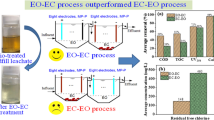
Abstract
Vinasse wastewater from tequila industry that has been conventionally treated is usually characterized by a chemical oxygen demand (COD) above 150 mg L−1, which is the maximum content permitted for discharge by Mexican Regulation. In order to increase the wastewater quality, different processes were applied, and from the experimental results, the advantages and limitations were analyzed. In this way, although Fenton experiments showed acceptable COD removal efficiencies (79–90%), operation as well as cost limit its adoption as a viable technology. Therefore, additional experiments explored electro-Fenton (EF) as well as adsorption coupled to EF in a tubular reactor. The corresponding data revealed that there was no additional increase in COD removal performance probably due to the low oxygen solubility in the electrolytic solution and the high pH that prevents the existence of Fe2+ ions necessary for the Fenton mixture. In view of these results, when an activated carbon (AC) filter was coupled to polarization at current densities between 0.5 and 2 mA cm−2, removal efficiencies from 71 to 81%, corresponding to final COD of 78 to 33 mg L−1, were achieved. Also, the adsorbent surface was continuously regenerated, promoting a more efficient adsorption and a longer service life for the AC filter. In this case, by using a current density of 0.5 mA cm−2, COD was reduced to sufficiently small values for discharge into natural water bodies, maintaining low energy consumption and therefore acceptable operation costs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
APHA/AWWA/WEF (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Arreola-Vargas J, Jaramillo-Gante NE, Celis LB, Corona-González RI, González-Álvarez V, Méndez-Acosta HO (2016) Biogas production in an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor by using tequila vinasses: effect of pH and temperature. Water Sci Technol 73:550–556. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.520
Bañuelos JA, García-Rodríguez O, Rodríguez-Valadez FJ, Manríquez J, Bustos E, Rodríguez A, Godínez LA (2015) Cathodic polarization effect on the electro-Fenton regeneration of activated carbon. J Appl Electrochem 45:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-015-0815-2
Becerril-Estrada V, Robles I, Martínez-Sánchez C, Godínez LA (2020) Study of TiO2/Ti4O7 photo-anodes inserted in an activated carbon packed bed cathode: towards the development of 3D-type photo-electro-Fenton reactors for water treatment. Electrochim Acta 340:135972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.135972
Comisión Federal de Electricidad (2020) Esquema tarifario vigente. https://app.cfe.mx/Aplicaciones/CCFE/Tarifas/TarifasCRENegocio/Negocio.aspx. Accessed 07 July 2020 (in Spanish)
Consejo Regulador del Tequila (2020) Informacion estadistica. https://www.crt.org.mx/EstadisticasCRTweb/. Accessed 07 July 2020 (in Spanish)
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M, Eltoukhy MM (2010) The use of artificial neural network (ANN) for modeling of COD removal from antibiotic aqueous solution by the Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 179:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.068
Fang C, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOP) to degrade per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). J Adv Oxid Technol 20:. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2017-0014
Fenton HJH (1894) Oxidation of tartaric acid in presence of Iron. J Chem Soc Trans 65:899–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/CT8946500899
Fernández D, Robles I, Rodríguez-Valadez FJ, Godínez LA (2018) Novel arrangement for an electro-Fenton reactor that does not require addition of iron, acid and a final neutralization stage. Towards the development of a cost-effective technology for the treatment of wastewater. Chemosphere 199:251–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.036
Ferral-Pérez H, Torres Bustillos LG, Méndez H, Rodríguez-Santillan JL, Chairez I (2016) Sequential treatment of tequila industry vinasses by biopolymer-based coagulation/flocculation and catalytic ozonation. Ozone Sci Eng 38:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2016.1158635
Foller PC, Bombard RT (1995) Processes for the production of mixtures of caustic soda and hydrogen peroxide via the reduction of oxygen. J Appl Electrochem 25:613–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241923
Guedes AMFM, Madeira LMP, Boaventura RAR, Costa CAV (2003) Fenton oxidation of cork cooking wastewater-overall kinetic analysis. Water Res 37:3061–3069. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00178-7
Jung YS, Lim WT, Park JY, Kim YH (2009) Effect of pH on Fenton and Fenton-like oxidation. Environ Technol 30:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330802468848
López-López A, Davila-Vazquez G, León-Becerril E, Villegas-García E, Gallardo-Valdez J (2010) Tequila vinasses: generation and full scale treatment processes. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-010-9204-9
Lucas MS, Peres JA, Li Puma G (2010) Treatment of winery wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes (O3, O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2) in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor and process economics. Sep Purif Technol 72:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2010.01.016
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.017
Méndez-Acosta HO, Snell-Castro R, Alcaraz-González V, González-Álvarez V, Pelayo-Ortiz C (2010) Anaerobic treatment of tequila vinasses in a CSTR-type digester. Biodegradation 21:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9306-7
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2015) Remediation of a winery wastewater combining aerobic biological oxidation and electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Water Res 75:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.029
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B Environ 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Oturan MA (2000) An ecologically efective water treatment technique using electrochemically generated hydroxyl radicals for in situ destruction of organic pollutants: Application to herbicide 2 , 4-D. J Appl Electrochem 30:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.05.011
Oturan MA, Brillas E (2007) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) for environmental applications. Port Electrochim Acta 25:1–18. https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.200701001
Ramírez J, Godínez LA, Méndez M, Meas Y, Rodríguez FJ (2010) Heterogeneous photo-electro-Fenton process using different iron supporting materials. J Appl Electrochem 40:1729–1736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-010-0157-z
Robles I, Becerra E, Barrios JA, Maya C, Jiménez B, Rodríguez-Valadez FJ, Rivera F, García-Espinoza JD, Godínez LA (2020) Inactivation of helminth eggs in an electro-Fenton reactor: towards full electrochemical disinfection of human waste using activated carbon. Chemosphere. 250:126260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126260
Rodriguez Arreola A, Sanchez Tizapa M, Zurita F, Morán-Lázaro JP, Castañeda Valderrama R, Rodríguez-López JL, Carreon-Alvarez A (2020) Treatment of tequila vinasse and elimination of phenol by coagulation–flocculation process coupled with heterogeneous photocatalysis using titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Technol 41:1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1518994
SAGARPA (2017) Planeación agrícola nacional 2017-2030: AGAVE TEQUILERO Y MEZCALERO, 1st. Mexico City, Mexico (in Spanish)
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (2018) Proyecto de Modificación de la Norma Oficial Mexicana PROY-NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2017. https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5510140&fecha=05/01/2018. Accessed 07 July 2020 (in Spanish)
Sultana S, Choudhury MR, Bakr AR, Anwar N, Rahaman MS (2018) Effectiveness of electro-oxidation and electro-Fenton processes in removal of organic matter from high-strength brewery wastewater. J Appl Electrochem 48:519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1185-3
Zárate-Guzmán AI, Manríquez-Rocha J, Antaño-López R, Rodríguez-Valadez FJ, Godínez LA (2018) Study of the electrical properties of a packed carbon bed for its potential application as a 3D-cathode in electrochemical processes. J Electrochem Soc 165:E460–E465. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0731810jes
Zepp RG, Faust BC, Jürg H (1992) Hydroxyl radical formation in aqueous reactions (pH 3-8) of Iron(II) with hydrogen peroxide: the photo-Fenton reaction. Environ Sci Technol 26:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00026a011
Zhou W, Rajic L, Chen L, Kou K, Ding Y, Meng X, Wang Y, Mulaw B, Gao J, Qin Y, Alshawabkeh AN (2019) Activated carbon as effective cathode material in iron-free electro-Fenton process: integrated H2O2 electrogeneration, activation, and pollutants adsorption. Electrochim Acta 296:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.052
Funding
LAG fully acknowledges Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, MX), for funding through grant PENTA 303758.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: LAG and IR. Investigation: JCM and IR. Formal analysis: JCM and AEV. Writing—original draft preparation: JCM and AEV. Writing—review and editing: LAG and IR. Funding acquisition: LAG. Resources: JCM, LAG, IR and AEV
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo-Monroy, J., Godínez, L.A., Robles, I. et al. Study of a coupled adsorption/electro-oxidation process as a tertiary treatment for tequila industry wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 23699–23706 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11031-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11031-4