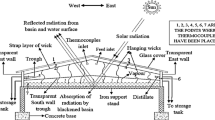
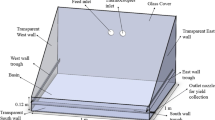
Abstract
Double slope solar stills are reported to give lower yields in winter season. In this work an attempt has been made to improve the performance of still with double slope in winter. A comparative experimental and theoretical analysis of conventional and modified single basin still with double slope augmented with black dye, pebbles and iron chips (5 kg each) is reported in this manuscript. The experiments are carried out in the month of November and December in 2017 at meteorological conditions of Jaypee University of Engineering and Technology, Guna (Latitude: 24°39'N, Longitude: 77°19'E). Distillate yield in a modified solar still due to the augmentation has improved by 28.4% as compared with conventional solar still at a common water depth of 0.025 m, whereas its overall heat transfer coefficient and overall thermal efficiency are improved by 55.7 and 25.01%, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data and material pertaining to this manuscript is available with the authors. They promise to present it to the editorial board or reviewers on demand.
Change history
08 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13246-5
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area (m2)
- C :
-
Constant
- c :
-
Specific heat (J/kg-K)
- d :
-
Characteristic dimension of solar still (m)
- \( \dot{E}x \) :
-
Exergy (W)
- F :
-
Heat transfer fraction
- F 12 :
-
View factor
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity (m/s2)
- Gr:
-
Grashof number
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K)
- H :
-
Height of still (m)
- I(t):
-
Incident solar radiation on inclined glass cover surface (W/m2)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of humid air (W/mK)
- L :
-
Latent heat of vaporization (J/kg)
- M :
-
Mass of basin water (kg)
- \( \dot{m} \) :
-
Distillate output (kg/m2hr)
- n :
-
Constant
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \( \dot{q} \) :
-
Rate of total internal heat transfer (W/m2)
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number
- T :
-
Temperature (oC)
- ΔT :
-
Effective temperature difference (oC)
- a :
-
Ambient
- b :
-
Basin
- c :
-
Convective
- ci :
-
Inner surface of glass cover
- d :
-
Destruction
- e :
-
Evaporative
- eff :
-
Effective
- E :
-
East
- Ex :
-
Exergy
- g :
-
Glass cover
- i :
-
Instantaneous
- in :
-
Input
- insu :
-
Insulation
- o :
-
Output
- p :
-
Constant pressure
- t :
-
Total
- trans :
-
Transfer
- w :
-
Water
- W :
-
West
- r :
-
Radiative
- α :
-
Absorptivity
- α ' :
-
Fraction by which solar radiation is absorbed
- β :
-
Expansion factor (K-1)
- σ :
-
Stefan Boltzmann constant (W/ m2 K4)
- ρ :
-
Density of humid air (kg/m3)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of humid air (Ns/m2)
- θ :
-
Glass cover inclination (o)
- ε :
-
Emissivity
- η :
-
Efficiency
- τ :
-
Transmissivity
References
Abderachid T, Abdenacer K (2013) Effect of orientation on the performance of a symmetric solar still with a double effect solar still (comparison study). DES 329:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.09.011
Abdullah AS, Essa FA, Ben H, Omara ZM (2020) Improving the trays solar still performance using re flectors and phase change material with nanoparticles. J Energy Storage 31:101744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101744
Arunkumar T, Wang J, Winfred DD et al (2020) Sensible desalting : Investigation of sensible thermal storage materials in solar stills. J Energy Storage 32:101824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101824
Bait O, Si-Ameur M (2018) Enhanced heat and mass transfer in solar stills using nanofluids: a review. Sol Energy 170:694–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.06.020
Balachandran GB, David PW, Rajendran G et al (2020) Investigation of performance enhancement of solar still incorporated with Gallus gallus domesticus cascara as sensible heat storage material. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10470-3
Clark JA (1990) The steady-state performance of a solar still. Sol Energy 44:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(90)90025-8
Dubey M, Mishra DR (2019) Experimental and theoretical evaluation of double slope single basin solar stills: study of heat and mass transfer. FME Trans 47:101–110. https://doi.org/10.5937/fmet1901101D
Dumka P, (2020) Comparative experimental evaluation of conventional solar still (CSS) and CSS augmented with wax filled metallic finned-cups, pp 482–495. https://doi.org/10.5937/fme2002482D
Dumka P, Mishra DR (2018a) Energy and exergy analysis of conventional and modified solar still integrated with sand bed earth : Study of heat and mass transfer. Desalination 437:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.026
Dumka P, Mishra DR (2018b) Experimental investigation of modified single slope solar still integrated with earth ( I ) & ( II ): Energy and exergy analysis. Energy 160:1144–1157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.083
Dumka P, Sharma A, Kushwah Y, Raghav AS, Mishra DR (2019) Performance evaluation of single slope solar still augmented with sand-filled cotton bags. J Energy Storage 25:100888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.100888
Dunkle R (1961) Solar water distillation: the roof type still and a multiple effect diffusion still. Int Dev Heat Transf ASME Proc Int Heat Transf Part V Univ Color 895–902
Edalatpour M, Aryana K, Kianifar A, Tiwari GN, Mahian O, Wongwises S (2016) ScienceDirect Solar stills : A review of the latest developments in numerical simulations. Sol Energy 135:897–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.03.005
Fathy M, Hassan H, Salem Ahmed M (2018) Experimental study on the effect of coupling parabolic trough collector with double slope solar still on its performance. Sol Energy 163:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.01.043
Grewal R, Manchanda H, Kumar M (2018) A review on applications of phase change materials in solar distillation. Conf: 2nd Int Conf on Emer Tren in Sci Engg & Tech pp 722–735
Hepbasli A (2008) A key review on exergetic analysis and assessment of renewable energy resources for a sustainable future. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 12:593–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2006.10.001
Jani HK, Modi KV (2018) A review on numerous means of enhancing heat transfer rate in solar-thermal based desalination devices. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 93:302–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.05.023
Kabeel AE, Omara ZM, Essa FA (2014) Enhancement of modified solar still integrated with external condenser using nanofluids: An experimental approach. Energy Convers Manag 78:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.11.013
Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M, Mahgoub M (2016) The performance of a modified solar still using hot air injection and PCM. Desalination 379:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.11.007
Kirkup L, Frenkel R (2006) An introduction to uncertainty in measurement using the GUM (guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement), 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kumar S, Tiwari GN (1996) Estimation of convective mass transfer in solar distillation systems. Sol Energy 57:459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-092X(96)00122-3
Lira I (2002) Evaluation the measurement uncertainty: Fundamental and practical guidance. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol
Madhu B, Balasubramanian E, Sathyamurthy R, Nagarajana PK, Mageshbabu D, Bharathwaaj R, Muthu Manokar Av (2018) Exergy analysis of solar still with sand heat energy storage. Appl Sol Energ 54(3):173–177. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0003701X1803009X
Malik MAS, Tiwari GN, Kumar A (1982) SMS Solar Distillation. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK
Manokar AM, Winston DP, Kabeel AE et al (2018) Integrated PV / T solar still- A mini-review. Desalination 435:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.04.022
Mishra DR, Tiwari AK (2013) Effect of coal and metal chip on the solar still. J Sci Tech Res 3:1–6
Modi KV, Nayi KH (2020) Ef fi cacy of forced condensation and forced evaporation with thermal energy storage material on square pyramid solar still. Renew Energy 153:1307–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.02.095
Omara ZM, Hamed MH, Kabeel AE (2011) Performance of finned and corrugated absorbers solar stills under Egyptian conditions. Desalination 277:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.042
Pal P, Dev R, Singh D, Ahsan A (2018) Energy matrices, exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic analysis of modified multi–wick basin type double slope solar still. Desalination 447:55–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.09.006
Panchal HN (2015) Enhancement of distillate output of double basin solar still with vacuum tubes. J King Saud Univ - Eng Sci 27:170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2013.06.007
Panchal H, Patel DK, Patel P (2017) Theoretical and experimental performance analysis of sandstones and marble pieces as thermal energy storage materials inside solar stills. Int J Ambient Energy 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2017.1298059
Petela R (1964) Exergy of Heat Radiation. J Heat Transfer 86:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3687092
Petela R (2003) Exergy of undiluted thermal radiation. Sol Energy 74:469–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-092X(03)00226-3
Profile SEE (2015) Solar distiller aqueduct for the desalination of sea water and its concomitant transport in arid zone : a first approach (in IJEEE (International journal of Energy, Environment and Economics) Solar distiller aqueduct for the desalination of sea water and its concomitant transport in arid zone : a first approach. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.2907.3448
Selvaraj K, Natarajan A (2018) Factors in fluencing the performance and productivity of solar stills - A review. Desalination 435:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.09.031
Sharma M, Tiwari AK, Mishra DR (2016) A review on desalination of water using single slope passive solar still. Int J Dev Res 06:10002–10012
Sharshir SW, Elsheikh AH, Peng G, Yang N, el-Samadony MOA, Kabeel AE (2017) Thermal performance and exergy analysis of solar stills – a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 73:521–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2017.01.156
Srithar K, Rajaseenivasan T (2018) Recent fresh water augmentation techniques in solar still and HDH desalination – a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:629–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.056
Tiwari GN, Tiwari AK (2008) Solar Distillation Practice for Water Desalination Systems. Anamaya, New Delhi
Toyama S, Aragak T, Salah HM et al (1987) Simulation of a multieffect solar still and the static characteristics. J Chem Eng Japan 20:473–478. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.20.473
Velmurugan V, Gopalakrishnan M, Raghu R, Srithar K (2008) Single basin solar still with fin for enhancing productivity. Energy Convers Manag 49:2602–2608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2008.05.010
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
Authors declare that no funding has been taken from any source or authority for the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this manuscript, MD has contributed in conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, performed experiments and writing—Original draft preparation. DRM has contributed in conceptualization, methodology, supervision, validation and writing—reviewing and editing of this manuscript. Both the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This declaration is not applicable to the above manuscript as no human or animal participants have participated in this work.
Consent for publication
This declaration is not applicable to the above manuscript as it does not contain any individual person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors hereby declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The format of Equations 10, 15 and 16 were modified in the published pdf version.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubey, M., Mishra, D.R. Experimental analysis of double slope solar still augmented with dye, pebbles and metal chips. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 22077–22090 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11869-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11869-8