Abstract
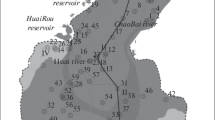
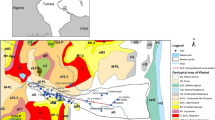
Managed aquifer recharge (MAR) is an important approach to address water security, water quality decline, ground subsidence, and aquifer degradation. In this study, the large-scale recharge experiments were conducted in a natural river with multiple water sources. The MAR with multi-source water was investigated by developing an improved matter-element model under a limited recharged quantity and period in Jinan, China. Results showed that the background levels (BL) of groundwater quality before recharge was relatively good. However, the use of different water sources would cause a significant increase in the content of some groundwater quality indexes, which might further induce deterioration of regional groundwater quality. And the water quality in porous and karst aquifer displayed deteriorating trends during different water source recharge. Additionally, the adverse effects of recharge water sources on regional groundwater quality in turn was South-to-North Water Diversion Project (SN) > Yellow River (YR) > Wohushan Reservoir (WR). Meanwhile, the high-risk indexes in groundwater quality were presented during different water source recharge. Accordingly, relevant suggestions and measures were then put forward to optimize the MAR with multi-source water and explore the high-efficiency and low-risk recharge mode.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Change history
16 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11965-9
References
Cai W (1999) Extension theory and its application. Chin Sci Bull 44:1538–1548
Chen X, Zhang Z-C, Zhang X-N, Chen YQ, Qian MK, Peng SF (2008) Estimation of groundwater recharge from precipitation and evapotranspiration by lysimeter measurement and soil moisture model. J Hydrol Eng 13:333–340
Dermatas D, Mpouras T, Chrysochoou M, Panagiotakis I, Vatseris C, Linardos N, Theologou E, Boboti N, Xenidis A, Papassiopi N, Sakellariou L (2015) Origin and concentration profile of chromium in a Greek aquifer. J Hazard Mater 281:35–46
Dillon P (2005) Future management of aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol J 13:313–316
Dillon P, Stuyfzand P, Grischek T, Lluria M, Pyne RDG, Jain RC, Bear J, Schwarz J, Wang W, Fernandez E, Stefan C, Pettenati M, van der Gun J, Sprenger C, Massmann G, Scanlon BR, Xanke J, Jokela P, Zheng Y, Rossetto R, Shamrukh M, Pavelic P, Murray E, Ross A, Bonilla Valverde JP, Palma Nava A, Ansems N, Posavec K, Ha K, Martin R, Sapiano M (2019) Sixty years of global progress in managed aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol J 27:1–30
Du X, Wang Z, Ye X (2013) Potential clogging and dissolution effects during artificial recharge of groundwater using potable water. Water Resour Manag 27:3573–3583
Ebrahim GY, Jonoski A, Al-Maktoumi A et al (2016) simulation-optimization approach for evaluating the feasibility of managed aquifer recharge in the Samail Lower Catchment, Oman. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142:05015007
Escalante EF, Sauto JSS, Gil RC (2019) Sites and indicators of MAR as a successful tool to mitigate climate change effects in Spain. Water 11:1943
Fernández Escalante E (2015) Practical management to minimize the effects of clogging in managed aquifer recharge wells at two sites in the Guadiana Basin, Spain. J Hydrol Eng 20:B5014002
Fiorillo F, Pagnozzi M, Stevanović Z, Ventafridda G (2019) Main hydrological features and recharge analysis of the Caposele Spring catchment, southern Italy. Acta Carsologica 48. https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v48i1.6738
Ganot Y, Holtzman R, Weisbrod N, Nitzan I, Katz Y, Kurtzman D (2017) Monitoring and modeling infiltration–recharge dynamics of managed aquifer recharge with desalinated seawater. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21:4479–4493
Gao Y, Tian Y (2018) Groundwater chemical characteristics in the upper reaches of the Langmaoshan Reservoir, Shandong. Resour Sci 40:359–368 (in Chinese)
Gao Z, Xu J, Wang S et al (2014) The distribution characteristics and hydrogeological significance of trace elements in karst water, Jinan, China. Earth Sci Front 21(4):135–146 (in Chinese)
Gong Y, Wang X, Hu B et al (2016) Groundwater contributions in water-salt balances of the lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. J Arid Land 8:694–706
Hou W, Sun S, Wang M, Li X, Zhang N, Xin X, Sun L, Li W, Jia R (2016) Assessing water quality of five typical reservoirs in lower reaches of Yellow River, China: using a water quality index method. Ecol Indic 61:309–316
Jiao F, Ren L, Wang X, Liu W (2017) Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of metals in the sediments of Xiaoqing River, Jinan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:15001–15011
Kang F, Jin M, Qin P (2011) Sustainable yield of a karst aquifer system: a case study of Jinan springs in northern China. Hydrogeol J 19:851–863
Leonard R, Mankad A, Alexander K (2015) Predicting support and likelihood of protest in relation to the use of treated stormwater with managed aquifer recharge for potable and non-potable purposes. J Clean Prod 92:248–256
Li B, Yang G, Wan R, Hörmann G (2017a) Dynamic water quality evaluation based on fuzzy matter–element model and functional data analysis, a case study in Poyang Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19138–19148
Li F, Wang W, Xu Q et al (2017b) Assessment of water quality risk from karst aquifer recharge with multi-source water in the Yufuhe river, Jinan. Carsologica Sin 36:751–758 (in Chinese)
Liang X, Zhan H, Zhang Y-K (2018) Aquifer recharge using a vadose zone infiltration well. Water Resour Res 54:8847–8863
Liu D, Zou Z (2012) Water quality evaluation based on improved fuzzy matter-element method. J Environ Sci 24:1210–1216
Liu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang F (2019) Challenges for water security and sustainable socio-economic development: a case study of industrial, domestic water use and pollution management in Shandong, China. Water 11:1630
Liu Y, Yang L, Jiang W (2020a) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the relationship between water pollution and economic growth: a case study in Nansi Lake catchment, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:4008–4020
Liu Y, Yang L, Jiang W (2020b) Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between social economy and water environmental quality – a case study from Nansi Lake catchment, China. Ecol Indic 119:106870
Luo Q, Yang Y, Qian J, Wang X, Chang X, Ma L, Li F, Wu J (2020) Spring protection and sustainable management of groundwater resources in a spring field. J Hydrol 582:124498
Malík P, Michalko J, Pažická A, Máša B, Stankovič J (2020) Detailed water quality monitoring at various points of the Krásnohorská Cave system (Slovakia). In: Bertrand C, Denimal S, Steinmann M, Renard P (eds) Eurokarst 2018, Besançon. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 199–212
Mankad A, Walton A, Alexander K (2015) Key dimensions of public acceptance for managed aquifer recharge of urban stormwater. J Clean Prod 89:214–223
Massmann G, Sültenfuß J (2008) Identification of processes affecting excess air formation during natural bank filtration and managed aquifer recharge. J Hydrol 359:235–246
Missimer TM, Guo W, Woolschlager J, Maliva RG (2017) Long-term managed aquifer recharge in a saline-water aquifer as a critical component of an integrated water scheme in Southwestern Florida, USA. Water 9:774
Page D, Dillon P, Vanderzalm J, Toze S, Sidhu J, Barry K, Levett K, Kremer S, Regel R (2010) Risk assessment of aquifer storage transfer and recovery with urban stormwater for producing water of a potable quality. J Environ Qual 39:2029–2039
Parker LV, Clark CH (2004) Study of five discrete-interval-type ground water sampling devices. Groundw Monit Remediat 24:111–123
Qi X, Wang Y, Yang L et al (2016) Time lags variance of groundwater level response to precipitation of Jinan karst spring watershed in recent 50 years. Carsologica Sin 35:384–393 (in Chinese)
Rodríguez Escales P-F, Canelles Garcia A, Sánchez Vila FJ, Folch Sancho A (2018) A risk assessment methodology to evaluate the risk failure of managed aquifer recharge in the Mediterranean Basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:3213–3227
Rodríguez-Escales P, Fernàndez-Garcia D, Drechsel J, Folch A, Sanchez-Vila X (2017) Improving degradation of emerging organic compounds by applying chaotic advection in managed aquifer recharge in randomly heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour Res 53:4376–4392
Tang Q-Y, Zhang C-X (2013) Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260
Urrutia J, Herrera C, Custodio E, Jódar J, Medina A (2019) Groundwater recharge and hydrodynamics of complex volcanic aquifers with a shallow saline lake: Laguna Tuyajto, Andean Cordillera of northern Chile. Sci Total Environ 697:134116
Wang J-J, Jing Y-Y, Zhang C-F, Zhao J-H (2009) Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sustainable energy decision-making. Renew Sust Energ Rev 13:2263–2278
Wang J, Jin M, Jia B, Kang F (2015a) Hydrochemical characteristics and geothermometry applications of thermal groundwater in northern Jinan, Shandong, China. Geothermics 57:185–195
Wang W, Page D, Zhou Y et al (2015b) Roof runoff replenishment of groundwater in Jinan, China. J Hydrol Eng 20:B5014005
Wang J, Jin M, Lu G, Zhang D, Kang F, Jia B (2016) Investigation of discharge-area groundwaters for recharge source characterization on different scales: the case of Jinan in northern China. Hydrogeol J 24:1723–1737
Wang J, Wang J, Jin M (2017a) Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of karst water in Jinan spring catchment. J China U Geosci 42:821–831 (in Chinese)
Wang X, Wang C, Wang B, Liu S, Song J (2017b) Protection of urban features during urbanization based on the roles of springs in Jinan. Chin J Popul Resour Environ 15:93–102
Wang G-F, Wu Y-X, Lu L, Li G, Shen JS (2019) Investigation of the geological and hydrogeological environment with relation to metro system construction in Jinan, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:1005–1024
Werner AD, Zhang Q, Xue L, Smerdon BD, Li X, Zhu X, Yu L, Li L (2013) An initial inventory and indexation of groundwater mega-depletion cases. Water Resour Manag 27:507–533
Wu Q, Xu H (2005) A three-dimensional model and its potential application to spring protection. Environ Geol 48:551–558
Xie L (2017) Advanced engineering and technology III: Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Congress on Advanced Engineering and Technology (CAET 2016), Hong Kong, 22-23 October 2016. CRC Press
Xing L, Huang L, Hou X, Yang L, Chi G, Xu J, Zhu H (2018) Groundwater hydrochemical zoning in inland plains and its genetic mechanisms. Water 10:752
Xu Z, Hu BX, Davis H, Kish S (2015) Numerical study of groundwater flow cycling controlled by seawater/freshwater interaction in a coastal karst aquifer through conduit network using CFPv2. J Contam Hydrol 182:131–145
Ye X, Cui R, Du X et al (2019) Mechanism of suspended kaolinite particle clogging in porous media during managed aquifer recharge. Groundwater 57:764–771
Yin D, Shu L, Chen X, Wang Z, Mohammed ME (2011) Assessment of sustainable yield of karst water in Huaibei, China. Water Resour Manag 25:287–300
Yin X, Wang Q, Feng W (2017) Hydro-chemical and isotopic study of the karst spring catchment in Jinan. Acta Geol Sin 91:1651–1660 (in Chinese)
Yu H, Huang G, Wu C (2014) Application of the stormwater management model to a piedmont city: a case study of Jinan City, China. Water Sci Technol 70:858–864
Zhang Z, Li Y (2020) Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between urbanization and geological hazards–a case study from China. Sci Total Environ 728:138825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138825
Zhang D, Shu J, Sun J (2017a) Observed deformation characteristics of a deep excavation for the spring area in Jinan, China. J Mt Sci 14:581–594
Zhang L, Qin X, Tang J, Liu W, Yang H (2017b) Review of arsenic geochemical characteristics and its significance on arsenic pollution studies in karst groundwater, Southwest China. Appl Geochem 77:80–88
Zhang Z, Wang W, Qu S, Huang Q, Liu S, Xu Q, Ni L (2018) A new perspective to explore the hydraulic connectivity of karst aquifer system in Jinan spring catchment, China. Water 10:1368
Zhu X, Wu J, Nie H, Guo F, Wu J, Chen K, Liao P, Xu H, Zeng X (2018) Quantitative assessment of the impact of an inter-basin surface-water transfer project on the groundwater flow and groundwater-dependent eco-environment in an oasis in arid northwestern China. Hydrogeol J 26:1475–1485
Funding
This study was supported by the Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Project (2017GSF17121) and the Danish Development Agency (DANIDA) coordinated by the DANIDA Fellowship Center (DFC) through the grant No. 17-M08-GEU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhengxian Zhang: methodology, modeling, validation, visualization, writing the original manuscript, and writing review and editing; Weiping Wang: conceptualization, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 107 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, W. Managing aquifer recharge with multi-source water to realize sustainable management of groundwater resources in Jinan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 10872–10888 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11353-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11353-3