Abstract
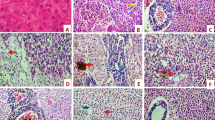
The present systematic experiment was conducted to estimate the impact of behavioral and pathological indices on freshwater fish Channa punctatus exposed to sub-lethal concentration (5 ppm) of an organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos (CPF). Fish were segregated into four experimental groups (G1, control; G2, 10 days; G3, 20 days; and G4, 30 days exposure), each group comprises 15 fish in triplicate. The behavioral and histological changes were assessed in each group. Severe behavioral changes were observed in the 30 days, moderate changes in the 20 days, and mild changes in the 10 days exposure groups respectively when compared with the control group. The pathologic lesions such as inter lamellae space, necrotic lamellae, fused lamellae, and lifting of lamellae epithelium in gills; vacuolation, blood conjunctions, and necrotic hepatocytes in the liver; and lamina propria, fusion of villi, and flattened villi in the intestine were observed. These structural alterations of the gills, liver, and intestine could affect respiration, osmotic and ionic regulation; absorption, storage and secretion; digestion; and absorption of nutrients respectively, which in turn could adversely affect the growth and survival of freshwater fish Channa punctatus. This study serves as a biomonitoring tool for the effects of organophosphorus insecticide CPF on the aquatic biota.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA [American Public Health Association] (1998) American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bartoskova M, Dobsikova R, Stancova V, Zivna D, Blahova J, Marsalek P, Zelníckova L, Bartos M, Di Tocco FC, Faggio C (2013) Evaluation of ibuprofen toxicity for zebrafish (Danio rerio) targeting on selected biomarkers of oxidative stress. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 34:102–108
Begum BH, Mithra D (2015) Effects of an organophosphate pesticide, malathion (50% E.C) on the liver of air breathing fish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Int Res J Environment Sci 4(9):21–24
Cengiz EI, Unlu E (2006) Sublethal effects of commercial deltamethrin on the structure of the gill, liver and gut tissues of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis: a microscopic study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 21:246–253
CNN Report (2018) https://edition.cnn.com/2018/08/10/health/monsanto-johnson-trial-verdict/index.html. Accessed 10 Aug 2018
Deb N, Das S (2013) Chlorpyrifos toxicity in fish: a review. Curr World Environ 8:77–84
Devi, Y and Mishra, A. (2013) Histopathological alterations in gill and liver anatomy of fresh water, air breathing fish Channa punctatus after Pesticide Hilban® (chlorpyrifos) treatment. Adv Biores 4(2):57– 62
Faggio C, Fedele G, Arfuso F, Panzera M, Fazio F (2014a) Haematological and biochemical response of Mugil cephalus after acclimation to captivity. Cah Biol Mar 55:31–36
Faggio C, Piccione G, Marafioti S, Arfuso F, Trischitta F, Fortino G, Fazio F (2014b) Monthly variations of haematological parameters of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax reared in Mediterranean land off-shore tanks. Cah Biol Mar 55:437–443
Ghanbahadur A, Ghanbahadur G (2012) Histopathological effect of organochloride endosulfan on intestine and stomach of larvivorous fish Rasbora daniconius. DAV Int J Sci 1(2):126–127
Ghasemzadeh J, Sinaei M, Bolouki M (2015) Biochemical and histological changes in fish, spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) exposed to diazinon. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94(2):164–170
Gobi N, Vaseeharan B, Rekha R, Vijayakumar S, Faggio C (2018) Bioaccumulation, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress of the acute exposure selenium in Oreochromis mossambicus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:147–151
IARC (2018) Response to criticisms of the monographs and the glyphosate evaluation. World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
IARC – Report (2017) Rejects false claims in Reuters article (in glyphosate review, WHO cancer agency edited out “non-carcinogenic” findings). World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Karmakar S, Patra K, Jana S, Mandal DP, & Bhattacharjee S (2015) Exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of malathion induces significant cellular, biochemical and histological alterations in Labeo rohita. YPEST. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.07.006
Katuli KK, Amiri BM, Massarsky A, Yelghi S (2014) Impact of a short-term diazinon exposure on the osmoregulation potentiality of Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus) fingerlings. Chemosphere 108:396–404
Khalil F, Kang IJ, Undap S, Tasmin R, Qiu X, Shimasaki Y et al (2013) Alterations in social behavior of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) in response to sublethal chlorpyrifos exposure. Chemosphere 92:125–130
Maksymiv IV, Husak VV, Mosiichuk NM, Matviishyn TM, Sluchyk IY, Storey JM et al (2015) Hepatotoxicity of herbicide Sencor in goldfish may result from induction of mild oxidative stress. Pestic Biochem Physiol 122:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.12.020
Marigoudar SR, Nagarjuna A, Karthikeyan P, Mohan D, & Sharma KV (2018) AC SC. ECSN. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.137
Mishra AK, Mohanty B (2008) Acute toxicity impacts of hexavalent chromium on behavior and histopathology of gill, kidney and liver of the 422 freshwater fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Environ Toxicol Pharmcol 26:136–141
NPIC (2017) Chlorpyrifos-technical fact sheet. National Pesticide Information Center, Corvallis http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/archive/chlorptech.html
Ogueji EO, Usman IB, Auta J (2013) Histopathology of liver and gill of C. gariepinus—(Burchell 1822) with swollen abdomen following exposure to acute and sub-lethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos-ethyl. Int J Basic Appl Sci 2:223
Oruç E (2012) Oxidative stress responses and recovery patterns in the liver of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to chlorpyrifos-ethyl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:678–684
Rosety-Rodrıǵ uez M, Ordoñez FJ, Rosety M, Rosety JM, Rosety I, Ribelles A, Carrasco C (2002) Morpho-histochemical changes in the gills of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L., induced by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 51(3):223–228
Selvi RT, & Ilavazhahan M (2012) Histopathological changes in gill tissue of the fish Catla catla exposed to sublethal concentration of pesticide methyl parathion and a metal ferous sulphate. Biomed Pharmacol J 5(2):305–312
Senapati T, Samanta P, Mandal S, Ghosh AR (2013) Study on histopathological, histochemical and enzymological alterations in stomach and intestine of Anabas testudineus (cuvier) exposed to Almix 20WP herbicide. International Journal of Food, Agriculture and Veterinary Sciences 3(2):100–111
Sharma RR, Pandey AK, Shukla GR (2001) Histopathological alterations in fish tissues induced by toxicity. Aquaculture 2(1):31–43
Velisek J, Stara A, Kolarova J, Svobodova Z (2011) Biochemical, physiological and morfological responses in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) after long-term exposure to terbutryn in real environmental concentration. Pestic Biochem Physiol 100(3):305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2011.05.004
Xing H, Li S, Wang Z, Gao X, Xu S, Wang X (2012) Oxidative stress response and histopathological changes due to atrazine and chlorpyrifos exposure in common carp. Pestic Biochem Physiol 103:74–80
Xing H, Liu T, Zhang Z, Wang X, Xu S (2015) Fish & shellfish immunology acute and subchronic toxic effects of atrazine and chlorpyrifos on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): immunotoxicity assessments. Fish and Shellfish Immunol (April):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.04.016
Zahran E, Risha E, Awadin W (2018) Acute exposure to chlorpyrifos induces reversible changes in health parameters of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). 197(November 2017):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.02.001
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at the King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for funding this Research Group project no RG-1437-005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stalin, A., Suganthi, P., Mathivani, S. et al. Impact of chlorpyrifos on behavior and histopathological indices in different tissues of freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 17623–17631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05165-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05165-3