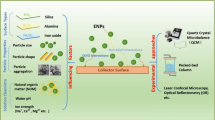
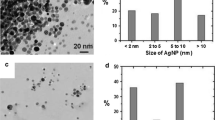
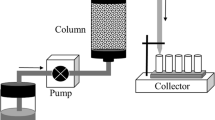
Abstract
The stability of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) stabilized electrostatically with citrate or (electro)sterically by commercially available amphiphilic block copolymers (PVP-VA or PVA-COOH) was studied under various physicochemical conditions. Subsequently, the mobility of the AuNPs in porous media (sand) was investigated in column studies under environmental relevant physicochemical conditions. Electrostatically stabilized AuNPs were unstable under most physicochemical conditions due to the compression of the electrical double layer. Consequently, aggregation and deposition rapidly immobilized the AuNPs. Sterically stabilized AuNPs showed significantly less sensitivity towards changes in the physicochemical conditions with high stability, high mobility with negligible retardation, and particle deposition rate coefficients ranging an order of magnitude (1.5 × 10−3 to 1.5 × 10−2 min−1) depending on the type and amount of stabilizer, and thereby the surface coverage and attachment affinity. The transport of sterically stabilized AuNPs is facilitated by reversible deposition in shallow energy minima with continuous reentrainment and blocking of available attachment sites by deposited AuNPs. The stability and mobility of NPs in the environment will thereby be highly dependent on the specific stabilizing agent and variations in the coverage on the NP. Under the given experimental conditions, transport distances of the most mobile AuNPs of up to 20 m is expected. Due to their size-specific plasmonic properties, the easily detectable AuNPs are proposed as potential model or tracer particles for studying transport of various stabilized NPs under environmental conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaighe N, Depner SW, Banerjee S, Sharma VK, Sohn M (2012) The effects of monovalent and divalent cations on the stability of silver nanoparticles formed from direct reduction of silver ions by Suwannee River humic acid/natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 441:277–289
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Baalousha M, Cornelis G, Kuhlbusch TAJ, Lynch I, Nickel C, Peijnenburg W, van den Brink NW (2016) Modeling nanomaterial fate and uptake in the environment: current knowledge and future trends. Environ Sci: Nano 3:323–345
Becker MD, Wang Y, Pennell KD, Abriola LM (2015) A multi-constituent site blocking model for nanoparticle and stabilizing agent transport in porous media. Environ Sci: Nano 2:155–166
Bijeljic B, Rubin S, Scher H, Berkowitz B (2011) Non-Fickian transport in porous media with bimodal structural heterogeneity. J Contam Hydrol 120-121:213–221
Cao G (2004) Nanostructures & nanomaterials. In: Synthesis, properties & applications. Imperial College Press, London
Chan MY, Vikesland PJ (2014) Porous media-induced aggregation of protein-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 48(3):1532–1540
Chen JY, Ko C-H, Bhattacharjee S, Elimelech M (2001) Role of spatial distribution of porous medium surface charge heterogeneity in colloid transport. Colloid Surface A 191:3–15
Chrysikopoulos CV, Katzourakis VE (2015) Colloid particle size-dependent dispersivity. Water Resour Res 51:4668–4683
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
El Hadri H, Louie SM, Hackley VA (2018) Assessing the interactions of metal nanoparticles in soil and sediment matrices – a quantitative analytical multi-technique approach. Environ Sci: Nano 5:203–214
Elimelech M, Gregory J, Jia X, Williams RA (1995) Particle deposition and aggregation: measurement, modelling and simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd:290–309
Franchi A, O’Melia CR (2003) Effects of natural organic matter and solution chemistry on the deposition and reentrainment of colloids in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 37(6):1122–1129
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn RL, Baveye PC (2009) Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43:1354–1359
Fritz G, Schädler V, Willenbacher N, Wagner NJ (2002) Electrosteric stabilization of colloidal dispersions. Langmuir 18(16):6381–6390
Gottschalk F, Sun TY, Nowack B (2013) Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ Pollut 181:287–300
Grolimund D, Elimelech M, Borkovec M, Barmettler K, Kretzschmar R, Sticher H (1998) Transport of in situ mobilized colloidal particles in packed soil columns. Environ Sci Technol 32(22):3562–3569
Hahn MW, Abadzic D, O’Melia CR (2004) Aquasols: on the role of secondary minima. Environ Sci Technol 38(22):5915–5924
Haiss W, Thanh NTK, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221
Han Y, Kim D, Hwang G, Lee B, Eom I, Kim PJ, Tong M, Kim H (2014) Aggregation and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by different methods: influence of ionic strength and humic acid. Colloid Surface A 451:7–15
Harvey RW, Garabedian SP (1991) Use of colloid filtration theory in modeling movement of bacteria through a contaminated sandy aquifer. Environ Sci Technol 25(1):178–185
Hogg R, Healy TW, Fuerstekau DW (1966) Mutual coagulation of colloidal dispersions. T Faraday Soc 62:1638–1651
Hurtado RB, Calderon-Ayala G, Cortez-Valadez M, Ramírez-Rodríguez LP, Flores-Acosta M (2017) Green synthesis of metallic and carbon nanostructures. Nanomechanics, InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.68483
Hwang G, Gomez-Flores A, Bradford SA, Choi S, Jo E, Kim SB, Tong M, Kim H (2018) Analysis of stability behavior of carbon black nanoparticles in ecotoxicological media: hydrophobic and steric effects. Colloid Surface A 554:306–316
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110:7238–7248
Johnson RL, Johnson GO, Nurmi JT, Tratnyek PG (2009) Natural organic matter enhanced mobility of nano zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 43(14):5455–5460
Kamrani S, Rezaei M, Kord M, Baalousha M (2018) Transport and retention of carbon dots (CDs) in saturated and unsaturated porous media: role of ionic strength, pH, and collector grain size. Water Res 133:338–347
Kasel D, Bradford SA, Šimůnek J, Heggen M, Vereecken H, Klumpp E (2013) Transport and retention of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in saturated porous media: effects of input concentration and grain size. Water Res 47:933–944
Keller AA, Lazareva A (2014) Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: from global to regional to local. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:65–70
Kim C, Lee J, Lee S (2015) TiO2 nanoparticle sorption to sand in the presence of natural organic matter. Environ Earth Sci 73:5585–5591
Koczkur KM, Mourdikoudis S, Polavarapu L, Skrabalak SE (2015) Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Trans 44:17883
Kumar N, Labille J, Bossa N, Auffan M, Doumenq P, Rose J, Bottero J-Y (2017) Enhanced transportability of zero valent iron nanoparticles in aquifer sediments: surface modifications, reactivity, and particle traveling distances. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:9269–9277
Lee J-Y, Oh JY, Putri KY, Baik MH, Yun J-I (2017) Redox behaviors of Fe(II/III) and U(IV/VI) studied in synthetic water and KURT groundwater by potentiometry and spectroscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 312:221–231
Li C, Li D, Wan G, Xu J, Hou W (2011) Facile synthesis of concentrated gold nanoparticles with low size-distribution in water: temperature and pH controls. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:440
Li T, Jin Y, Huang Y, Li B, Shen C (2017) Observed Dependence of Colloid Detachment on the Concentration of Initially Attached Colloids and Collector Surface Heterogeneity in Porous Media. Environ Sci Technol 51:2811–2820
Louie SM, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2016) Critical review: impacts of macromolecular coatings on critical physicochemical processes controlling environmental fate of nanomaterials. Environ Sci.: Nano 3:283–310
Lu K (2008) Theoretical analysis of colloidal interaction energy in nanoparticle suspensions. Ceram Int 34:1353–1360
Marchon D, Mantellato S, Eberhardt AB, Flatt RJ (2016) Adsorption of chemical admixtures. In: Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures, pp 219–256
Metin CO, Lake LW, Miranda CR, Nguyen QP (2011) Stability of aqueous silica nanoparticle dispersions. J Nanopart Res 13:839–850
Molnar IL, Johnson WP, Gerhard JI, Willson CS, O’Carroll1, D.M. (2015) Predicting colloid transport through saturated porous media: a critical review. Water Resour Res 51:6804–6845
Montaño MD, Lowry GV, von der Kammer F, Blue J, Ranville JF (2014) Current status and future direction for examining engineered nanoparticles in natural systems. Environ Chem 11:351–366
Napper DH (1983) Polymeric stabilization of colloidal dispersions. Academic Press INC (London) Ltd, London
Pamies R, Cifre JGH, Espín VF, Collado-González M, Banõs FGD, de la Torre JG (2014) Aggregation behaviour of gold nanoparticles in saline aqueous media. J Nanopart Res 16:2376
Park J-A, Kim S-B (2015) DLVO and XDLVO calculations for bacteriophage MS2 adhesion to iron oxide particles. J Contam Hydrol 181:131–140
Park JW, Shumaker-Parry JS (2014) Structural study of citrate layers on gold nanoparticles: role of intermolecular interactions in stabilizing nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 136:1907–1921
Park CM, Heo Y, Her N, Chu KH, Jang M, Yoon Y (2016) Modeling the effects of surfactant, hardness, and natural organic matter on deposition and mobility of silver nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Water Res 103:38–47
Park CM, Chu KH, Her N, Jang M, Baalousha M, Heo J, Yoon Y (2017) Occurrence and removal of engineered nanoparticles in drinking water treatment and wastewater treatment processes. Sep Purif Rev 46:255–272
Pavlin M, Bregar VB (2012) Stability of nanoparticle suspensions in different biologically relevant media. Dig J Nanomater Bios 7(4):1389–1400
Peng C, Zhang W, Gao H, Li Y, Tong X, Li K, Zhu X, Wang Y, Chen Y (2017) Behavior and potential impacts of metal-based engineered nanoparticles in aquatic environments. Nanomaterials 7:21
Petosa AR, Öhl C, Rajput F, Tufenkji N (2013) Mobility of nanosized cerium dioxide and polymeric capsules in quartz and loamy sands saturated with model and natural groundwaters. Water Res 47:5889–5900
Pfeiffer C, Rehbock C, Hühn D, Carrillo-Carrion C, de Aberasturi DJ, Merk V, Barcikowski S, Parak WJ (2014) Interaction of colloidal nanoparticles with their local environment: the (ionic) nanoenvironment around nanoparticles is different from bulk and determines the physico-chemical properties of the nanoparticles. J R Soc Interface 11:20130931
Quik JTK, Vonk JA, Hansen SF, Baun A, Van De Meent D (2011) How to assess exposure of aquatic organisms to manufactured nanoparticles? Environ Int 37:1068–1077
Saberinasr A, Rezaei M, Nakhaei M, Hosseini SM (2016) Transport of CMC-stabilized nZVI in saturated sand column: the effect of particle concentration and soil grain size. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:394
Sagee O, Dror I, Berkowitz B (2012) Transport of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in soil. Chemosphere 88:670–675
Saleh N, Kim H-J, Phenrat P, Matyjaszewski K, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2008) Ionic strength and composition affect the mobility of surface-modified Fe0 nanoparticles in water-saturated sand columns. Environ Sci Technol 42:3349–3355
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW (2009) Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25:13840–13851
Schärtl W (2010) Current directions in core–shell nanoparticle design. Nanoscale 2:829–843
Smith BM, Pike DJ, Kelly MO, Nason JA (2015) Quantification of heteroaggregation between citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles and hematite colloids. Environ Sci Technol 49:12789–12797
Song JE, Phenrat T, Marinakos S, Xiao Y, Liu J, Wiesner MR, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2011) Hydrophobic interactions increase attachment of gum Arabic- and PVP-coated Ag nanoparticles to hydrophobic surfaces. Environ Sci Technol 45:5988–5995
Stuart MAC, Mulder JW (1985) Adsorbed polymers in aqueous media the relation between zeta potential, layer thickness and ionic strength. Colloid Surf 15:49–55
Sun P, Shijirbaatar A, Fang J, Owens G, Lin D, Zhang K (2015) Distinguishable transport behavior of zinc oxide nanoparticles in silica sand and soil columns. Sci Total Environ 505:189–198
Surette MC, Nason JA (2016) Effects of surface coating character and interactions with natural organic matter on the colloidal stability of gold nanoparticles. Environ Sci: Nano 3:1144–1152
Tadros TF (2007) Colloid stability: the role of surface forces, part I. Colloids and interface science series, vol 1. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, Weinheim
Tufenkji N, Elimelech M (2004) Correlation equation for predicting single-collector efficiency in physicochemical filtration in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Technol 38(2):529–536
van Genuchten MT (1981) Analytical solutions of the one-dimensional convective-dispersive solute transport equation. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Technical Bulletin No. 1661, 151 p.
van Oss CJ, Giese RF, Costanzo PM (1990) DLVO and non-DLVO interactions in hectorite. Clay Clay Miner 38(2):151–159
von der Kammer F, Ferguson PL, Holden PA, Masion A, Rogers KR, Klaine SJ, Koelmans AA, Horne N, Unrine JM (2012) Analysis of engineered nanamaterials in complex matrices (environment and biota): general considerations and conceptual case studies. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(1):32–49
Worthen AJ, Tran V, Cornell KA, Truskett TM, Johnston KP (2016) Steric stabilization of nanoparticles with grafted low molecular weight ligands in highly concentrated brines including divalent ions. Soft Matter 12:2025–2039
Xu X, Xu N, Cheng X, Guo P, Chen Z, Wang D (2017) Transport and aggregation of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media in the presence of ammonium. Chemosphere 169:9–17
Yang J, Xu P, Hu L, Zeng G, Chen A, He K, Huang Z, Yi H, Qin L, Wan J (2018) Effects of molecular weight fractionated humic acid on the transport and retention of quantum dots in porous media. Environ Sci: Nano 5:2699–2711
Yao Q, Luo Z, Yuan X, Yu Y, Zhang C, Xie J, Lee JY (2014) Assembly of nanoions via electrostatic interactions: ion-like behavior of charged noble metal nanoclusters. Sci Rep 4:3848
Yecheskel Y, Dror I, Berkowitz B (2018) Silver nanoparticle (Ag-NP) retention and release in partially saturated soil: column experiments and modelling. Environ Sci: Nano 5:422–435
Zamborini FP, Hicks JF, Murray RW (2000) Quantized double layer charging of nanoparticle films assembled using carboxylate/(Cu2+ or Zn2+)/carboxylate bridges. J Am Chem Soc 122:4514–4515
Zhou J, Ralston J, Sedev R, Beattie DA (2009) Functionalized gold nanoparticles: synthesis, structure and colloid stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:251–262
Zuber A, Purdey M, Schartner E, Forbes C, van der Hoek B, Giles D, Abell A, Monro T, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H (2016) Detection of gold nanoparticles with different sizes using absorption and fluorescence based method. Sensors Actuators B 227:117–127
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge B.Sc. Eva Caspersen for her contribution to the laboratory work.
Funding
This work was funded by the joint Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology and Technical University of Denmark (KAIST-DTU) signature project, INtegrated WAter Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 193 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fjordbøge, A.S., Uthuppu, B., Jakobsen, M.H. et al. Mobility of electrostatically and sterically stabilized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 29460–29472 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06132-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06132-8