Abstract
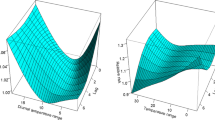
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the most serious manifestation of thromboembolic conditions. Its incidence varies considerably between countries, suggesting its interaction with the external environment. To analyze the influence of climate and air pollution on the occurrence of idiopathic PE in the region of Sousse (Tunisia). A total of 142 patients with idiopathic PE at two academic hospitals in Sousse (Tunisia) were enrolled in the study over a 7-year period. An analysis of two time series (environmental data and PE cases) was performed. Climatic data were collected from the National Institute of Meteorology. Air pollution data were obtained from the modeling platform of the National Agency for Protection of the Environment. The year 2015 was marked by the occurrence of the highest number of cases (24.6%). A statistically significant decrease in PE risk of 41.9% was observed during the summer with an OR of 0.59 (95% CI [0.36–0.94] and p = 0.026), compared with other seasons. Poisson GLM regression showed a significant increased risk of PE of 3.3% for each 1 °C temperature drop. After multiple binary logistic regression, the elevation of PM10 concentration was independently associated with an increased risk of PE (p < 10−3, OR 79.55, 95% CI [42.28–149.6]). Some environmental parameters may predispose to the onset of idiopathic PE. Understanding their accurate influence may have preventive and curative implications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrignani MG, Corrao S, Biondo GB, Renda N, Braschi A, Novo G, di Girolamo A, Braschi GB, Novo S (2009) Influence of climatic variables on acute myocardial infarction hospital admissions. Int J Cardiol 137(2):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.06.036
Abrignani MG, Corrao S, Biondo GB, Lombardo RM, Di Girolamo P, Braschi A et al (2012) Effects of ambient temperature, humidity, and other meteorological variables on hospital admissions for angina pectoris. Eur J Prev Cardiol 19(3):342–348. https://doi.org/10.1177/1741826711402741
Anar C, İnal T, Erol S, Polat G, Ünsal İ, Ediboğlu Ö et al (2015) Are meteorological parameters a risk factor for pulmonary embolism? A retrospective analysis of 530 patients. Balkan Med J 32(3):279–284. https://doi.org/10.5152/balkanmedj.2015.15686
Atkinson RW, Carey IM, Kent AJ, van Staa TP, Anderson HR, Cook DG (2013) Long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution and incidence of cardiovascular diseases. Epidemiology 24(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e318276ccb8
Bahloul M, ChaariA DH, Abid L, Daoud S, Ksibi H (2014) L’embolie pulmonaire fibrino-cruorique: Fréquence, physiopathologie, tableau Clinique et traitement. Tunis Med 92(7):435–447
Bonzini M, Tripodi A, Artoni A, Tarantini L, Marinelli B, Bertazzi PA et al (2010) Effects of inhalable particulate matter on blood coagulation. J Thromb Haemost 8(4):662–668. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03694.x
Boulay F, Berthier F, Schoukroun G, Raybaut C, Gendreike Y, Blaive B (2001) Seasonal variations in hospital admission for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: analysis of discharge data. BMJ 323(7313):601–602. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.323.7313.601
Bull GM, Brozovic M, Chakrabarti R, Meade TW, Morton J, North WR et al (1979) Relationship of air temperature to various chemical, haematological, and haemostatic variables. J Clin Pathol 32(1):16–20. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.32.1.16
Clauss R, Mayes J, Hilton P, Lawrenson R (2005) The influence of weather and environment on pulmonary embolism: pollutants and fossil fuels. Med Hypotheses 64(6):1198–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2004.11.024
D’Amato G, Cecchi L, D’Amato M, Liccardi G (2010) Urban air pollution and climate change as environmental risk factors of respiratory allergy: an update. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 20(2):95–102
D’Amato G, Holgate ST, Pawankar R, Ledford DK, Cecchi L, Al-Ahmad M et al (2015) Meteorological conditions, climate change, new emerging factors, and asthma and related allergic disorders. A statement of the World Allergy Organization. World Allergy Organ J 8(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40413-015-0073-0
Dales RE, Cakmak S, Vidal CB (2010) Air pollution and hospitalization for venous thromboembolic disease in Chile. J Thromb Haemost 8(4):669–674. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03760.x
Dentali F, Ageno W, Rancan E, Donati AV, Galli L, Squizzato A, Venco A, Mannucci P, Manfredini R (2011) Seasonal and monthly variability in the incidence of venous thromboembolism. A systematic review and a meta-analysis of the literature. Thromb Haemost 106(3):439–447. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH11-02-0116
Filleul L, Zeghnoun A, Decmercq C, Le Goaster C, Le Tetre A, Eilstein D et al (2001) Relations à court terme entre la pollution atmosphérique urbaine et la mortalité respiratoire: la place des études temporelles. Rev Mal Resp 18:361–453
Franchini M, Mannucci PM (2011) Thrombogenicity and cardiovascular effects of ambient air pollution. Blood 118(9):2405–2412. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-04-343111
Franchini M, Mannucci PM (2012) Air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Thromb Res 129(3):230–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2011.10.030
Franchini M, Mengoli C, Cruciani M, Bonfanti M, Mannucci PM (2016) Association between particulate air pollution and venous thromboembolism: a systematic literature review. Eur J Intern Med 27:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2015.11.012
Hoek G, Brunekreef B, Fischer P, vanWijnen J (2001) The association between air pollution and heart failure, arrhythmia, embolism, thrombosis, and other cardiovascular causes of death in a time series study. Epidemiology 12(3):355–357
Horan JT, Francis CW, Falsey AR, Kolassa J, Smith BH, Hall WJ (2001) Prothrombotic changes in hemostatic parameters and C-reactive protein in the elderly with winter acute respiratory tract infections. ThrombHaemost 85(2):245–249
Keatinge WR, Coleshaw SR, Cotter F, Mattock M, Murphy M, Chelliah R (1984) Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 289(6456):1405–1408. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.289.6456.1405
Law Y, Chan CY, Cheng SWK (2018) Epidemiological updates of venous thromboembolism in a Chinese population. Asian J Surg 41(2):176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2016.11.005
Li XY, Gilmour PS, Donaldson K, Mac Nee W (1996) Free radical activity and pro-inflammatory effects of particulate air pollution (PM10) in vivo and in vitro. Thorax 51(12):1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.51.12.1216
Manfredini R, Imberti D, Gallerani M, Verso M, Pistelli R, Ageno W, Agnelli G (2009) Seasonal variation in the occurrence of venous thromboembolism: data from the MASTER Registry. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 15(3):309–315. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029608319947
Manfredini R, Gallerani M, Salmi R, Dentali F, Ageno W (2011) Winter and venous thromboembolism: a dangerous liaison? Futur Cardiol 7(6):717–719. https://doi.org/10.2217/fca.11.61
Martinelli N, Girelli D, Cigolini D, Sandri M, Ricci G, Rocca G, Olivieri O (2012) Access rate to the emergency department for venous thromboembolism in relationship with coarse and fine particulate matter air pollution. PLoS One 7(4):e34831. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034831
Masotti L, Ceccarelli E, Forconi S, Cappelli R (2005) Seasonal variations of pulmonary embolism in hospitalized patients. Respir Med 99(11):1469–1473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2005.04.006
Mavri A, Guzic-Salobir B, Salobir-Pajnic B, Keber I, Stare J, Stegnar M (2001) Seasonal variation of some metabolic and haemostatic risk factors in subjects with and without coronary artery disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 12(5):359–365
Miguel-Díez J, Jiménez-García R, de Andrés AL, Hernández-Barrera V, Carrasco-Garrido P, Monreal M et al (2016) Analysis of environmental risk factors for pulmonary embolism: a case-crossover study (2001–2013). Eur J Intern Med 31:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2016.03.001
Milojevic A, Wilkinson P, Armstrong B, Bhaskaran K, Smeeth L, Hajat S (2014) Short-term effects of air pollution on a range of cardiovascular events in England and Wales: case-crossover analysis of the MINAP database, hospital admissions and mortality. Heart 100(14):1093–1098. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304963
Nimako K, Poloniecki J, Draper A, Rahman T (2012) Seasonal variability and meteorological factors: retrospective study of the incidence of pulmonary embolism from a large United Kingdom teaching hospital. Respir Care 57(8):1267–1272. https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.01129
Oztuna F, Ozsu S, Topbaş M, Bülbül Y, Koşucu P, Ozlü T (2008) Meteorological parameters and seasonal variations in pulmonary thromboembolism. Am J Emerg Med 26(9):1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2007
Pope CA (2009) The expanding role of air pollution in cardiovascular disease: does air pollution contribute to risk of deep vein thrombosis? Circulation 119(24):3050–3052. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.870279
Pun VC, Hart JE, Kabrhel C, Camargo C Jr, Baccarelli A, Laden F (2015) Prospective study of ambient particulate matter exposure and risk of pulmonary embolism in the nurses’ health study cohort. Environ Health Perspect 123(12):1265–1270. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408927
Romero-Lankao P, Qin H, Borbor-Cordova M (2013) Exploration of health risks related to air pollution and temperature in three Latin American cities. SocSci Med 83:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.01.009
Shih RA, Griffin BA, Salkowski N, Jewell A, Eibner C, Bird CE, Liao D, Cushman M, Margolis HG, Eaton CB, Whitsel EA (2011) Ambient particulate matter air pollution and venous thromboembolism in the Women’s Health Initiative Hormone Therapy trials. Environ Health Perspect 119(3):326–331. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002256
Spiezia L, Campello E, Bon M, Maggiolo S, Pelizzaro E, Simioni P (2014) Short-term exposure to high levels of air pollution as a risk factor for acute isolated pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res 134(2):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2014.05.011
Tapson VF (2008) Acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 358(10):1037–1052. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra072753
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Data availability
Readers can access the data underlying the findings of our study, by sending a mail to the corresponding author.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kacem, I., Kahloul, M., Hafsia, M. et al. Influence of weather and air pollution on the occurrence of idiopathic pulmonary embolism in the region of Sousse (Tunisia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 37660–37667 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09893-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09893-9