Abstract
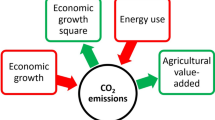
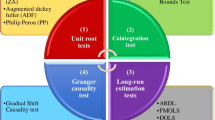
Increasing population and food demand has led to steadily declining resources as a result of over-exploitation and fossil fuel consumption that cause air contamination and reduce soil fertility. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the correlation between air pollution, energy consumption, and the contribution of agriculture to national GDP. Secondary study data covering two decades were collected from different sources, and an autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) bounds testing model was employed to determine long-run and short-run correlations. First, the unit root test was used to determine the stationarity of variables, and results showed that variables were integrated at level, ARDL co-integration equation estimation, which rejected the null hypothesis at less than 5% significance level. Further, based on the results of the ARDL bounds testing model, F-statistic values exceeded the upper bound value. This entire model was adjusted at a speed of −2.364 towards long-run equilibrium. In addition, CUSUM test and CUSUMSQ test results confirmed the goodness of fit of this model. In light of the resulting policy implications, the Chinese government may consider measures to improve the agricultural industry to meet the food demand for the fast-growing population while maintaining a healthy environment and safeguarding the available limited resources for future generations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acaravci A, Ozturk I (2010) On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 35(12):5412–5420
Afzal M, Farooq MS et al (2010) Relationship between school education and economic growth in Pakistan: ARDL bounds testing approach to cointegration. Pakistan Econ Soc Rev 39–60
Ahmada R, Zulkiflib SAM et al (2016) The impact of economic activities on Co 2 emission. Int Acad Res J Soc Sci 2(1):81–88
Ahmed V, Zeshan M (2014) Decomposing change in energy consumption of the agricultural sector in Pakistan. Agrar S J Polit Econ 3(3):369–402
Al-Mulali U, Weng-Wai C et al (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10):4772–4778
Apergis N, Payne JE (2009) Energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from the Commonwealth of Independent States. Energy Econ 31(5):641–647
Asumadu-Sarkodie S, Owusu PA (2016) The relationship between carbon dioxide and agriculture in Ghana: a comparison of VECM and ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(11):10968–10982
Awad A, Abugamos H (2017) Income-carbon emissions nexus for Middle East and North Africa countries: a semi-parametric approach. Int J Energy Econ Policy 7(2):152–159
Bakhsh K, Rose S et al (2017) Economic growth, CO2 emissions, renewable waste and FDI relation in Pakistan: New evidences from 3SLS. J Environ Manag 196:627–632
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2017) Renewable energy consumption and agriculture: evidence for cointegration and Granger causality for Tunisian economy. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 24(2):149–158
Bhattacharya M, Churchill SA et al (2017) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renew Energy 111:157–167
Binh PT (2011) Energy consumption and economic growth in Vietnam: Threshold cointegration and causality analysis. Int J Energy Econ Policy 1(1):1–17
Burney J, Ramanathan V (2014) Recent climate and air pollution impacts on Indian agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(46):16319–16324
Burney JA, Davis SJ et al (2010) Greenhouse gas mitigation by agricultural intensification. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(26):12052–12057
Chandio AA, Jiang Y et al (2018) Energy consumption and agricultural economic growth in Pakistan: is there a nexus? Int J Energy Sect Manag
Chavunduka CM, Bromley DW (2013) Considering the multiple purposes of land in Zimbabwe’s economic recovery. Land Use Policy 30(1):670–676
Chen J, Cheng S et al (2018) "Changes in energy-related carbon dioxide emissions of the agricultural sector in China from 2005 to 2013." Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 94:748–761.
Dantama YU, Abdullahi YZ et al (2012) Energy consumption-economic growth nexus in Nigeria: an empirical assessment based on ARDL bound test approach. Eur Sci J 8(12)
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74(366a):427–431
Dong K, Hochman G et al (2018a) CO2 emissions, economic and population growth, and renewable energy: empirical evidence across regions. Energy Econ 75:180–192
Dong K, Sun R et al (2018b) CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: what roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J Clean Prod 196:51–63
Dong N, Prentice IC et al (2017) Leaf nitrogen from first principles: field evidence for adaptive variation with climate, Biogeosciences, 14:481–495.
Engle RF, Granger CW (1987) Co-integration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econ J Econ Soc 251–276
Fais B, Sabio N et al (2016) The critical role of the industrial sector in reaching long-term emission reduction, energy efficiency and renewable targets. Appl Energy 162:699–712
Fan M, Shao S et al (2015) Combining global Malmquist–Luenberger index and generalized method of moments to investigate industrial total factor CO2 emission performance: a case of Shanghai (China). Energy Policy 79:189–201
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO 2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15663–15676
Fuglie K, McDonald J et al (2007) Productivity growth in US agriculture. Economic Brief Number 9. Economic Research Service, Washington, DC, September
Ghosh S (2010) Examining carbon emissions economic growth nexus for India: a multivariate cointegration approach. Energy Policy 38(6):3008–3014
Guan X, Zhou M et al (2015) Using the ARDL-ECM approach to explore the nexus among urbanization, energy consumption, and economic growth in Jiangsu Province, China. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 51(2):391–399
Halicioglu F (2009) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37(3):1156–1164
Hatemi JA, Hacker RS (2009) Can the LR test be helpful in choosing the optimal lag order in the VAR model when information criteria suggest different lag orders? Appl Econ 41(9):1121–1125
Hitaj C, Suttles S (2016) Trends in US agriculture’s consumption and production of energy: renewable power, Shale Energy, and Cellulosic Biomass
Huang CJ, Tang AM et al (1986) Two views of efficiency in Indian agriculture. Can J Agric Econ/Revue canadienne d’agroeconomie 34(2):209–226
Huang J, Rozelle S (1996) Technological change: Rediscovering the engine of productivity growth in China’s rural economy. J Dev Econ 49(2):337–369
Huang Y, Li H et al (2011) Defending false data injection attack on smart grid network using adaptive CUSUM test. 2011 45th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, IEEE
Huo H, Zhang Q et al (2014) Examining air pollution in China using production-and consumption-based emissions accounting approaches. Environ Sci Technol 48(24):14139–14147
Iwata H, Okada K et al (2010) Empirical study on the environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 in France: the role of nuclear energy. Energy Policy 38(8):4057–4063
Jalil A, Mahmud SF (2009) Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy 37(12):5167–5172
Jin S, Ma H et al (2010) Productivity, efficiency and technical change: measuring the performance of China’s transforming agriculture. J Prod Anal 33(3):191–207
Johansen S, Juselius K (1990) Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—with applications to the demand for money. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 52(2):169–210
Johnson JM-F, Franzluebbers AJ et al (2007) Agricultural opportunities to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Environ Pollut 150(1):107–124
Kaika D, Zervas E (2013) The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) theory—Part A: concept, causes and the CO2 emissions case. Energy Policy 62:1392–1402
Kang Y-Q, Zhao T et al (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in China: a spatial panel data approach. Ecol Indic 63:231–239
Karkacier O, Goktolga ZG et al (2006) A regression analysis of the effect of energy use in agriculture. Energy Policy 34(18):3796–3800
Khan AN, Ghauri B et al (2011) Climate Change: emissions and Sinks of greenhouse gases in Pakistan. Proceedings of the Symposium on Changing Environmental Pattern and its impact with Special Focus on Pakistan
Khan MTI, Ali Q et al (2018) The nexus between greenhouse gas emission, electricity production, renewable energy and agriculture in Pakistan. Renew Energy 118:437–451
Koondhar MA, Qiu L et al (2018) A nexus between air pollution, energy consumption and growth of economy: a comparative study between the USA and China-based on the ARDL bound testing approach. Agric Econ 64(6):265–276
Kulak M, Graves A et al (2013) Reducing greenhouse gas emissions with urban agriculture: a Life Cycle Assessment perspective. Landsc Urban Plan 111:68–78
Lean HH, Smyth R (2010) CO2 emissions, electricity consumption and output in ASEAN. Appl Energy 87(6):1858–1864
Lee S, Ha J et al (2003) The cusum test for parameter change in time series models. Scand J Stat 30(4):781–796
Li T, Wang Y et al (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve in China: new evidence from dynamic panel analysis. Energy Policy 91:138–147
Li W, Ou Q et al (2014) Decomposition of China’s CO 2 emissions from agriculture utilizing an improved Kaya identity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(22):13000–13006
Lin JY, Liu Z (2000) Fiscal decentralization and economic growth in China. Econ Dev Cult Chang 49(1):1–21
Liu W, Hussain S et al (2016) Greenhouse gas emissions, soil quality, and crop productivity from a mono-rice cultivation system as influenced by fallow season straw management. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(1):315–328
Liu X, Zhang X et al (2010) Feeding China’s growing needs for grain. Nature 465(7297):420
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16478–16494
Mackinnon, J. G., A. A. Haug, et al. "Numerical Distribution Functions of Likelihood Ratio Tests for Cointegration." Journal of Applied Econometrics 14(5):563–577
Mardani A, Streimikiene D et al (2018) Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and economic growth: a systematic review of two decades of research from 1995 to 2017. Sci Total Environ
McMillan J, Whalley J et al (1989) The impact of China’s economic reforms on agricultural productivity growth. J Polit Econ 97(4):781–807
Moghaddasi R, Pour AA (2016) Energy consumption and total factor productivity growth in Iranian agriculture. Energy Rep 2:218–220
Nadeem S, Munir K (2016) Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in Pakistan: A Sectoral Analysis
Narayan P (2004) Reformulating critical values for the bounds F-statistics approach to cointegration: an application to the tourism demand model for Fiji, Monash University Australia
Nasir M, Rehman FU (2011) Environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: an empirical investigation. Energy Policy 39(3):1857–1864
Nayak D, Saetnan E et al (2015) Management opportunities to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from Chinese agriculture. Agric Ecosyst Environ 209:108–124
Norse D, Ju X (2015) Environmental costs of China’s food security. Agric Ecosyst Environ 209:5–14
Ozcan B (2013) The nexus between carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Middle East countries: a panel data analysis. Energy Policy 62:1138–1147
Ozturk I (2010) A literature survey on energy–growth nexus. Energy Policy 38(1):340–349
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Clean Prod 187:770–779
Perron P (1990) Testing for a unit root in a time series with a changing mean. J Bus Econ Stat 8(2):153–162
Pesaran MH, Shin Y (1998) An autoregressive distributed-lag modelling approach to cointegration analysis. Econom Soc Monogr 31:371–413
Pesaran MH, Shin Y et al (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Phillips PC, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 75(2):335–346
Ploberger W, Krämer W (1992) The CUSUM test with OLS residuals. Econ J Econ Soc 271–285
Rafindadi AA, Yusof Z et al (2014) The relationship between air pollution, fossil fuel energy consumption, and water resources in the panel of selected Asia-Pacific countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(19):11395–11400
Rehman A, Rauf A et al (2019) The effect of carbon dioxide emission and the consumption of electrical energy, fossil fuel energy, and renewable energy, on economic performance: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–14
Reynolds L, Wenzlau S (2012) Climate-friendly agriculture and renewable energy: working hand-in-hand toward climate mitigation. Worldwatch Institute. ed
Richmond AK, Kaufmann RK (2006) Is there a turning point in the relationship between income and energy use and/or carbon emissions? Ecol Econ 56(2):176–189
Saidi K, Mbarek MB (2016) Nuclear energy, renewable energy, CO2 emissions, and economic growth for nine developed countries: Evidence from panel Granger causality tests. Prog Nucl Energy 88:364–374
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019) Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 646:862–871
Seker F, Ertugrul HM et al (2015) The impact of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: a bounds testing and causality analysis for Turkey. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 52:347–356
Shahbaz M, Bhattacharya M et al (2017) CO2 emissions in Australia: economic and non-economic drivers in the long-run. Appl Econ 49(13):1273–1286
Shahbaz M, Khraief N et al (2014) Environmental Kuznets curve in an open economy: a bounds testing and causality analysis for Tunisia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 34:325–336
Shahbaz M, Lean HH et al (2012) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Pakistan: cointegration and Granger causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(5):2947–2953
Shahbaz M, Sinha A (2019) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a literature survey. J Econ Stud 46(1):106–168
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK et al (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shuai C, Chen X et al (2018) Identifying the key impact factors of carbon emission in China: Results from a largely expanded pool of potential impact factors. J Clean Prod 175:612–623
Sinaga O, Alaeddin O et al (2018) The impact of hydropower energy on the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia. Int J Energy Econ Policy 9(1):308–315
Soytas U, Sari R (2009) Energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon emissions: challenges faced by an EU candidate member. Ecol Econ 68(6):1667–1675
Stern DI (2017) The environmental Kuznets curve after 25 years. J Bioecon 19(1):7–28
Stern DI (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve. Companion to Environmental Studies, ROUTLEDGE in association with GSE Research. 49:49–54
Sugiawan Y, Managi S (2016) The environmental Kuznets curve in Indonesia: Exploring the potential of renewable energy. Energy Policy 98:187–198
Tang CF, Tan BW et al (2016) Energy consumption and economic growth in Vietnam. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:1506–1514
Timmer CP (2000) The macro dimensions of food security: economic growth, equitable distribution, and food price stability. Food Policy 25(3):283–295
Wang S, Li G et al (2018) Urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: Empirical evidence from countries with different income levels. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:2144–2159
Wang S, Li Q et al (2016) The relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 542:360–371
Wang S, Zhou D et al (2011) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China: A panel data analysis. Energy Policy 39(9):4870–4875
Wei J, Guo X et al (2014) Industrial SO2 pollution and agricultural losses in China: evidence from heavy air polluters. J Clean Prod 64:404–413
Westerlund J (2005) A panel CUSUM test of the null of cointegration. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 67(2):231–262
Xiao Z, Phillips PC (2002) A CUSUM test for cointegration using regression residuals. J Econom 108(1):43–61
Yildirim E, Aslan A (2012) Energy consumption and economic growth nexus for 17 highly developed OECD countries: further evidence based on bootstrap-corrected causality tests. Energy Policy 51:985–993
Yu J, Wu J (2018) The sustainability of agricultural development in China: the agriculture–environment nexus. Sustainability 10(6):1776
Yuan X, Mu R et al (2015) Economic development, energy consumption, and air pollution: a critical assessment in China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 21(3):781–798
Zaman K, Khan MM et al (2012) The relationship between agricultural technology and energy demand in Pakistan. Energy Policy 44:268–279
Zoundi Z (2017) CO2 emissions, renewable energy and the Environmental Kuznets Curve, a panel cointegration approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:1067–1075
Acknowledgements
This study was financial supported by the College of Agricultural Economics and Management, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, through the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project no. NSFC 71773094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made significant contributions to the study conception and design. The generation of ideas, collection of data, and analysis was performed by Houjian Li, Huiling Wang, and Sanchir Bold. The first draft was completed by Mansoor Ahmed Koondhar, and all authors were involved in providing feedback and critical revision of the manuscript. The whole work was carried out under the supervision of Prof Dr. Rong Kong, who approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Muhammad Shahbaz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix



Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koondhar, M.A., Li, H., Wang, H. et al. Looking back over the past two decades on the nexus between air pollution, energy consumption, and agricultural productivity in China: a qualitative analysis based on the ARDL bounds testing model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 13575–13589 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07501-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07501-z