Abstract
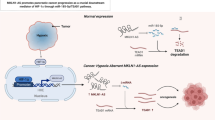
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common type of human malignancies, leads to increasing incidence and fairly high mortality. An increasing number of studies have verified that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) played key roles in the development of multiple human cancers. As a biomarker, SLC16A1-AS1 has been reported in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Thus, we decided to investigate whether SLC16A1-AS1 exerts its biological function in HCC. In this study, we discovered that SLC16A1-AS1 was obviously downregulated in HCC tissues and cells. Overexpression of SLC16A1-AS1 inhibited HCC cell proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process as well as promoted cell apoptosis. Moreover, SLC16A1-AS1 was confirmed to enhance the radiosensitivity of HCC cells. Molecular mechanism exploration suggested that SLC16A1-AS1 served as a sponge for miR-301b-3p and CHD5 was the downstream target gene of miR-301b-3p in HCC cells. Rescue assays implied that CHD5 knockdown could recover the effects of SLC16A1-AS1 overexpression on HCC cellular processes. In brief, our study clarified that SLC16A1-AS1 acted as a tumor suppressor in HCC by targeting the miR-301b-3p/CHD5 axis, which may be a promising diagnostic biomarker and provide promising treatment for HCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfattah N et al (2018) MiR-584-5p potentiates vincristine and radiation response by inducing spindle defects and DNA damage in medulloblastoma. 9:4541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06808-8
Bao J, Chen X, Hou Y, Kang G, Li Q, Xu Y (2018) LncRNA DBH-AS1 facilitates the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-138 via FAK/Src/ERK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 107:824–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.079
Bao MH, Lv QL, Szeto V, Wong R, Zhu SZ, Zhang YY, Feng ZP, Sun HS (2019) TRPM2-AS inhibits the growth, migration, and invasion of gliomas through JNK, c-Jun, and RGS4. J Cell Physiol 235:4594–4604. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29336
Baykara O, Tansarikaya M, Bulut P, Demirkaya A, Buyru N (2017) CHD5 is a potential tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Gene 618:65–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.04.010
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Chen X, Zhang N (2019) Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1_2 radiosensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulation of miR-101-3p/WEE1 axis. Cell Biol Int 43:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11077
Fan H, Jin X, Liao C, Qiao L, Zhao W (2019) MicroRNA-301b-3p accelerates the growth of gastric cancer cells by targeting zinc finger and BTB domain containing 4. Pathol Res Pract 215:152667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.152667
Fang L, Cai J, Chen B, Wu S, Li R, Xu X, Yang Y, Guan H, Zhu X, Zhang L, Yuan J, Wu J, Li M (2015) Aberrantly expressed miR-582-3p maintains lung cancer stem cell-like traits by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Nat Commun 6:8640. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9640
Fatemi M, Paul TA, Brodeur GM, Shokrani B, Brim H, Ashktorab H (2014) Epigenetic silencing of CHD5, a novel tumor-suppressor gene, occurs in early colorectal cancer stages. Cancer 120:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28316
Feng H, Zhang X (2020) Long non-coding RNA SLC16A1-AS1: its multiple tumorigenesis features and regulatory role in cell cycle in oral squamous cell carcinoma:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2020.1762048
Frenette CT, Isaacson AJ, Bargellini I, Saab S, Singal AG (2019) A practical guideline for hepatocellular carcinoma screening in patients at risk. Mayo Clinic proceedings Innovations, quality & outcomes 3:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2019.04.005
Guo J, Ma Y, Peng X, Jin H, Liu J (2019a) LncRNA CCAT1 promotes autophagy via regulating ATG7 by sponging miR-181 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 120:17975–17983. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29064
Guo Y et al. (2019b) MicroRNA-301b-3p contributes to tumour growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing vestigial like family member 4. 23:5037-5047. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14361
Hall WA, Petrova AV, Colbert LE, Hardy CW, Fisher SB, Saka B, Shelton JW, Warren MD, Pantazides BG, Gandhi K, Kowalski J, Kooby DA, el-Rayes BF, Staley CA 3rd, Volkan Adsay N, Curran WJ, Landry JC, Maithel SK, Yu DS (2014) Low CHD5 expression activates the DNA damage response and predicts poor outcome in patients undergoing adjuvant therapy for resected pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 33:5450–5456. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.488
Huang S, Zou C, Tang Y, Wa Q, Peng X, Chen X, Yang C, Ren D, Huang Y, Liao Z, Huang S, Zou X, Pan J (2019) miR-582-3p and miR-582-5p suppress prostate Cancer metastasis to bone by repressing TGF-β signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 16:91–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.01.004
Huarte M (2015) The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med 21:1253–1261. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3981
Kolla V, Zhuang T, Higashi M, Naraparaju K, Brodeur GM (2014) Role of CHD5 in human cancers: 10 years later. Cancer Res 74:652–658. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-13-3056
Lai X, Eberhardt M, Schmitz U, Vera J (2019) Systems biology-based investigation of cooperating microRNAs as monotherapy or adjuvant therapy in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 47:7753–7766. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz638
Li CH, Chen Y (2013) Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancers: progress and prospects. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:1895–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.030
Li Q, Li Z, Wei S, Wang W, Chen Z, Zhang L, Chen L, Li B, Sun G, Xu J, Li Q, Wang L, Xu Z, Xia Y, Zhang D, Xu H, Xu Z (2017) Overexpression of miR-584-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0532-2
Li J, Zhai DS, Huang Q, Chen HL, Zhang Z, Tan QF (2019a) LncRNA DCST1-AS1 accelerates the proliferation, metastasis and autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cell by AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences 23:6091-6104. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201907_18423
Li P, Xing W, Xu J, Yuan D, Liang G, Liu B, Ma H (2019b) microRNA-301b-3p downregulation underlies a novel inhibitory role of long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Stem cell research & therapy 10:144. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1235-8
Liang Q, Shen X, Sun G (2018) Precision medicine: update on diagnosis and therapeutic strategies of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Med Chem 25:1999–2008. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180117101532
Liao X, Yang C, Huang R, Han C, Yu T, Huang K, Liu X, Yu L, Zhu G, Su H, Wang X, Qin W, Deng J, Zeng X, Ye X, Peng T (2018) Identification of potential prognostic long non-coding RNA biomarkers for predicting survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology 48:1854–1869. https://doi.org/10.1159/000492507
Lin X, Qiu W, Xiao Y, Ma J, Xu F, Zhang K, Gao Y, Chen Q, Li Y, Li H, Qian A (2019) MiR-199b-5p suppresses tumor angiogenesis mediated by vascular endothelial cells in breast cancer by targeting ALK1. Front Genet 10:1397. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.01397
Liu ML, Zhang Q, Yuan X, Jin L, Wang LL, Fang TT, Wang WB (2018) Long noncoding RNA RP4 functions as a competing endogenous RNA through miR-7-5p sponge activity in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 24:1004–1012. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i9.1004
Liu F, Zhang G, Lv S, Wen X, Liu P (2019) miRNA-301b-3p accelerates migration and invasion of high-grade ovarian serous tumor via targeting CPEB3/EGFR axis. J Cell Biochem 120:12618–12627. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28528
Liu HY et al. (2020) lncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. 68:52-59. https://doi.org/10.1136/jim-2019-001080
Lorenzi L, Avila Cobos F, Decock A, Everaert C, Helsmoortel H, Lefever S, Verboom K, Volders PJ, Speleman F, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P (2019) Long noncoding RNA expression profiling in cancer: challenges and opportunities. Genes, chromosomes & cancer 58:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22709
Lovat F, Valeri N, Croce CM (2011) MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis of cancer. Semin Oncol 38:724–733. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2011.08.006
Ma Y, Zhang H, Li G, Hu J, Liu X, Lin L (2019) LncRNA ANRIL promotes cell growth, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via sponging miR-144. Anti-Cancer Drugs 30:1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1097/cad.0000000000000807
Man X, Piao C, Lin X, Kong C, Cui X, Jiang Y (2019) USP13 functions as a tumor suppressor by blocking the NF-kB-mediated PTEN downregulation in human bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1262-4
Olgun G, Sahin O, Tastan O (2018) Discovering lncRNA mediated sponge interactions in breast cancer molecular subtypes. BMC Genomics 19:650. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5006-1
Ozer Etik D, Suna N, Boyacioglu AS (2017) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: prevention, surveillance, diagnosis, and staging. Experimental and clinical transplantation : official journal of the Middle East Society for Organ Transplantation 15:31–35. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.TOND16.L9
Paraskevopoulou MD, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2016) Analyzing MiRNA-LncRNA interactions. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 1402:271-286. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3378-5_21
Rashid F, Shah A, Shan G (2016) Long non-coding RNAs in the cytoplasm. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 14:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2016.03.005
Ryu SH, Jang MK, Kim WJ, Lee D, Chung YH (2014) Metastatic tumor antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma: golden roads toward personalized medicine. Cancer Metastasis Rev 33:965–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-014-9522-4
Sayiner M, Golabi P, Younossi ZM (2019) Disease burden of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global perspective. Dig Dis Sci 64:910–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05537-2
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29:452–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y (2013) Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett 339:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.013
Song M et al (2019a) Large-scale analyses identify a cluster of novel long noncoding RNAs as potential competitive endogenous RNAs in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 11:10422–10453. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102468
Song W, Zhang J, Xia Q, Sun M (2019b) Down-regulated lncRNA TP73-AS1 reduces radioresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 18:3177–3188. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1671089
Thomas PB, Seim I, Jeffery P, Gahete M, Maugham M, Crisp G, Stacey A, Shah E, Walpole C, Whiteside E, Nelson C, Herington A, Luque R, Veedu R, Chopin L (2019) The long non-coding RNA GHSROS facilitates breast cancer cell migration and orthotopic xenograft tumour growth. Int J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4891
Wang X, Lau KK, So LK, Lam YW (2009) CHD5 is down-regulated through promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. J Biomed Sci 16:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-16-95
Wang Y, Jiang F, Xiong Y, Cheng X, Qiu Z, Song R (2019a) LncRNA TTN-AS1 sponges miR-376a-3p to promote colorectal cancer progression via upregulating KLF15. Life sciences:116936 doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116936
Wang YG, Wang T, Shi M, Zhai B (2019b) Long noncoding RNA EPB41L4A-AS2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development by sponging miR-301a-5p and targeting FOXL1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1128-9
Wei H, Hu J, Pu J, Tang Q, Li W, Ma R, Xu Z, Tan C, Yao T, Wu X, Long X, Wang J (2019a) Long noncoding RNA HAGLROS promotes cell proliferation, inhibits apoptosis and enhances autophagy via regulating miR-5095/ATG12 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol 73:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.049
Wei H et al. (2019b) miR-584-5p regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through targeting KCNE2. 7:e702. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.702
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL (2009) Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev 23:1494–1504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1800909
Xu J, Bai J, Zhang X, Lv Y, Gong Y, Liu L, Zhao H, Yu F, Ping Y, Zhang G, Lan Y, Xiao Y, Li X (2017) A comprehensive overview of lncRNA annotation resources. Brief Bioinform 18:236–249. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw015
Yang N, Zhu S, Lv X, Qiao Y, Liu YJ, Chen J (2018) MicroRNAs: pleiotropic regulators in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol 9:2491. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02491
Yen YP et al (2018) Dlk1-Dio3 locus-derived lncRNAs perpetuate postmitotic motor neuron cell fate and subtype identity. eLife 7. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38080
Yong H, Fu J, Gao G, Shi H, Zheng D, Zhou X (2020) MiR-34a suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by modulating PDL1 in the immune microenvironment. Molecular and cellular probes:101601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101601
Yu C, Zhang F (2019) LncRNA AC009022.1 enhances colorectal cancer cells proliferation, migration, and invasion by promoting ACTR3B expression via suppressing miR-497-5p. Journal of cellular biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29428
Yu S, Wu Y, Li C, Qu Z, Lou G, Guo X, Ji J, Li N, Guo M, Zhang M, Lei L, Tai S (2020) Comprehensive analysis of the SLC16A gene family in pancreatic cancer via integrated bioinformatics. Sci Rep 10:7315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64356-y
Zhang X et al (2018) circRNA_104075 stimulates YAP-dependent tumorigenesis through the regulation of HNF4a and may serve as a diagnostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9:1091. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1132-6
Zhao R, Meng F, Wang N, Ma W, Yan Q (2014a) Silencing of CHD5 gene by promoter methylation in leukemia. PLoS One 9:e85172. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085172
Zhao R, Wang N, Huang H, Ma W, Yan Q (2014b) CHD5 a tumour suppressor is epigenetically silenced in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver 34:e151–e160. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12503
Zheng H, Bai L (2019) Hypoxia induced microRNA-301b-3p overexpression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells by targeting LRP1B. Exp Mol Pathol 111:104301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104301
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all participators.
Funding
This work was supported by Key Project of Guangxi Science and Technology Department (Guike AB18221103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PNG 1122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, S., Chen, Z., Tan, H. et al. SLC16A1-AS1 enhances radiosensitivity and represses cell proliferation and invasion by regulating the miR-301b-3p/CHD5 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 42778–42790 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09998-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09998-1