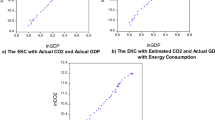
Abstract
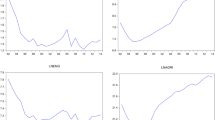
This study investigates the long-run equilibrium relationship among carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, real income, energy consumption, and agriculture, thus testing the existence of the agriculture-induced environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in the case of China for the period of 1971–2014. The level relationship among the variables in the conducted model is confirmed by the bounds test approach under the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) mechanism. Error correction model under the ARDL mechanism suggests that short-run values of CO2 emissions converge to its long-run equilibrium level by 73.8% speed of adjustment every year by the contribution of energy consumption, real income, and agriculture. ARDL estimation results suggest that real income and energy consumption have a positive, elastic impact; agricultural development has positive, inelastic impact on CO2 emissions where squared real income has a negative and inelastic impact on air pollution. Conditional Granger causality test results reveal that there are unidirectional causalities running from real income, squared real income, energy consumption, and agricultural development in long run as well as in the short run.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mulali U, Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) Investigating the presence of the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in Kenya: an autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach. Nat Hazards 80(3):1729–1747
Amri F (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions, total factor productivity, ICT, trade, financial development, and energy consumption: testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Apergis N, Payne JE (2009) CO2 emissions, energy usage, and output in Central America. Energy Policy 37(8):3282–3286
Asumadu-Sarkodie S, Owusu PA (2017) The causal nexus between carbon dioxide emissions and agricultural ecosystem -an econometric approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(2):1608–1618
Baek J, Pride D (2014) On the income–nuclear energy–CO2 emissions nexus revisited. Energy Econ 43:6–10
Balaguer J, Cantavella M (2016) Estimating the environmental Kuznets curve for Spain by considering fuel oil prices (1874–2011). Ecol Indic 60:853–859
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2017a) Renewable energy consumption and agriculture: evidence for cointegration and Granger causality for Tunisian economy. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 24(2):149–158
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2017b) The role of renewable energy and agriculture in reducing CO2 emissions: evidence for North Africa countries. Ecol Indic 74:295–301
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2017c) Renewable energy, arable land, agriculture, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in Morocco (No. 76798). University Library of Munich, Munich
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2019) Combustible renewables and waste consumption, agriculture, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in Brazil. Carbon Manag 10(3):309–321
Bhatia A, Jain N, Pathak H (2013) Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from Indian rice paddies, agricultural soils and crop residue burning. Greenh Gases Sci Technol 3(3):196–211
BP statistical review of world energy, Retrieved November 07, 2018, from https://www.bp.com
BP (2014). BP statistical review of world energy. http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2014/ph240/milic1/docs/bpreview.pdf
Brown RL, Durbin J, Evans JM (1975) Techniques for testing the constancy of regression relationships over time. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol:149–192
Chakravarty D, Mandal SK (2016) Estimating the relationship between economic growth and environmental quality for the BRICS economies-a dynamic panel data approach. J Dev Areas 50(5):119–130
Coderoni S, Esposti R (2011) Long-term agricultural GHG emissions and economic growth: the agricultural environmental Kuznets Curve across Italian regions. In 2011 International Congress, August 30-September 2, 2011, Zurich, Switzerland (No. 114426). European Association of Agricultural Economists.
Cole CV, Duxbury J, Freney J, Heinemeyer O, Minami K, Mosier A et al (1997) Global estimates of potential mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions by agriculture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 49(1-3):221–228
De Vita G, Katircioglu S, Altinay L, Fethi S, Mercan M (2015) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in a tourism development context. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(21):16652–16663
Dijkgraaf E, Vollebergh HR (2005) A test for parameter homogeneity in CO2 panel EKC estimations. Environ Resour Econ 32(2):229–239
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization, and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213
Dong B, Wang F, Guo Y (2016) The global EKCs. Int Rev Econ Financ 43:210–221
Dong K, Sun R, Li H, Liao H (2018) Does natural gas consumption mitigate CO2 emissions: testing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for 14 Asia-Pacific countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 94:419–429
Duong T, Hultberg PT (2018) Trade openness, economic growth, and environmental degradation in Asian developing countries. J Appl Bus Econ 20(5):1–10
Garnier J, Le Noë J, Marescaux A, Sanz-Cobena A, Lassaletta L, Silvestre M et al (2019) Long-term changes in greenhouse gas emissions from French agriculture and livestock (1852–2014): From traditional agriculture to conventional intensive systems. Sci Total Environ 660:1486–1501
Gill AR, Viswanathan KK, Hassan S (2017) Is environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) still relevant? Int J Energy Econ Policy 7(1):156–165
Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N (2018) Testing the agriculture-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):1–13
Grossman GM (1995) Pollution and growth: what do we know? Econ Sustain Dev 19:19–46
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement (No. w3914). National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge
Han M, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Guan C (2019) Agricultural CH4 and N2O emissions of major economies: consumption-vs. production-based perspectives. J Clean Prod 210:276–286
Haseeb A, Xia E, Baloch MA, Abbas K (2018) Financial development, globalization, and CO2 emission in the presence of EKC: Evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(31):1–14
He Z, Shi X, Wang X, Xu Y (2017) Urbanisation and the geographic concentration of industrial SO2 emissions in China. Urban Stud 54(15):3579–3596
Hervieux MS, Darné O (2016) Production and consumption-based approaches for the environmental Kuznets curve using ecological footprint. J Environ Econ Policy 5(3):318–334
Hettige H, Mani M, Wheeler D (2000) Industrial pollution in economic development: the environmental Kuznets curve revisited. J Dev Econ 62(2):445–476
Horry HR, Jalaee SA, Jafari S (2013) Examining the impact of financial development and energy consumption on the environmental degradation in Iran in the framework of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis (EKC). Iran Energy Econ 2(6):27–48
Im KS, Pesaran MH, & Shin Y (2003). Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. Journal of Econometrics, 115(1), 53-74.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [IPCC] (2013). Climate Change 2013 The Physical Science Basis. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/WG1AR5_SummaryVolume_FINAL.pdf
International Energy Agency (2016). CO2 Emissions Statistics. https://www.iea.org/statistics/co2emissions/
International Monetary Funds, Retrieved November 07, 2018, from https://www.imf.org
Jaforullah M, King A (2017) The econometric consequences of an energy consumption variable in a model of CO2 emissions. Energy Econ 63:84–91
Jalil A, Feridun M (2011) The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: a cointegration analysis. Energy Econ 33(2):284–291
Janzen HH (2004) Carbon cycling in earth systems—a soil science perspective. Agric Ecosyst Environ 104(3):399–417
Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2015) The environmental Kuznets curve, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy, and trade in Tunisia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:173–185
Jebli MB, Youssef SB, Ozturk I (2016) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Indic 60:824–831
Katircioğlu ST (2014) Testing the tourism-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Singapore. Econ Model 41:383–391
Katircioğlu ST, Taşpinar N (2017) Testing the moderating role of financial development in an environmental Kuznets curve: empirical evidence from Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:572–586
Khan MTI, Ali Q, Ashfaq M (2018) The nexus between greenhouse gas emission, electricity production, renewable energy, and agriculture in Pakistan. Renew Energy 118:437–451
Kuznets S (1955) Economic growth and income inequality. Am Econ Rev 45(1):1–28
Kwiatkowski, D., Phillips, P. C., Schmidt, P., & Shin, Y. (1992). Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: How sure are we that economic time series have a unit root?. Journal of Econometrics, 54(1-3), 159-178.
Levin, A., Lin, C. F., & Chu, C. S. J. (2002). Unit root tests in panel data: Asymptotic and finite-sample properties. Journal of Econometrics, 108(1), 1-24.
Li Y, Barton L, Chen D (2012) Simulating response of N2O emissions to fertiliser N application and climatic variability from a rain-fed and wheat-cropped soil in Western Australia. J Sci Food Agric 92(5):1130–1143
Li K, An X, Park KH, Khraisheh M, Tang J (2014) A critical review of CO2 photoconversion: catalysts and reactors. Catal Today 224:3–12
Li T, Wang Y, Zhao D (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve in China: new evidence from dynamic panel analysis. Energy Policy 91:138–147
Lin B, Xu B (2018) Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China's agriculture sector: A quantile regression. Renew Sust Energ Rev 94:15–27
Liu X, Zhang S, Bae J (2017a) The impact of renewable energy and agriculture on carbon dioxide emissions: investigating the environmental Kuznets curve in four selected ASEAN countries. J Clean Prod 164:1239–1247
Liu X, Zhang S, Bae J (2017b) The nexus of renewable energy-agriculture-environment in BRICS. Appl Energy 204:489–496
Managi S (2006) Are there increasing returns to pollution abatement? Empirical analytics of the Environmental Kuznets Curve in pesticides. Ecol Econ 58(3):617–636
Mazzanti M, Montini A, Zoboli R (2008) Environmental Kuznets curves for air pollutant emissions in Italy: evidence from environmental accounts (NAMEA) panel data. Econ Syst Res 20(3):277–301
Miah MD, Masum MFH, Koike M (2010) Global observation of EKC hypothesis for CO2, SOx and NOx emission: a policy understanding for climate change mitigation in Bangladesh. Energy Policy 38(8):4643–4651
Moghadam HE, Dehbashi V (2018) The impact of financial development and trade on environmental quality in Iran. Empir Econ 54(4):1777–1799
Mohamad RS, Verrastro V, Al Bitar L, Roma R, Moretti M, Al Chami Z (2016) Effect of different agricultural practices on carbon emission and carbon stock in organic and conventional olive systems. Soil Res 54(2):173–181
Munir K, Ameer A (2018) Effect of economic growth, trade openness, urbanization, and technology on environment of Asian emerging economies. Manag Environ Qual 29(6):1123–1134
Narayan PK (2005) The saving and investment nexus for China: evidence from cointegration tests. Appl Econ 37(17):1979–1990
Narayan PK, Smyth R (2004) Crime rates, male youth unemployment and real income in Australia: evidence from Granger causality tests. Appl Econ 36(18):2079–2095
National bureau of statistics of China, Retrieved November 07, 2018, from http://www.stats.gov.cn
National Development and Reform Commission [NDRC] (2007). China's Energy Conditions and Policies. http://en.ndrc.gov.cn/policyrelease/200712/P020071227502260511798.pdf
Ozatac N, Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N (2017) Testing the EKC hypothesis by considering trade openness, urbanization, and financial development: the case of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(20):16690–16701
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2015) Investigating the validity of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Cambodia. Ecol Indic 57:324–330
Peng SJ, Bao Q (2006) Economic growth and environmental pollution: an empirical test for the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in China [J]. Res Financ Econ Issues 8(273):3–17
Perron P (1990) Testing for a unit root in a time series with a changing mean. J Bus Econ Stat 8(2):153–162
Pesaran MH, Pesaran B (1997) Working with Microfit 4.0: interactive econometric analysis;[Windows version]. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Phillips, P. C., & Perron, P. (1988). Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika, 75(2), 335-346.
Plassmann F, Khanna N (2006) Household income and pollution: implications for the debate about the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. J Environ Dev 15(1):22–41
Qiao H, Zheng F, Jiang H, Dong K (2019) The greenhouse effect of the agriculture-economic growth-renewable energy nexus: evidence from G20 countries. Sci Total Environ 671:722–731
Raeeni AAG, Hosseini S, Moghaddasi R (2019) How energy consumption is related to agricultural growth and export: an econometric analysis on Iranian data. Energy Rep 5:50–53
Raggad B (2018) Statistical assessment of changes in extreme maximum temperatures over Saudi Arabia, 1985–2014. Theor Appl Climatol 132(3-4):1217–1235
Regina K, Heikkinen J, Maljanen M (2019) Greenhouse gas fluxes of agricultural soils in Finland. In: Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Springer, Singapore, pp 7–22
Rehman MU, Rashid M (2017) Energy consumption to environmental degradation, the growth appetite in SAARC nations. Renew Energy 111:284–294
Sapkota P, Bastola U (2017) Foreign direct investment, income, and environmental pollution in developing countries: panel data analysis of Latin America. Energy Econ 64:206–212
Saravia-Matus SL, Hörmann PA, Berdegué JA (2019) Environmental efficiency in the agricultural sector of Latin America and the Caribbean 1990–2015: are greenhouse gas emissions reducing while agricultural production is increasing? Ecol Indic 102:338–348
Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S (1992) Economic growth and environmental quality: Time-series and cross-country evidence, vol 904. World Bank Publications
Shahbaz M, Sinha A (2018) Environmental Kuznets Curve for CO2 Emission: A Literature Survey (No. 86281). University Library of Munich, Munich
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018a) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New Threshold Analysis. Environ Model Assess 23(5):557–568
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK, Hammoudeh S (2018b) Does globalisation worsen environmental quality in developed economies? Environ Model Assess 23(2):141–156
Sinha A, Bhatt MY (2017) Environmental Kuznets Curve for CO2and NOx emissions: a case study of India. Eur J Sustain Dev 6(1):267–276
Sinha A, Sen S (2016) Atmospheric consequences of trade and human development: a case of BRIC countries. Atmos Pollut Res 7(6):980–989
Smith P (2004) Carbon sequestration in croplands: the potential in Europe and the global context. Eur J Agron 20(3):229–236
Tabar IB, Keyhani A, Rafiee S (2010) Energy balance in Iran’s agronomy (1990–2006). Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(2):849–855
Tang CF, Tan BW (2015) The impact of energy consumption, income and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 79:447–454
Tapio P (2005) Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transport Policy 12 (2):137-151
The World Bank (2017). World Development Indicators. https://wdi.worldbank.org
Tubiello FN, Salvatore M, Ferrara AF, House J, Federici S, Rossi S et al (2015) The contribution of agriculture, forestry and other land use activities to global warming, 1990–2012. Glob Chang Biol 21(7):2655–2660
Tutulmaz O (2015) Environmental Kuznets curve time series application for Turkey: why controversial results exist for similar models? Renew Sust Energ Rev 50:73–81
Wagner M (2008) The carbon Kuznets curve: a cloudy picture emitted by bad econometrics? Resour Energy Econ 30(3):388–408
Waheed R, Chang D, Sarwar S, Chen W (2018) Forest, agriculture, renewable energy, and CO2 emission. J Clean Prod 172:4231–4238
Wang S, Yang F, Wang XE, Song J (2017) A microeconomics explanation of the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) and an empirical investigation. Pol J Environ Stud 26(4):1757–1764
World Bank, Retrieved November 07, 2018, from https://www.worldbank.org
World economic outlook, Retrieved November 07, 2018, from https://www.imf.org
Wu JG, Cui YS, Shao HL (2013) The analysis on impact of the input of agricultural film material to the sustainable development of vegetable industry of Hebei-based on the environmental kuznets curve. Appl Mech Mater 320:774–779
Xu B, Lin B (2017) Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: evidence from geographically weighted regression model. Energy Policy 104:404–414
Yang X, Wang S, Zhang W, Li J, Zou Y (2016) Impacts of energy consumption, energy structure, and treatment technology on SO2 emissions: a multi-scale LMDI decomposition analysis in China. Appl Energy 184:714–726
You W, Lv Z (2018) Spillover effects of economic globalization on CO2 emissions: a spatial panel approach. Energy Econ 73:248–257
Zafeiriou E, Azam M (2017) CO2 emissions and economic performance in EU agriculture: some evidence from Mediterranean countries. Ecol Indic 81:104–114
Zaman K, Shahbaz M, Loganathan N, Raza SA (2016) Tourism development, energy consumption, and environmental Kuznets curve: trivariate analysis in the panel of developed and developing countries. Tour Manag 54:275–283
Zambrano-Monserrate MA, Fernandez MA (2017) An environmental Kuznets curve for N2O emissions in Germany: an ARDL approach. Nat Res Forum 41(2):119–127
Zhang S (2018) Is trade openness good for environment in South Korea? The role of non-fossil electricity consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Zhang L, Gao J (2016) Exploring the effects of international tourism on China’s economic growth, energy consumption and environmental pollution: evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 53:225–234
Zhang T, Wooster MJ, Green DC, Main B (2015) New field-based agricultural biomass burning trace gas, PM2.5, and black carbon emission ratios and factors measured in situ at crop residue fires in Eastern China. Atmos Environ 121:22–34
Zhang S, Liu X, Bae J (2017) Does trade openness affect CO2 emissions: evidence from ten newly industrialized countries? Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(21):17616–17625
Zhang L, Pang J, Chen X, Lu Z (2019) Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from the agricultural sector of China's main grain-producing areas. Sci Total Environ 665:1017–1025
Zhangwei L, Xungangb Z (2011) Study on relationship between Sichuan agricultural carbon dioxide emissions and agricultural economic growth. Energy Procedia 5:1073–1077
Zhao Z, Qin W, Bai Z, Ma L (2019) Agricultural nitrogen and phosphorus emissions to water and their mitigation options in the Haihe Basin, China. Agric Water Manag 212:262–272
Zivot E, Andrews DW (1992) Further evidence on the Great Crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J Bus Econ Stat 10(3):251–270
Zoundi Z (2017) CO2 emissions, renewable energy and the environmental Kuznets curve, a panel cointegration approach. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:1067–1075
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokmenoglu, K.K., Taspinar, N. & Kaakeh, M. Agriculture-induced environmental Kuznets curve: the case of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 37137–37151 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06685-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06685-8