Abstract
This study explores the interaction among coal consumption, pollutant emissions, and real income for South Africa in a multivariate setting. To achieve this objective, annual frequency data spanning from 1965 to 2017 is used for analysis. A series of econometrics tests were conducted ranging from stationarity and non-stationarity tests for unit root properties of the variables under consideration. Empirical evidence finds support for the inverted U-shaped pattern between energy consumption and environmental degradation in South Africa. The Toda-Yamamoto Granger causality test shows a feedback causality between economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions, as well as between GDP and coal consumption. All these highlighted findings have inherent environmental implications. Based on these outcomes, policy directions such as diversification of the South Africa energy mix to renewables and cleaner energy sources and also the adoption of carbon capturing and storage techniques were suggested to engender a cleaner and friendlier environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
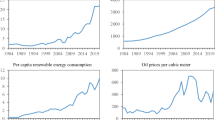
The data span is selected based on data availability.
This study is also conducted the ARDL Bounds testing for robustness check. The result is consistent with Maki cointegration results. See Appendix for the ARDL Bounds test results.
References
Abuoliem N, Nor SM, Matar A, Hallahan T (2019) Crude oil prices, macroeconomic indicators and the financial sector in Jordan: dynamic causes and responses. J Int Stud 12(3):131–146
Al-mulali U, Che Sab CNB (2018) The impact of coal consumption and CO2 emission on economic growth. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 13(4):218–223
Amiri A, Ventelou B (2012) Granger causality between total expenditure on health and GDP in OECD: evidence from the Toda-Yamamoto approach. Econ Lett 116(3):541–544
Amuakwa-Mensah F, Adom PK (2017) Quality of institution and the FEG (forest, energy intensity, and globalization) – environment relationships in sub-Saharan Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(21):17455–17473
Balcilar M, Ozdemir ZA, Arslanturk Y (2010) Economic growth and energy consumption causal nexus viewed through a bootstrap rolling window. Energy Econ 32(6):1398–1410
Balcilar M, Bekun FV, Uzuner G (2019) Revisiting the economic growth and electricity consumption nexus in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):12158–12170
Beg N, Morlot JC, Davidson O, Afrane-Okesse Y, Tyani L, Denton F, Parikh K (2002) Linkages between climate change and sustainable development. Clim Pol 2(2–3):129–144
Bekhet HA, Matar A, Yasmin T (2017) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development in GCC countries: dynamic simultaneous equation models. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:117–132
Bekun FV, Emir F, Sarkodie SA (2019a) Another look at the relationship between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in South Africa. Sci Total Environ 655:759–765
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019b) Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S, Ozturk I (2015) The role of renewable energy consumption and trade: environmental Kuznets curve analysis for sub-Saharan Africa countries. Afr Dev Rev 27(3):288–300
Bildirici ME, Bakirtas T (2014) The relationship among oil, natural gas and coal consumption and economic growth in BRICTS (Brazil, Russian, India, China, Turkey and South Africa) countries. Energy 65:134–144
Caraiani C, Lungu CI, Dascălu C (2015) Energy consumption and GDP causality: a three-step analysis for emerging European countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:198–210
Department of Minerals and Energy (DEM) (2016) Digest of South African Energy Statistics. Republic of South Africa Available at https://unstats.un.org/oslogroup/meetings/og-06/docs/6th%20mtg%20DAY_3_Paper_Energy_Accounts_Statistics_South_Africa.pdf (Access date 15.02.2019)
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74:427–431
Elliott G, Rothenberg TJ, Stock JH (1996) Efficient tests for an autoregressive unit root. Econometrica 64:813–836
Emir F, Bekun FV (2019) Energy intensity, carbon emissions, renewable energy, and economic growth nexus: new insights from Romania. Energy & Environment 30(3):427–443
Energy Information Administration (EIA) (2018) Annual Energy Outlook 2019 (access date 04.03.2019)
Engle RF, Granger CWJ (1987) Co-integration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica 55:251–276
Farhani S, Shahbaz M, Ozturk I (2014) Coal consumption, industrial production and CO2 emissions in China and India. Department of Research – Ipag Business School Working Papers:2014–2225
Fatai K, Oxley L, Scrimgeour FG (2004) Modelling the causal relationship between energy consumption and GDP in New Zealand, Australia, India, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand. Math Comput Simul 64:431–445
Ferguson CD (2007) Nuclear energy: balancing benefits and risks. Council of Foreign Relations 28
Gnansounou E (2008) Assessing the energy vulnerability: the case of industrial countries. Energy Policy 36:3734–3744
Gong B, Zheng X, Guo Q, Ordieres-Meré J (2019) Discovering the patterns of energy consumption, GDP, and CO2 emissions in China using the cluster method. Energy 166:1149–1167
Gregory AW, Hansen BE (1996) Residual-based tests for cointegration in models with regime shifts. J Econ 70(1):99–126
Gregory AW, Nason JM, Watt DG (1996) Testing for structural breaks in cointegrated relationships. J Econ 71(1–2):321–341
Hao Y, Liu Y, Weng JH, Gao Y (2016) Does the environmental Kuznets curve for coal consumption in China exist? New evidence from spatial econometric analysis. Energy 114:1214–1223
International Energy Agency (IEA) (2017) World energy outlook (access date 10.03.2019)
Jinke L, Hualing S, Dianming G (2008) Causality relationship between coal consumption and GDP: difference of major OECD and non-OECD countries. Appl Energy 85:421–429
Johansen S (1991) Estimation and hypothesis testing of cointegration vectors in Gaussian vector autoregressive models. Econometrica:1551–1580
Johansen S, Juselius K (1990) Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration – with applications to the demand for money. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 52(2):169–210
Kapetanios G, Shin Y (2008) GLS detrending-based unit root tests in nonlinear STAR and SETAR models. Econ Lett 100:377–380
Kapetanios G, Shin Y, Snell A (2003) Testing for a unit root in the nonlinear STAR framework. J Econ 112:359–379
Khobai H, Le Roux P (2017) The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon dioxide emission: the case of South Africa. Int J Energy Econ Policy 7(3):102–109
Kim HM, Yoo SH (2016) Coal consumption and economic growth in Indonesia. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 11(6):547–552
Kohler M (2013) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade: a south African perspective. Energy Policy 63:1042–1050
Kurniawan R, Managi S (2018) Coal consumption, urbanization, and trade openness linkage in Indonesia. Energy Policy 121:576–583
Kwiatkowski D, Phillips PC, Schmidt P, Shin Y (1992) Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: how sure are we that economic time series have a unit root? J Econ 54(1–3):159–178
Lee CC, Chang CP (2005) Structural breaks, energy consumption and economic growth revisited: evidence from Taiwan. Energy Econ 27:857–872
Leybourne SJ (1995) Testing for unit roots using forward and reverse Dickey-Fuller regressions. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 57:559–571
Li R, Leung GCK (2012) Coal consumption and economic growth in China. Energy Policy 40:438–443
Li J, Song H, Geng D (2008) Causality relationship between coal consumption and GDP: difference of major OECD and non-OECD countries. Appl Energy 85:421–429
Lin FL, Inglesi-Lotz R, Chang T (2018) Revisit coal consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth nexus in China and India using a newly developed bootstrap ARDL bound test. Energy Explor Exploit 36(3):450–463
Magazzino C (2016a) The relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Italy. Int J Sustain Energy 35(9):844–857
Magazzino C (2016b) The relationship between real GDP, CO2 emissions and energy use in the GCC countries: a time-series approach. Cogent Econ Finance 4:1
Magazzino C (2017a) Stationarity of electricity series in MENA countries. Electr J 30(10):16–22
Magazzino C (2017b) The relationship among economic growth, CO2 emissions, and energy use in the APEC countries: a panel VAR approach. Environment Systems and Decisions 37(3):353–366
Magazzino C (2019) Testing the stationarity and convergence of CO2 emissions series in MENA countries. International Journal of Energy Sector Management 13(4):977–990
Magazzino C, Cerulli G (2019) The determinants of CO2 emissions in MENA countries: a responsiveness scores approach. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology 26(6):522–534
Maki D (2012) Tests for cointegration allowing for an unknown number of breaks. Econ Model 29(5):2011–2015
Mapapu B, Phiri A (2018) Carbon emissions and economic growth in South Africa: a quantile regression analysis. Int J Energy Econ Policy 8(1):195–202
Matar A, Bekhet HA (2015) Causal interaction among electricity consumption, financial development, exports and economic growth in Jordan: dynamic simultaneous equation models. Int J Energy Econ Policy 5(4):955–967
Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010) Energy consumption, pollutant emissions and economic growth in South Africa. Energy Econ 32:1374–1382
Mohiuddin O, Asumadu-Sarkodie S, Obaidullah M (2016) The relationship between carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, and GDP: a recent evidence from Pakistan. Cogent Engineering 3(1):1210491
Nasiru I (2012) Coal consumption and economic growth in Nigeria: a two-step residual-based test approach to cointegration. Eur Sci J 8(9):140–155
Nathaniel S, Nwodo O, Adediran A, Sharma G, Shah M, Adeleye N (2019) Ecological footprint, urbanization, and energy consumption in South Africa: including the excluded. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27168–27179
Odhiambo NM (2009) Electricity consumption and economic growth in South Africa: a trivariate causality test. Energy Econ 31(5):635–640
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith R (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Phillips PC, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 75(2):335–346
Ratshomo K, Nembahe R (2018) South African energy sector report. Department of Energy – Republic of South Africa, November
Raza MY, Shah MTS (2019) Analysis of coal-related energy consumption in Pakistan: an alternative energy resource to fuel economic development. Environment, Development and Sustainability, pp 1–22
Reynolds DB, Kolodziej M (2008) Former Soviet Union oil production and GDP decline: Granger-causality and the multi-cycle Hubert curve. Energy Econ 30:271–289
Saint Akadiri S, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Contemporaneous interaction between energy consumption, economic growth and environmental sustainability in South Africa: what drives what? Sci Total Environ 686:468–475
Shafiee S, Topal E (2008) An econometric view of worldwide fossil fuel consumption and the role of US. Energy Policy 36:775–786
Shahbaz M, Sinha A (2019) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a literature survey. J Econ Stud 46(1):106–168
Shahbaz M, Tiwari A, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shahbaz M, Mahalik MK, Shah SH, Sato JR (2016) Time-varying analysis of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth nexus: statistical experience in next 11 countries. Energy Policy 98:33–48
Soytas U, Sari R (2006) Energy consumption and income in G-7 countries. J Policy Model 28(7):739–750
Tang CF, Tan EC (2013) Exploring the nexus of electricity consumption, economic growth, energy prices and technology innovation in Malaysia. Appl Energy 104:297–305
Toda HY, Yamamoto T (1995) Statistical inference in vector autoregressions with possibly integrated processes. J Econ 66(1–2):225–250
Toth FL, Rogner HH (2006) Oil and nuclear power: past, present, and future. Energy Economy 28:1–25
WDI (2019) World Bank Development Indicator. https://data.worldbank.org/ (access date March, 2019)
Winkler H (2007) Long term mitigation scenarios technical report. Available at https://www.africaportal.org/documents/9813/07-Winkler-LTMS-Technical_Report.pdf (access date 15.02.2019)
Wolde-Rufael Y (2004) Disaggregated industrial energy consumption and GDP: the case of Shanghai, 1952–1999. Energy Econ 26:69–75
Wolde-Rufael Y (2010) Coal consumption and economic growth revisited. Appl Energy 87:160–167
World Coal Association (WCA) (2019) Available at https://www.worldcoal.org/coal (access data 08.03.2019)
Yang HY (2000) Coal consumption and economic growth in Taiwan. Energy Sources 22(2):109–115
Yoo SH (2006) Causal relationship between coal consumption and economic growth in Korea. Appl Energy 83:1181–1189
Yuan JH, Kang JG, Zhao CH, Hu ZG (2008) Energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from China at both aggregated and disaggregated levels. Energy Econ 30:3077–3094
Zhang M, Bai C, Zhou M (2018) Decomposition analysis for assessing the progress in decoupling relationship between coal consumption and economic growth in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:454–462
Zhou G, Chau KW (2006) Short and long-run effects between oil consumption and economic growth in China. Energy Policy 34:3644–3655
Ziramba E (2009) Disaggregate energy consumption and industrial production in South Africa. Energy Policy 37(6):2214–2220
Zivot E, Andrews D (1992) Further evidence on the great crash, the oil price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J Bus Econ Stat 10:251–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Muhammad Shahbaz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magazzino, C., Bekun, F.V., Etokakpan, M.U. et al. Modeling the dynamic Nexus among coal consumption, pollutant emissions and real income: empirical evidence from South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 8772–8782 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07345-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07345-7