Abstract
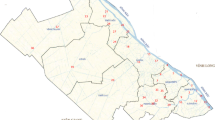
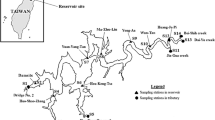
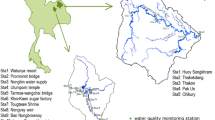
With the use of different multivariate statistical analysis methods, spatio-temporal fluctuations in the water parameters of Tiru reservoir located at the Marathwada drought-prone area of Maharashtra, India, have been analysed and reported in this case study. Tiru reservoir, situated on the tributary of the Godavari River, was regularly monitored at five different sites from August 2017 to January 2019 for the estimation of 20 water quality parameters. Various multivariate methods such as pattern reorganisation using cluster analysis (CA), factor analysis/principal component analysis (FA/PCA), and discriminant analysis (DA) were used for handling complex datasets. CA extracted three different clusters from five sampling sites with similar water quality characteristics. FA/PCA extracted thirteen factors (65% of 20 measured) required to explain 74% of the data variability and identified the factors accountable for variation in water quality and also evaluated the prevalence of each cluster on the overall dissimilarity at five different sampling sites. Discriminant analysis extracted a total of 16 parameters with 97.7% right assignations. Varifactors (VFs) acquired by factor analysis recommended that the water quality parameters accounted for variation were linked to two groups. The first group included water quality parameters like T, DO, SDD, turbidity, TDS, PA, and MA, whereas the second group covered most of the nutrients Cl−, silicates, PP, TP, NO3-N, NO2-N, and NH3-N; hardness; and CHL-a and mainly entered the reservoir during surface runoff from agriculture fields and the surrounding area containing domestic as well as animal waste. Thus, the present work showed the efficiency of multivariate methods for the assessment of spatial as well as a temporal variation in the water quality of a small reservoir.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Adams S, Titus R, Pietesen K, Tredoux G, Harris C (2001) Hydrochemical characteristic of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste-water, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Banerjee M, Mukherjee J, Ray SA (2017) Review on reservoir system and its ecology in Indian perspective. Proc Zool Soc 70:5–20
Barakat A, Baghdadi ME, Rais J, Aghezzaf B, Slassi MM (2016) Assessment of spatial and seasonal water quality variation of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using multivariate statistical techniques. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 4:284–292
Bengraine K, Marhaba TF (2003) Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. J Hazard Mater B 100:179–195
Bhat SA, Meraj G, Yaseen S, Pandit AK (2014) Statistical assessment of water quality parameters for pollution source identification in Sukhnag stream: an inflow stream of lake Wular (Ramsar Site), Kashmir Himalaya. J Ecosyst 898054:18
Carpenter SR, Stanley EH, Zanden MJV (2011) State of the world’s freshwater ecosystems: physical, chemical, and biological changes. Annu Rev Environ Resour 36:75–99
Child D (2006) The essentials of factor analysis, 3rd edn. Continuum International Publishing Group, New York
Cooley H, Ajami N, Ha ML, Srinivasan V, Morrison J, Donnelly K, Christian-Smith (2014) Global water governance in the twenty-first century. In: Ajami N et al (eds) The world’s water. The World’s Water. Island Press, Washington, DC
Garg RK, Rao RJ, Uchchariya D, Shukla G, Saksena DN (2010) Seasonal variations in water quality and major threats to Ramsagar reservoir, India. Afr Environ Sci Technol 4(2):061–076
Giri A, Bharti VK, Kalia S, Kumar K, Raj T, Chaurasia OP (2019) Utility of multivariate statistical analysis to identify factors contributing river water quality in two different seasons in cold-arid high-altitude region of Leh-Ladakh, India. Appl Water Sci 9:26
Gyimah RAA, Gyamfi C, Anornu GK, Karikari AY, Tsyawo FW (2020) Multivariate statistical analysis of water quality of the Densu River, Ghana. Int J River Basin Manag
Helena B, Pardo R, Vega M, Barrado E, Fernandez JM, Fernandez L (2000) Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res 34:807–816
Ibrahim A, Juahir H, Toriman ME, Mustapha A, Azid A, Isiyaka HA (2015) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in the Terengganu River Basin. Malays J Anal Sci 19(2):338–348
Jhingran AG (1988) Reservoir fisheries in India. J Indian Fish Assoc 18:261–273
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (2007) Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 6th edn. Pintice-Hall International, Englewood Cliffs, p 773
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20(1):141–151
Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK, Jalbani N, Afridi HI, Sarfraz RA, Baig JA, Shah AQ (2009) Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(2):301–309
Khaledian Y, Ebrahimi S, Natesan U, Basatnia N, Nejad BB, Bagmohammadi H, Zeraatpisheh M (2018) Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical analysis in the Gharaso River, Northern Iran. In: Sarma A, Singh V, Bhattacharjya R, Kartha S (eds) Urban ecology, water quality and climate change. Water Science and Technology Library, vol 84. Springer, Cham
Kim JH, Kim RH, Lee J, Cheong TJ, Yum BW, Chang HW (2005) Multivariate statistical analysis to identify the major factors governing groundwater quality in the coastal area of Kimje, South Korea. Hydrol Process 19:1261–1276
Kükrer S, Mutlu E (2019) Assessment of surface water quality using water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses in Saraydüzü Dam Lake, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 191:71
Lee JY, Cheon JY, Lee KK, Lee SY, Lee MH (2001) Statistical evaluation of geochemical parameter distribution in a ground water system contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. J Environ Qual 30:1548–1563
Ling TY, Soo CL, Liew JJ, Nyanti L, Sim SF, Grinang J (2017) Application of multivariate statistical analysis in evaluation of surface river water quality of a tropical river. J Chem 2017:Article ID 5737452
Liu CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313(1-3):77–89
Lopes FB, de Andrade EM, Meireles ACM, Becker H, Batista AA (2014) Assessment of the water quality in a large reservoir in semiarid region of Brazil. Rev Bras Engenharia Agríc Ambient 18(4):437–445
Markad AT, Landge AT, Nayak BB, Inamdar AB, Mishra AK (2019) Trophic state modeling for shallow freshwater reservoir: a new approach. Environ Monit Assess 191:586
Muangthong S, Shrestha S (2015) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: case study of the Nampong River and Songkhram River, Thailand. Environ Monit Assess 187:548
Naaz A, Anshumali (2015) Seasonal variation in Ph and alkalinity of groundwaters in Sidhi District, Central India. Curr World Environ 10(3):1017–1021
Otto M (1998) Multivariate methods. In Analytical chemistry. Ed. Kellner R, Mermet JM, Otto M and Widmer HM, 916 pp. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Park S, Kazama F, Lee S (2014) Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Nakdong River basin, Korea. Environ Eng Res 19(3):197–203
Reghunath R, Murthy TRS, Raghavan BR (2002) The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: an example from Karnataka, India. Water Res 36:2437–2442
Saluja R, Garg JK (2017) Trophic state assessment of Bhindawas Lake Haryana. Environ Monit Assess 189:32
Sharma V, Walia YK (2016) Water quality assessment of Gobind Sagar Lake during rainy season in Himachal Pradesh, India. Biol Forum 8(1):559–564
Sheela AM, Letha J, Joseph S, Ramachandran KK, Sanalkumar SP (2011) Trophic state index of a lake system using IRS (P6-LISS III) satellite imagery. Environ Monit Assess 177(1-4):575–592
Shiklomanov IA (2000) Appraisal and assessment of world water resources. Water Int 25(1):11–32
Shil S, Singh UK, Mehta P (2019) Water quality assessment of a tropical river using water quality index (WQI), multivariate statistical techniques and GIS. Appl Water Sci 9:168
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M, Kouimtzis T (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res 37:4119–4124
Simeonov V, Simeonova P, Tsitouridou R (2004) Chemometric quality assessment of surface waters: two case studies. Chem Eng Ecol 11(6):449–469
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India): a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Singh KP, Malik A, Sinha S (2005) Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Anal Chim Acta 538:355–374
Solanki VR, Hussain MM, Raja SS (2010) Water quality assessment of Lake Pandu Bodhan, Andhra Pradesh State, India. Environ Monit Assess 163:411–419
Tokatli C (2013) Use of statistical methods in water quality assessment: a case study of Balkan Arboretum Area in Trakya University (Edirne, Turkey). J Appl Biol Sci 7(3):79–83
Tomaz A, Palma P, Fialho S, Lima A, Alvarenga P, Potas M, Salgado R (2020) Spatial and temporal dynamics of irrigation water quality under drought conditions in a large reservoir in Southern Portugal. Environ Monit Assess 192:93
Varol M, Şen B (2009) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 159:543–553
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Deban L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3592
Vijayvergia RP (2008). Eutrophication: a case study of highly eutrophicated Lake Udaisagar, Udaipur (Raj.), India with regards to its nutrient enrichment and emerging consequences. Procedings of Taal2007: The 12th World Lake Conference, Jaipur, India 1557-1560
Vogl AL, Lopes VL (2009) Impacts of water resources development on flow regimes in the Brazos River. Environ Monit Assess 157:331–345
Voncina DB, Dobcnik D, Novic M, Zupan J (2002) Chemometric characterisation of the quality of river water. Anal Chim Acta 462:87–100
Wunderlin DA, Diaz MP, Ame MV, Pesce SF, Hued AC, Bistoni MA (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba, Argentina). Water Res 35:2881–2894
Zhao J, Fu G, Lei K, Li YW (2011) Multivariate analysis of surface water quality in the Three Gorges area of China and implications for water management. J Environ Sci 23(9):1460–1471
Acknowledgments
The first author (ATM) is thankful to Dr. Gopal Krishna, director, ICAR - Central Institute of Fisheries Education (CIFE), Mumbai, India, for offering the required facilities to conduct this research work. The author is deeply grateful to Dr. Ashish Paturkar, Vice Chancellor, Maharashtra Animal and Fishery Sciences University, Nagpur, and Maharashtra, India, for allowing me to complete this research work. The author is thankful to Mr. V.B. Sutar for providing unconditional help and support during fieldwork and laboratory analysis.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organisation for the submitted work. All of the authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organisation or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. A.T. Markad, Dr. A.T. Landge, Dr. B.B. Nayak, Dr. A.B. Inamdar, and Dr. A.K. Mishra have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markad, A.T., Landge, A.T., Nayak, B.B. et al. A multivariate statistical approach for the evaluation of spatial and temporal dynamics of surface water quality from the small reservoir located in the drought-prone area of South-West India: a case study of Tiru reservoir (India). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 31013–31031 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12001-6