZnO 36%. The optical energy gap of nanocomposite was 2.9 eV, which made it an efficient catalyst under sunlight. Raman and FTIR spectra have further confirmed the formation of the nanocomposite. SEM images revealed agglomerated rod-shaped morphology. EDX results showed the atomic percentage of a constituent element in this order Cu>Zn>Mg. PL results demonstrate the presence of intrinsic defects. The photocatalytic activity against methylene blue (MB), methyl orange (MO), rhodamine-B (RhB), cresol red (CR), and P-nitroaniline (P-Nitro) dyes has shown the excellent degradation efficiencies 88.5%, 93.5%, 75.9%, 98.8%, and 98.6% at 5 ppm dye concentration and 82.6%, 83.6%, 64.3%, 93.1%, and 94.3% at 10 ppm dye concentration in 100 min, respectively, under sunlight illumination. The higher degradation is due to the generation of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. The recyclability test showed the reusability of catalyst up to the 5th cycle. The antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus Vulgaris, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria with the zone of inhibition 30, 31, 30, 30, and 30 mm, respectively, was achieved.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Abou Dalle A, Domergue L, Fourcade F et al (2017) Efficiency of DMSO as hydroxyl radical probe in an electrochemical advanced oxidation process − reactive oxygen species monitoring and impact of the current density. Electrochim Acta 246:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.06.024
Adeleke JT, Theivasanthi T, Thiruppathi M et al (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by ZnO/NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 455:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.184
Alla SK, Verma AD, Kumar V et al (2016) Solvothermal synthesis of CuO-MgO nanocomposite particles and their catalytic applications. RSC Adv 6:61927–61933. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra03762c
Azzaz AA, Assadi AA, Jellali S et al (2018) Discoloration of simulated textile effluent in continuous photoreactor using immobilized titanium dioxide: effect of zinc and sodium chloride. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 358:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.01.032
Balachandramohan J, Anandan S, Sivasankar T (2018) A simple approach for the sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4-guargum nanocomposite and its catalytic reduction of p-nitroaniline. Ultrason Sonochem 40:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.06.012
Balakrishnan G, Velavan R, Mujasam Batoo K, Raslan EH (2020) Microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties of MgO nanoparticles. Results Phys 16:103013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103013
Balu AR, Srivind J, Narasimman V et al (2018) Multi metal oxide CdO–Al2O3–NiO nanocomposite—synthesis, photocatalytic and magnetic properties. Mater Res Express 6:015022. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae5af
Belkhaoui C, Mzabi N, Smaoui H, Daniel P (2019) Enhancing the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanopowders through (Al + Mn) doping. Results Phys 12:1686–1696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.01.085
Beura R, Pachaiappan R, Thangadurai P (2018) A detailed study on Sn4+ doped ZnO for enhanced photocatalytic degradation. Appl Surf Sci 433:887–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.127
Butler MA, Ginley DS (1978) Prediction of flatband potentials at semiconductor-electrolyte interfaces from atomic electronegativities. J Electrochem Soc 125:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2131419
Camargo PHC, Satyanarayana KG, Wypych F (2009) Nanocomposites: synthesis, structure, properties and new application opportunities. Mater Res 12:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392009000100002
Chachvalvutikul A, Jakmunee J, Thongtem S et al (2019) Novel FeVO4/Bi7O9I3 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic dye degradation and photoelectrochemical properties. Appl Surf Sci 475:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.214
Cuscó R, Alarcón-Lladó E, Ibáñez J et al (2007) Temperature dependence of Raman scattering in ZnO. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 75:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.165202
Dinesha ML, Jayanna HS, Mohanty S, Ravi S (2010) Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Co and Fe co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion method. J Alloys Compd 490:618–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.10.120
El-Desoky MM, Ali MA, Afifi G et al (2018) Effects of annealing temperatures on the structural and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Silicon 10:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9445-5
Elimelech M, Phillip WA (2011) The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333:712–717. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1200488
Epie EN, Chu WK (2016) Ionoluminescence study of Zn - and O - implanted ZnO crystals: An additional perspective. Appl Surf Sci 371:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.174
Gnanasekaran L, Hemamalini R, Saravanan R et al (2017) Synthesis and characterization of metal oxides (CeO2, CuO, NiO, Mn3O4, SnO2 and ZnO) nanoparticles as photo catalysts for degradation of textile dyes. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 173:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.05.027
Hezam A, Namratha K, Drmosh QA et al (2018) Direct Z-scheme Cs2O-Bi2O3-ZnO heterostructures for photocatalytic overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A 6:21379–21388. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta08033j
Huang W, Liu R (2011) Photocatalytic degradation of p-Nitroaniline with composite photocatalyst H3P12W40/TiO2. Adv Mater Res 233–235:967–970. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.233-235.967
Huang H, Wang S, Zhang Y, Chu PK (2014) Band gap engineering design for construction of energy-levels well-matched semiconductor heterojunction with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 40:41219–41227. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra05708b
Ishikawa K, Fujima N, Komura H (1985) First-order Raman scattering in MgO microcrystals. J Appl Phys 57:973–975. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.334701
Jana TK, Maji SK, Pal A et al (2016) Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of cadmium sulphide / zinc oxide nanocomposite with varied morphology. J Colloid Interface Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.073
Jiajie Y, Kiwi J, Wang T, Pulgarin C, Rtimi S (2019) Duality in the mechanism of hexagonal ZnO/CuxO Nanowires inducing sulfamethazine degradation under solar or visible light. Catalysts 9:916. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110916
Juma A, Arbab E, Afirca S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of CuO-NiO-ZnO mixed metal oxide nanocomposite. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.288
Kamagate M, Assadi AA, Kone T et al (2018) Use of laterite as a sustainable catalyst for removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from contaminated water. Chemosphere 195:847–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.165
Kant R, Kumar D, Ghose R (2015) Synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnO – NiO mixed metal oxide powder by homogeneous precipitation method. Ceram Int:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.081
Karthik K, Dhanuskodi S, Gobinath C et al (2018) Multifunctional properties of microwave assisted CdO–NiO–ZnO mixed metal oxide nanocomposite: enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:5459–5471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8513-y
Khayatian SA, Kompany A, Shahtahmassebi N, Khorsand Zak A (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of Al-Doped ZnO NPs-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for removing of methyl orange dye from water under visible-light irradiation. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28:2677–2688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0940-6
Khokhra R, Bharti B, Lee HN, Kumar R (2017) Visible and UV photo-detection in ZnO nanostructured thin films via simple tuning of solution method. Sci Rep 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15125-x
Klubnuan S, Amornpitoksuk P, Suwanboon S (2015) Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of MgO/ZnO nanocomposites prepared by a hydrothermal method. Mater Sci Semicond Process 39:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.05.049
Kumar PS, Selvakumar M, Bhagabati P et al (2014) CdO/ZnO nanohybrids: facile synthesis and morphologically enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 4:32977–32986. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra02502d
Kumar K, Priya A, Arun A et al (2019) Antibacterial and natural room-light driven photocatalytic activities of CuO nanorods. Mater Chem Phys 226:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.020
Lei Y, Huo J, Liao H (2017) Microstructure and photocatalytic properties of polyimide/heterostructured NiO-Fe2O3-ZnO nanocomposite films via an ion-exchange technique. RSC Adv 7:40621–40631. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra07611h
Li W, Wang G, Feng Y, Li Z (2018) Efficient photocatalytic performance enhancement in Co-doped ZnO nanowires coupled with CuS nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 428:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.049
Linda T, Muthupoongodi S, Shajan XS, Balakumar S (2016) Fabrication and characterization of chitosan templated CdO/NiO nano composite for dye degradation. Optik (Stuttg) 127:8287–8293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.06.025
Mamba G, Kiwi J, Pulgarin C et al (2018) Evidence for the degradation of an emerging pollutant by a mechanism involving iso-energetic charge transfer under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 233:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.109
Maria Magdalane C, Kaviyarasu K, Judith Vijaya J et al (2017) Facile synthesis of heterostructured cerium oxide/yttrium oxide nanocomposite in UV light induced photocatalytic degradation and catalytic reduction: synergistic effect of antimicrobial studies. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 173:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.05.024
Mondal S, Bobde K, Aikat K, Halder G (2016) Biosorptive uptake of ibuprofen by steam activated biochar derived from mung bean husk: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, modeling and eco-toxicological studies. J Environ Manag 182:581–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.018
Mukhtar F, Munawar T, Shahid M et al (2020) Multi metal oxide NiO-Fe2O3-CdO nanocomposite - synthesis , photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03776-z
Mukhtar F, Munawar T, Nadeem MS et al (2021) Dual S-scheme heterojunction ZnO-V2O5-WO3 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. Mater Chem Phys 263:124372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124372
Munawar T, Iqbal F, Yasmeen S et al (2020a) Multi metal oxide NiO-CdO-ZnO nanocomposite – synthesis , structural , optical , electrical properties and enhanced sunlight driven photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 46:2421–2437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.236
Munawar T, Mukhtar F, Nadeem MS et al (2020b) Novel photocatalyst and antibacterial agent; direct dual Z-scheme ZnO–CeO2-Yb2O3 heterostructured nanocomposite. Solid State Sci 109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106446
Munawar T, Mukhtar F, Nadeem MS et al (2020c) Multifunctional properties of Zn0.9Mn0.05M0.05O (M = Al, Bi, Sr, Ag) nanocrystals-structural and optical study: Enhance sunlight driven photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.316
Munawar T, Mukhtar F, Nadeem MS et al (2020d) Novel direct dual-Z-scheme ZnO-Er2O3-Nd2O3@reduced graphene oxide heterostructured nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and superior antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys:123249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123249
Munawar T, Mukhtar F, Nadeem MS et al (2020e) Structural, optical, electrical, and morphological studies of rGO anchored direct dual-Z-scheme ZnO-Sm2O3–Y2O3 heterostructured nanocomposite: an efficient photocatalyst under sunlight. Solid State Sci:106307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106307
Munawar T, Yasmeen S, Hasan M et al (2020f) Novel tri-phase heterostructured ZnO–Yb2O3–Pr2O3 nanocomposite; structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.130
Munawar T, Yasmeen S, Hussain A et al (2020g) Novel direct dual-Z-scheme ZnO-Er2O3-Yb2O3 heterostructured nanocomposite with superior photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Mater Lett 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127357
Munawar T, Yasmeen S, Hussain F et al (2020h) Synthesis of novel heterostructured ZnO-CdO-CuO nanocomposite: characterization and enhanced sunlight driven photocatalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys 249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122983
Munawar T, Yasmeen S, Mukhtar F et al (2020i) Zn0.9Ce0.05M0.05O (M = Er, Y, V) nanocrystals: structural and energy bandgap engineering of ZnO for enhancing photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Ceram Int 46:14369–14383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.232
Munawar T, Nadeem MS, Mukhtar F et al (2021) Rare earth metal co-doped Zn0·9La0.05M0.05O (M = Yb, Sm, Nd) nanocrystals; energy gap tailoring, structural, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Mater Sci Semicond Process 122:105485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105485
Nadeem MS, Munawar T, Mukhtar F et al (2020) Enhancement in the photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanoparticles by structural variations and energy bandgap tuning through Fe and Co co-doping. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.234
Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A, Karimi-Shamsabadi M (2014) Comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of supported CuO onto micro and nano particles of zeolite X in photodecolorization of methylene blue and methyl orange aqueous mixture. Appl Catal A Gen 477:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.02.031
Nouri A, Yaraki MT, Ghorbanpour M et al (2018) Enhanced antibacterial effect of chitosan film using montmorillonite/CuO nanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 109:1219–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.119
Nuengmatcha P, Chanthai S, Mahachai R, Oh WC (2016) Sonocatalytic performance of ZnO/graphene/TiO2 nanocomposite for degradation of dye pollutants (methylene blue, texbrite BAC-L, texbrite BBU-L and texbrite NFW-L) under ultrasonic irradiation. Dyes Pigments 134:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.08.006
Ong CB, Ng LY, Mohammad AW (2018) A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:536–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.020
Rashad M, Rüsing M, Berth G, Lischka K, Pawlis A (2013) CuO and Co3O4 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterizations, and Raman spectroscopy. J Nanomater 2013:6. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP06815K
Rattan Paul D, Nehra SP (2021) Graphitic carbon nitride: a sustainable photocatalyst for organic pollutant degradation and antibacterial applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:3888–3896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09432-6
Ravichandran K, Chidhambaram N, Gobalakrishnan S (2016) Copper and graphene activated ZnO nanopowders for enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J Phys Chem Solids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2016.02.013
Reddy CV, Babu B, Shim J (2018) Synthesis, optical properties and efficient photocatalytic activity of CdO/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite. J Phys Chem Solids 112:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.09.003
Revathi V, Karthik K (2018) Microwave assisted CdO–ZnO–MgO nanocomposite and its photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:18519–18530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9968-1
Ruddaraju LK, Pammi SVN, Pallela PNVK et al (2019) Antibiotic potentiation and anti-cancer competence through bio-mediated ZnO nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109756
Sangeeta M, Karthik KV, Ravishankar R et al (2017) Synthesis of ZnO, MgO and ZnO/MgO by solution combustion method: characterization and photocatalytic studies. Mater Today Proc 4:11791–11798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.09.096
Santhosh C, Velmurugan V, Jacob G et al (2016) Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: a review. Chem Eng J 306:1116–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.053
Saravanakkumar D, Sivaranjani S, Kaviyarasu K et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO-CuO nanocomposites powder by modified perfume spray pyrolysis method and its antimicrobial investigation. J Semicond 39. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/39/3/033001
Sathya M, Pushpanathan K (2018) Synthesis and optical properties of Pb doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 449:346–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.127
Sharma D, Jha R (2017) Transition metal (Co, Mn) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: effect on structural and optical properties. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.227
Singh V, Srivastava VC (2020) Self-engineered iron oxide nanoparticle incorporated on mesoporous biochar derived from textile mill sludge for the removal of an emerging pharmaceutical pollutant. Environ Pollut 259:113822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113822
Siedl N, Koller D, Kurt AS, et al (2014) Photoluminescence quenching in compressed MgO nanoparticle systems. Phys Chem Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP54582B
Singh H, Yadav KL (2015) Structural, dielectric, vibrational and magnetic properties of Sm doped BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics prepared by a rapid liquid phase sintering method. Ceram Int 41:9285–9295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.03.212
Subhan A, Ahmed T, Uddin N et al (2015a) Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy synthesis , characterization , PL properties , photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of nano multi-metal oxide NiO.CeO2.ZnO. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 136:824–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.09.100
Subhan MA, Ahmed T, Uddin N (2015b) Synthesis, structure, PL and photocatalytic activities of la2O2CO3·CeO2·ZnO fabricated by co-precipitation method. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 138:827–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.10.114
Subhan MA, Uddin N, Sarker P et al (2015c) Photoluminescence, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of CeO2·CuO·ZnO nanocomposite fabricated by co-precipitation method. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 149:839–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.05.024
Subhan MA, Uddin N, Sarker P et al (2015d) Synthesis, characterization, low temperature solid state PL and photocatalytic activities of Ag2O·CeO2·ZnO nanocomposite. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 151:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.06.094
Sutradhar N, Sinhamahapatra A, Pahari SK et al (2011) Controlled synthesis of different morphologies of MgO and their use as solid base catalysts. J Phys Chem C 115:12308–12316. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2022314
Tang R, Su H, Sun Y et al (2016) Enhanced photocatalytic performance in Bi2WO6/SnS heterostructures: facile synthesis, influencing factors and mechanism of the photocatalytic process. J Colloid Interface Sci 466:388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.12.054
Thaya R, Malaikozhundan B, Vijayakumar S et al (2016) Chitosan coated Ag/ZnO nanocomposite and their antibiofilm, antifungal and cytotoxic effects on murine macrophages. Microb Pathog 100:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.09.010
Tju H, Taufik A, Saleh R (2016) Enhanced UV photocatalytic performance of magnetic Fe3O4/CuO/ZnO/NGP nanocomposites. J Phys Conf Ser 710. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/710/1/012005
Tran TH, Nguyen VT (2014) Copper oxide nanomaterials prepared by solution methods, some properties, and potential applications: a brief review. Int Sch Res Notices 2014:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/856592
Wang X, Fan H, Ren P (2013) Self-assemble flower-like SnO2/Ag heterostructures: correlation among composition, structure and photocatalytic activity. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 419:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.11.050
Yao K, Li J, Shan S, Jia Q (2017) One-step synthesis of urchinlike SnS/SnS2 heterostructures with superior visible-light photocatalytic performance. Catal Commun 101:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2017.07.019
Yasmeen S, Iqbal F, Munawar T et al (2019) Synthesis, structural and optical analysis of surfactant assisted ZnO–NiO nanocomposites prepared by homogeneous precipitation method. Ceram Int 45:17859–17873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.001
Yasmeen S, Munawar T, Asghar M et al (2020) Synthesis and photocatalytic study of Zn0.90Co0.10O and Zn0.90Co0.05M0.05O (M = Ca, Ba, Cr, Pb) nanocrystals: structural, optical and electrical investigations. J Mater Res Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.02.034
Zeghioud H, Assadi AA, Khellaf N et al (2019) Photocatalytic performance of CuxO/TiO2 deposited by HiPIMS on polyester under visible light LEDs: oxidants, ions effect, and reactive oxygen species investigation. Materials (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030412
Zhang Y, Ram MK, Stefanakos EK, Goswami DY (2012) Synthesis, characterization, and applications of ZnO nanowires. J Nanomater 2012:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/624520
Zhen JB, Kang PW, Zhao MH, Yang KW (2020) Silver nanoparticle conjugated star PCL- b-AMPs copolymer as nanocomposite exhibits efficient antibacterial properties. Bioconjug Chem 31:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00739
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Faisal Iqbal: methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing. Muhammad Monsoor: formal analysis, validation. Faisal Mukhtar, Muhammad Shahid Nadeem, Muhammad Riaz, and Muhammad Naveed-ur-Rehman: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, visualization. Tauseef Manwar and Sadaf Yasmeen: writing—original draft; methodology; formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munawar, T., Mukhtar, F., Yasmeen, S. et al. Sunlight-induced photocatalytic degradation of various dyes and bacterial inactivation using CuO–MgO–ZnO nanocomposite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 42243–42260 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13572-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13572-8