Abstract
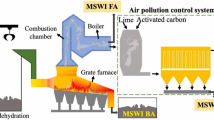
In this study, the physicochemical properties, microstructure, and heavy metal leaching potential of various municipal solid waste incinerated-bottom ash (MSWI-BA) particle sizes were detected. The environmental risks that possibly result from the utilization of MSWI-BA aggregate in road construction are discussed. The air-dried MSWI-BA was sieved into four groups, including 4.75–9.5 mm, 2.36–4.75 mm, 0.075–2.36 mm, and < 0.075 mm. X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses were conducted. It was found that the main elements of MSWI-BA are Ca, Si, and Al; the major heavy metals are Zn, Cu, Cr, and Pb, and the main mineral compositions are quartz and calcite. Even though the major elements were found to be related to MSWI-BA particle size, the micropores, attached particles, and hydration products were shown to be independent on the particle size. The standard leaching test and a simulated leaching experiment with four solid/liquid ratios were implemented to study the leaching behavior of Zn, Cu, Pb, and Cr. Results showed that the leaching characteristics of selected metals were affected by the species of metal, MSWI-BA particle size, solid/liquid ratio, and the test method. The MSWI-BA aggregate was found to be an appropriate substitute material for natural aggregate in road construction due to its low metal leaching potential.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov S, He J, Wimmer D, Lemloh ML, Muehe EM, Gann B, Roehm E, Kirchhof R, Babechuk MG, Schoenberg R, Thorwarth H, Helle T, Kappler A (2018) Heavy metal mobility and valuable contents of processed municipal solid waste incineration residues from southwestern Germany. Waste Manag 79:735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.08.010
Allegrini E, Vadenbo C, Boldrin A, Astrup TF (2015) Life cycle assessment of resource recovery from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. J Environ Manag 151:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.11.032
An J, Golestani B, Nam BH, Lee JL (2015) Sustainable utilization of MSWI bottom ash as road construction materials. Part I: Physical and Mechanical Evaluation Airfield and Highway Pavements:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479216.021
Azarsa P, Gupta R (2018) Monitoring the in-situ Freeze-Thaw performance and leaching of K-based geopolymer concrete pavers. 1st International conference on new horizons in green civil engineering (NHICE-01), Victoria, B.C., Canada, April 25–27
Bayuseno AP, Schmahl WW (2010) Understanding the chemical and mineralogical properties of the inorganic portion of MSWI bottom ash. Waste Manag 30(8):1509–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.03.010
Becquart F, Bernard F, Abriak NE, Zentar R (2009) Monotonic aspects of the mechanical behaviour of bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration and its potential use for road construction. Waste Manag 29(4):1320–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.08.019
Birgisdóttir H, Pihl KA, Bhander G, Hauschild MZ, Christensen TH (2006) Environmental assessment of roads constructed with and without bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 11(5):358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2006.07.001
Cao Y, Liu R, Xu Y, Ye F, Xu R, Han Y (2019) Effect of SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO on characteristics of lightweight aggregates produced from MSWI bottom ash sludge (MSWI-BAS). Constr Build Mater 205:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.104
Caprai V, Florea M, Brouwers H (2017) Evaluation of the influence of mechanical activation on physical and chemical properties of municipal solid waste incineration sludge. J Environ Manag 216:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.024
Chimenos JM, Fernandez AI, Miralles L, Segarra M, Espiell F (2003) Short-term natural weathering of MSWI bottom ash as a function of particle size. Waste Manag 23:887–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(03)00074-6
Ciarán JL, Ravindra KDOBE, Gurmel SG (2016) Municipal incinerated bottom ash characteristics and potential for use as aggregate in concrete. Constr Build Mater 127:504–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.09.132
Dabo D, Badreddine R, Windt LD, Drouadaine I (2009) Ten-year chemical evolution of leachate and municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash used in a test road site. J Hazard Mater 172(2-3):904–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.083
Dijkstra J, Van Zomeren A, Meeussen JCL, Comans RNJ (2006) Effect of accelerated aging of MSWI bottom ash on the leaching mechanisms of copper and molybdenum. Environ Sci Technol 40(14):4481–4487. https://doi.org/10.1021/es052214s
Forteza R, Far M, Seguíb C, Cerdá V (2004) Characterization of bottom ash in municipal solid waste incinerators for its use in road base. Waste Manag 24(9):899–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2004.07.004
Hartmann S, Koval L, Krobankova H, Matysek D, Winter F, Purgar A (2015) Possibilities of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash utilisation. Waste Manag Res 33(8):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X15587545
Hassan MM, Khalid H (2010) Mechanical and environmental characteristics of bituminous mixtures with incinerator bottom ash aggregates. Int J Pavement Eng 11(2):83–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298430802524800
Huang CM, Chiu CT, Li KC, Yang WF (2006) Physical and environmental properties of asphalt mixtures containing incinerator bottom ash. J Hazard Mater 137(3):1742–1749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.016
Hu MJ, Li LH, Cui HJ (2018) Experimental study on the property and treatment mechanism of municipal solid waste bottom ash aggregate treated soil. J Building Mat 1-9 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1764.TU.20180910.1641.016.html
Izquierdo M, Soler-López A, Ramonich EV, Barra M, Querol X (2002) Characterisation of bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration in Catalonia. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77(5):576–583. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.605
Izquierdo M, Querol X, Vazquez E (2011) Procedural uncertainties of proctor compaction tests applied on MSWI bottom ash. J Hazard Mater 186(2–3):1639–1644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.045
Lam CHK, Ip AWM, Barford JP, Mckay G (2010) Use of incineration MSW ash: a review. Sustainability 2(7):1943–1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/su2071943
Le NH, Razakamanantsoa A, Nguyen ML, Phan VT, Dao PL, Nguyen DH (2018) Evaluation of physicochemical and hydromechanical properties of MSWI bottom ash for road construction. Waste Manag 80:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.007
Lin CL, Weng MC, Chang CH (2012) Effect of incinerator bottom-ash composition on the mechanical behavior of backfill material. J Environ Manag 113(1):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.09.013
Li XG, Lv Y, Ma BG, Chen QB, Yin XB, Jian SW (2012) Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash in blended cement. J Clean Prod 32(3):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.03.038
Liu D, Li LH, Cui HJ (2014) Experimental study on the influence of slag aggregate on the performance of asphalt mixture. J Build Mat 18(2): 307–311 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=JZCX201502024&DbName=CJFQ2015
Lynn CJ, Ghataora GS, Dhir RK (2016) Municipal incinerated bottom ash (MIBA) characteristics and potential for use in road pavements. Int J Pavement Res Technol 10(2):185–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijprt.2016.12.003
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (2010) Solid waste-extraction procedure for leaching toxicity- horizontal vibration method (HJ 557–2010). China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese)
Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China (2005) Test methods of aggregate for highway engineering: JTG E42–2005. People’s Communications Press (in Chinese)
National Development and Reform Commission, and Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (2016) China’s 13th Five-Year Construction Plan for MSW Safe Treatment Facilities. (in Chinese)
National Environmental Protection Administration of China (1998) Technical specification for sampling and sample preparation from industrial solid waste (HJ/T 20–1998). China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese)
National Environmental Protection Administration of China (2007) Technical specifications on identification for hazardous waste (HJ/T 298–2007). China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
National Statistical Bureau of the People’s Republic of China (2019) China statistical yearbook. China Statistical Publishing House. (in Chinese)
Nan XJ (2015) Co-stabilization of MSWI bottom ash and municipal sludge with an emphasis on geoenvironmental behavior of heavy metals. Dissertation, Chongqing University (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=1015970277.nh&DbName=CMFD2016
Shi AJ, He PJ, Shao LM, Li XJ, Zhang CG (2004) Study on engineering properties of municipal solid waste incinerator slag. Environ Eng 22 (1):47-50+4 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13205/j.hjgc.2004.01.014
Tasneem KM, Eun J, Nam BH (2017) Leaching behaviour of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash mixed with hot-mix asphalt and Portland cement concrete used as road construction materials. Road Materials and Pavement Design 18(3):26. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2016.1186108
Van Gerven T, Van Keer E, Aricks S, Jaspers M, Wauters G, Vandecasteele C (2005) Carbonation of MSWI-bottom ash to decrease heavy metal leaching, in view of recycling. Waste Manag 25:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2004.07.008
Wongsa A, Boonserm K, Waisurasingha C, Sata V, Chindaprasirt P (2017) Use of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) bottom ash in high calcium fly ash geopolymer matrix. J Clean Prod 148:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.147
Xie R, Xu Y, Huang M, Zhu H, Chu F (2017) Assessment of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash as a potential road material. Road Materials and Pavement Design 18(4):992–998. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2016.1206483
Xue YJ, Hou HB, Zhu SJ, Zha J (2009) Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration ash in stone mastic asphalt mixture: pavement performance and environmental impact. Construction & Building Materials 23(2):989–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.05.009
Yang ZZ, Ji R, Liu LL, Wang XD, Zhang ZT (2018a) Recycling ground MSWI bottom ash in cement composites: long-term environmental impacts. Waste Manag 78:841–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.002
Yang ZZ, Ji R, Liu LL, Zhang ZT (2018b) Recycling of municipal solid waste incineration by-product for cement composites preparation. Construction & Building Materials 162:794–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.081
Yu J, Sun L, Xiang J, Jin L, Hu S, Su S, Qiu J (2013) Physical and chemical characterization of ashes from a municipal solid waste incinerator in China. Waste Manag Res 31(7):663–673. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X13485793
Zhang DQ, Tan SK, Gersberg RM (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: status, problems and challenges. J Environ Manag 91(8):1623–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.03.012
Zhu YT, Zhao Y, Zhao C (2018) Laboratory study on environmental safety of cement stabilized MSWI-BA macadam base. Bulletin of the Chinese ceramic society 37 (10): 3296-3302+3316 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2018.10.048
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China, grant number [17KJB580007]; the Basic Research Program (Natural Science Foundation) of Jiangsu Province, China, grant number [BK20170933]; the Science and Technology Plan Program of Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, grant number [2018-K9-074; 2019-K-160]; the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, China, grant number (KYCX17_0867); and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). The authors would like to thank the Civil Engineering Experimental Center of Nanjing Forestry University, China for all of the support provided to us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhao, C. et al. Physicochemical characterization and heavy metals leaching potential of municipal solid waste incinerated bottom ash (MSWI-BA) when utilized in road construction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 14184–14197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08007-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08007-9