Abstract
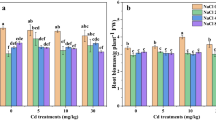
Cadmium (Cd) has already caused worldwide concern because of its high biotoxicity to human and plants. This study investigated how nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) enrichment alter the toxic morpho-physiological impacts of and accumulation of Cd in hydroponically grown Salix matsudana Koidz cuttings. Our results showed that Cd significantly depressed growth and induced a physiological response on S. matsudana cuttings, exhibiting by reduced biomass, decreased photosynthetic pigment concentrations, and increased soluble protein and peroxidase activity of shoots and roots. N and P enrichment alleviated the Cd toxic effects by increasing production of proline which prevented cuttings from damage by Cd-induced ROS, displaying with decreased malondialdehyde concentration, and stimulated overall Cd accumulation. Enrichment of N and P significantly decreased the upward Cd transfer, combing with enhanced root uptake (stimulated root activity) and retranslocation from stem, resulted in extensive Cd sequestration in S. matsudana roots. In both root and xylem, concentration of Cd is positively correlated with N and P. The improved phytoextraction potential by N and P enrichment was mainly via elevating Cd concentration in roots, probably by increased production of phytochelatins (e.g., proline) which form Cd chelates and help preventing damage from Cd-induced ROS. This study provides support for the application of S. matsudana in Cd phytoextraction even in eutrophic aquatic environments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Hadi F, Ali N (2015) Effective phytoextraction of cadmium (Cd) with increasing concentration of total phenolics and free proline in Cannabis sativa (L) plant under various treatments of fertilizers, plant growth regulators and sodiumsalt. Int J Phytoremediat 17:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2013.828018
Ahmad A, Hadi F, Ali N, Jan AU (2016) Enhanced phytoremediation of cadmium polluted water through two aquatic plants Veronica anagallis-aquatica and Epilobium laxum. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:17715–17729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6960-2
Alexander TJ, Vonlanthen P, Seehausen O (2017) Does eutrophication-driven evolution change aquatic ecosystems? Philos Trans R Soc B 372:20160041. https://doi.org/10.1098/Rstb.2016.0041
Anagnostou E, Gianni A, Zacharias I (2017) Ecological modeling and eutrophication A review. Nat Resour Model 30:e12130. https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12130
Bai XL, Sun JH, Zhou YK, Gu L, Zhao HY, Wang JH (2017) Variations of different dissolved and particulate phosphorus classes during an algae bloom in a eutrophic lake by P-31 NMR spectroscopy. Chemosphere 169:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.116
Balestri M, Ceccarini A, Forino LMC, Zelko I, Martinka M, Lux A, Castiglione MR (2014) Cadmium uptake, localization and stress-induced morphogenic response in the fern Pteris vittata. Planta 239:1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2036-z
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Beaucham C, Fridovic I (1971) Superoxide dismutase - improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Boutraa T (2010) Effects of water stress on root growth, water use efficiency, leaf area and chlorophyll content in the desert shrub Calotropis procera. J Int Environ Appl Sci 5:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1674-2370(15)30016-8
Calero-Muñoz N, Exposito-Rodriguez M, Collado-Arenal AM, Rodríguez-Serrano MM, Laureano-Marín AM, Santamaría ME, Gotor C, Díaz I, Mullineaux PM, Romero-Puertas MC (2019) Cadmium induces ROS-dependent pexophagy in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell Environ. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13597
Chaffei C, Pageau K, Suzuki A, Gouia H, Ghorbel MH, Masclaux-Daubresse C (2004) Cadmium toxicity induced changes in nitrogen management in Lycopersicon esculentum leading to a metabolic safeguard through an amino acid storage strategy. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1681–1693. https://doi.org/10.1093/Pcp/Pch192 doi:10.2166/wst.2011.800
Chang YS, Chang YJ, Lin CT, Lee MC, Wu CW, Lai YH (2013) Nitrogen fertilization promotes the phytoremediation of cadmium in Pentas lanceolata. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 85:709–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.05.021
Chaudhary I, Cornfield A (1966) The determination of total sulphur in soil and plant material. Analyst 91:528–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88469-X
Cheng MM, Wang AA, Tang CX (2017) Ammonium-based fertilizers enhance Cd accumulation in Carpobrotus rossii grown in two soils differing in pH. Chemosphere 188:689–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.032
Coutinho SR, With E, Rehfeld JF, Kulseng B, Truby H, Martins C (2018) The impact of rate of weight loss on body composition and compensatory mechanisms during weight reduction: a randomized control trial. Clin Nutr 37:1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2017.04.008
Curie C, Cassin G, Couch D, Divol F, Higuchi K, Jean M, Misson J, Schikora A, Czernic P, Mari S (2009) Metal movement within the plant: contribution of nicotianamine and yellow stripe 1-like transporters. Ann Bot 103:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcn207
Fu J, Zhao C, Luo Y, Liu C, Kyzas GZ, Luo Y, Zhao D, An S, Zhu H (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.044
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Lannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.006
Groth SFS, Webster R, Datyner A (1963) Two new staining procedures for quantitative estimation of proteins on electrophoretic strips. Biochim Biophys Acta 71:377–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3002(63)91092-8
Grotz N, Fox T, Connolly E, Park W, Guerinot ML, Eide D (1998) Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from Arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:7220–7224. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.12.7220
Herzog V, Fahimi H (1973) Determination of the activity of peroxidase. Anal Biochem 55:e62
Horie I, Abiru N, Hongo R, Nakamura T, Ito A, Haraguchi A, Natsuda S, Sagara I, Ando T, Kawakami A (2018) Increased sugar intake as a form of compensatory hyperphagia in patients with type 2 diabetes under dapagliflozin treatment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 135:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.11.016
Hrynkiewicz K, Baum C (2013) Selection of ectomycorrhizal willow genotype in phytoextraction of heavy metals. Environ Technol 34:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.689369
Hu PJ, Yin YG, Ishikawa S, Suzui N, Kawachi N, Fujimaki S, Igura M, Yuan C, Huang JX, Li Z, Makino T, Luo YM, Christie P, Wu LH (2013) Nitrate facilitates cadmium uptake, transport and accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6306–6316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1680-3
Kopittke PM, Blamey FPC, Menzies NW (2010) Toxicity of Cd to signal grass (Brachiaria decumbens Stapf.) and Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth.). Plant Soil 330:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0224-6
Kubatova P, Hejcman M, Szakova J, Vondrackova S, Tlustos P (2016) Effects of sewage sludge application on biomass production and concentrations of Cd, Pb and Zn in shoots of Salix and Populus clones: improvement of phytoremediation efficiency in contaminated soils. Bioenerg Res 9:809–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-016-9727-1
Kumar A (2016) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria in agriculture biotechnology: diversity, mechanism and their role in plant growth and crop yield. Int J Adv Res 4:116–124. https://doi.org/10.21474/IJAR01/111
Kupper H, Andresen E (2016) Mechanisms of metal toxicity in plants. Metallomics 8:269–285. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mt00244c
Kupper H, Kupper FC, Spiller M (1996) Environmental relevance of heavy metal-substituted chlorophylls using the example of water plants. J Exp Bot 47:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1093/Jxb/47.2.259
Lei M, Wan X-m, Z-c H, T-b C, X-w L, Y-r L (2012) First evidence on different transportation modes of arsenic and phosphorus in arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Environ Pollut 161:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.02.001
Li NY, Fu QL, Zhuang P, Guo B, Zou B, Li ZA (2012) Effect of fertilizers on Cd uptake of Amaranthus hypochondriacus, a high biomass, fast growing and easily cultivated potential Cd hyperaccumulator. Int J Phytoremediat 14:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.587479
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0110591
Liu D, Kottke I, Adam D (2007) Localization of cadmium in the root cells of Allium cepa by energy dispersive X-ray analysis. Biol Plant 51:363–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0075-z
Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Han WX, Tang AH, Shen JL, Cui ZL, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang FS (2013a) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11917
Liu Y, Zhuang P, Li ZA, Zou B, Wang G, Li NY, Qiu J (2013b) Effects of fertiliser and intercropping on cadmium uptake by maize. Chem Ecol 29:489–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2013.810720
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq281
Maathuis FJ (2009) Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.003
Maathuis FJ, Podar D, Hawkesford M, Barraclough P (2011) Uptake, distribution, and physiological functions of potassium, calcium, and magnesium. In: The Molecular and Physiological Basis of Nutrient Use Efficiency in Crops, pp 265–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470960707.ch13
Mao L, Mo D, Guo Y, Fu Q, Yang J, Jia Y (2013) Multivariate analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments from lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River, southern China. Environ Earth Sci 69:765–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1959-6
Mendoza-Cozatl DG, Butko E, Springer F, Torpey JW, Komives EA, Kehr J, Schroeder JI (2008) Identification of high levels of phytochelatins, glutathione and cadmium in the phloem sap of Brassica napus. A role for thiol-peptides in the long-distance transport of cadmium and the effect of cadmium on iron translocation. Plant J 54:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03410.x
MEPC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of China) (2002) Environmental quality standard for surface water in China (GB3838–2002), Beijing, April, p 28
Mico C, Recatala L, Peris A, Sanchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.016
Mleczek M, Rutkowski P, Golinski P, Kaczmarek Z, Szentner K, Waliszewska B, Stolarski M, Szczukowski S (2017) Biological diversity of Salix taxa in Cu, Pb and Zn phytoextraction from soil. Int J Phytoremediat 19:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1207597
Muh F, Glockner C, Hellmich J, Zouni A (2012) Light-induced quinone reduction in photosystem II. Bba-Bioenergetics 1817:44–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.05.021
Pedas P, Schjoerring JK, Husted S (2009) Identification and characterization of zinc-starvation-induced ZIP transporters from barley roots. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.01.006
Poschenrieder C, Cabot C, Martos S, Gallego B, Barcelo J (2013) Do toxic ions induce hormesis in plants? Plant Sci 212:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.07.012
Rai PK (2008) Heavy metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems and its phytoremediation using wetland plants: an ecosustainable approach. Int J Phytoremediat 10:133–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510801913918
Rao KVM, Sresty TVS (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci 157:113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00273-9
Reimann C, Fabian K, Flem B (2019) Cadmium enrichment in topsoil: separating diffuse contamination from biosphere-circulation signals. Sci Total Environ 651:1344–1355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.272
Richter AK, Frossard E, Brunner I (2007) Polyphenols in the woody roots of Norway spruce and European beech reduce TTC. Tree Physiol 27:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/27.1.155
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2006) The significance of amino acids and amino acid-derived molecules in plant responses and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J Exp Bot 57:711–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj073
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.11.009
Song Y, Jin L, Wang XJ (2017) Cadmium absorption and transportation pathways in plants. Int J Phytoremediat 19:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1207598
Sood A, Uniyal PL, Prasanna R, Ahluwalia AS (2012) Phytoremediation potential of aquatic macrophyte, Azolla. Ambio 41:122–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-011-0159-z
Takenaka C, Kobayashi M, Kanaya S (2009) Accumulation of cadmium and zinc in Evodiopanax innovans. Environ Geochem Health 31:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9205-6
Tao Q, Jupa R, Luo JP, Lux A, Kovac J, Wen Y, Zhou YM, Jan J, Liang YC, Li TQ (2017) The apoplasmic pathway via the root apex and lateral roots contributes to Cd hyperaccumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Exp Bot 68:739–751. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw453
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2004) Relationship between copper- and zinc-induced oxidative stress and proline accumulation in Scenedesmus sp. Planta 219:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1237-2
Utmazian MND, Wenzel WW (2007) Cadmium and zinc accumulation in willow and poplar species grown on polluted soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200622073
Wang W-w, Cheng L, Jw H, Guan X, X-j T (2016a) Phytoextraction of initial cutting of Salix matsudana for Cd and Cu. Int J Phytoremediat:00–00. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1183574
Wang WW, Wu YJ, Akbar S, Jia XQ, He ZH, Tian XJ (2016b) Effect of heavy metals combined stress on growth and metals accumulation of three Salix species with different cutting position. Int J Phytoremediat 18:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2015.1131237
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq085
Willick IR, Plaxton WC, Lolle SJ, Macfie SM (2019) Transcriptional and post-translational upregulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Arabidopsis thaliana (L. Heynh) under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 164:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.04.018
Wong CKE, Cobbett CS (2009) HMA P-type ATPases are the major mechanism for root-to-shoot Cd translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 181:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02638.x
Wu J, Mock H-P, Giehl RF, Pitann B, Mühling KH (2019) Silicon decreases cadmium concentrations by modulating root endodermal suberin development in wheat plants. J Hazard Mater 364:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.052
Xin JL, Huang BF, Yang ZY, Yuan JG, Dai HW, Qiu Q (2010) Responses of different water spinach cultivars and their hybrid to Cd, Pb and Cd-Pb exposures. J Hazard Mater 175:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.029
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76:167–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2009.10.007
Yang YJ, Xiong J, Chen RJ, Fu GF, Chen TT, Tao LX (2016) Excessive nitrate enhances cadmium (Cd) uptake by up-regulating the expression of OsIRT1 in rice (Oryza sativa). Environ Exp Bot 122:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.10.001
Yoshimoto K, Shibata M, Kondo M, Oikawa K, Sato M, Toyooka K, Shirasu K, Nishimura M, Ohsumi Y (2014) Organ-specific quality control of plant peroxisomes is mediated by autophagy. J Cell Sci 127:1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.139709
Young PG, Bartel B (2016) Pexophagy and peroxisomal protein turnover in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res 1863:999–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.005
Zancheta ACF, De Abreu CA, Zambrosi FCB, Erismann ND, Lago AMMA (2015) Cadmium accumulation by jack-bean and sorghum in hydroponic culture. Int J Phytoremediat 17:298–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2014.883492
Zaragueta M, Acebes P (2017) Controlling eutrophication in a Mediterranean shallow reservoir by phosphorus loading reduction: the need for an integrated management approach. Environ Manag 59:635–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0815-y
Zhang P, Wang R, Ju Q, Li W, Tran L-SP XJ (2019) The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB49 regulates cadmium accumulation. Plant Physiol 180:529–542. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01380
Zhao H, Wang L, Zhao FJ, Wu L, Liu A, Xu W (2019) SpHMA1 is a chloroplast cadmium exporter protecting photochemical reactions in the Cd hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. Plant Cell Environ 42:1112–1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13456
Zhuang P, McBride MB, Xia HP, Li NY, Lia ZA (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 407:1551–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.061
Zou JH, Wang G, Ji J, Wang JY, Wu HF, Ou YJ, Li BB (2017) Transcriptional, physiological and cytological analysis validated the roles of some key genes linked Cd stress in Salix matsudana Koidz. Environ Exp Bot 134:116–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.11.005
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Amanda Gallinat at the Boston University for her assistance with English language and grammatical editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2016YFD0600204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31870598, 31560205 and 31670624), the Innovation Platform Open Fund Project for Universities of Hunan Province (No. 18K080), the Open Fund Project of Hunan Key Laboratory of Ecotourism (No. STLV19012), the Sanxin Forestry Project in Jiangsu Province (No. LYSX[2016]46), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31530007), and the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (No. 2018063), the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2012ZX07204-004-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 349 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, X., Zhao, Y., Tian, K. et al. Insight into nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on cadmium phytoextraction of hydroponically grown Salix matsudana Koidz cuttings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 8406–8417 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07499-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07499-4