Abstract
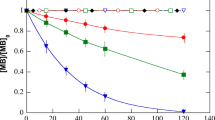
In this work, CuWO4 is prepared and its effect of improving photocatalytic degradation of atrazine by TiO2 as well as the synergetic mechanism is studied. Results show that the addition of CuWO4 (50 mg/L) into the reaction system can significantly enhance the efficiency of atrazine degradation, resulting in an increased degradation efficiency of 92.1% after 270 min, which is 1.94 times higher than that of the single TiO2. As the sintering temperate of CuWO4 was increased, the degradation efficiency of atrazine increased initially and then deceased after reaching a maximum at 500 °C. The origin of the synergistic effect of TiO2-CuWO4 is attributed to the introduction of solid CuWO4. The photochemical test results indicate that the photogenerated electrons transfer from irradiated TiO2 to CuWO4, which is beneficial to the O2 reduction and H2O2 formation in aqueous solution thus promoting the photocatalytic activity of TiO2. These observations unveil the importance of improving photocatalytic activity of TiO2 with Cu-bearing semiconductors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lima AEB, Costa MJS, Santos RS (2017) Facile preparation of CuWO4 porous films and their photoelectrochemical properties. Electrochim Acta 256:139–145
Palanisamy B, Babu CM, Sundaravel B, Anandan S, Murugesan V (2013) Sol-gel synthesis of mesoporous mixed Fe2O3/TiO2 photocatalyst: application for degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J Hazard Mater 252:452–455
Pan CS, Zhu YF (2010) New type of BiPO4 oxy-acid salt photocatalyst with high photocatalytic activity on degradation of dye. Environ Sci Technol 44:5570–5574
Li G, Dimitrijevic NM, Chen L, Rajh T, Gray KA (2008) Role of surface/interfacial Cu2+ sites in the photocatalytic activity of coupled CuO−TiO2 nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 112:19040–19044
Bader H, Sturzenegger V, Hoigne J (1988) Photometric method for the determination of low concentrations of hydrogen peroxide by the peroxidase catalyzed oxidation of N, N-diethyl-p-phenylendiamine (DPD). Water Res 22:1109–1115
Chen H, Xu Y (2014) Enhanced visible-light photoactivity of CuWO4 through a surface-deposited CuO. J Phys Chem C 118:9982–9989
Mohamed HH, Mendive CB, Dillert R, Bahnemann DW (2011) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of multielectron transfer reactions induced by stored electrons in TiO2 nanoparticles: a stopped flow study. J Phys Chem A 115:2139–2147
Hill JC, Choi KS (2013) Synthesis and characterization of high surface area CuWO4 and Bi2WO6 electrodes for use as photoanodes for solar water oxidation. J Mater Chem A 1:5006–5014
Yourey JE, Pyper KJ, Kurtz JB, Bartlett BM (2013) Chemical stability of CuWO4 for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. J Phys Chem C 117:8708–8718
Kum JM, Yoo SH, Ali G, Cho SO (2013) Photocatalytic hydrogen production over CuO and TiO2 nanoparticles mixture. Int J Hydrogen Energ 38:13541–13546
Tauc J (1968) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater Res Bull 3:37–46
Hassan K, Sayed KS (2016) Photocataltyic degradation of methyl orange and cyanide by using TiO2/CuO composite. Desalin Water Treat:1–10
Dalrymple OK (2007) Removing pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting compounds from wastewater by photocatalysis. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:122–143
González-Márquez LC, Hansen AM, González-Farias FA (2018) Effect of mono and divalent salts on the conformation and composition of a humic acid and on atrazine adsorption. Eviron Sci Pollut R 25:17509–17518
Wan L, Sheng J, Chen H, Xu Y (2013) Different recycle behavior of Cu2+ and Fe3+ ions for phenol photodegradation over TiO2 and WO3. J Hazard Mater 262:114–120
Biesinger MC, Lau LM, Gerson AR, Smart RC (2010) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl Surf Sci 257:887–898
Ghows N, Entezari MH (2011) Exceptional catalytic efficiency in mineralization of the reactive textile azo dye (RB5) by a combination of ultrasound and core-shell nanoparticles (CdS/TiO2). J Hazard Mater 195:132–138
Lei N, Wang L, Zhu H (2016) Photocatalytic reductive degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on CuO/TiO2 nanocomposites: a mechanism based on the switching of photocatalytic reduction potential being controlled by the valence state of copper. Appel Catal B-Environ 182:414–423
Ribeiro RA, Nunes CO, Pereira MFR et al (2015) An overview on the advanced oxidation processes applied for the treatment of water pollutants defined in the recently launched Directive 2013/39/EU. Environ Int 75:33–51
Lam SW, Hermawan M, Coleman HW (2007) The role of copper (II) ions in the photocatalytic oxidation of 1, 4-dixoane. J Mol Catal A Chem 278:152–159
Xu S, Sun DD (2009) Significant improvement of photocatalytic hydrogen generation rate over TiO2 with deposited CuO. Int J Hydrogen Energ 34:6096–6104
Zhao W, Zhu B, Dong J, Song J (2012) Photocatalytic properties of Au/Ti02 prepared by impregnation and deposition method. Mater Rev 26:27–30
Ren XH, Yuan XJ, Sun HW (2018) Dynamic changes in atrazine and phenanthrene sorption behaviors during the aging of biochar in soils. Eviron Sci Pollut R 25:81–90
Xiong X, Chen H, Xu Y (2015) Improved ptotocatalytic activity of TiO2 on the addition of CuWO4. J Phys Chem C 119:5946–5953
Du Y, Zhou M, Lei L (2006) Role of the intermediates in the degradation of phenolic compounds by Fenton-like process. J Hazard Mater 136:859–862
Liu Y, Peng B, Chai L, Liu L (2009) Surface modification of silver-doped nanometer titania with stearic acid. TSM Press, San Francisco, pp 19–22
Nosaka Y, Takahashi S, Sakamoto H, Nosaka AY (2011) Reaction mechanism of Cu(II)-grafted visible-light responsive TiO2 and WO3 photocatalysts studied by means of ESR spectroscopy and chemiluminescence photometry. J Phys Chem C 115:21283–21290
Wang Y, Zhu S, Chen X, Tang Y, Jiang Y, Peng Z, Wang H (2014) One step template-free fabrication of mesoporous ZnO/TiO2 hollow microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 307:263–271
Li Y, Cao T, Wang C, Shao C (2011) Fabrication and enhanced photocatalytic properties of heterostructures SnO2/TiO2 composite nanofibers. Chem J Chinese U 32:822–827
Funding
This work was financially supported by the 2017 Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (JCYJ20170306144117642).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The combination of sintered CuWO4 and TiO2 could significantly enhance the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of atrazine.
• The TiO2-CuWO4 photocatalyst showed robust stability and the high degradation efficiency for atrazine was ascribed to solid CuWO4.
• The photogenerated electrons transfer from the irradiated TiO2 to CuWO4 in which CuWO4 acts as a ecb− scavenger.
• There were no photogenerated hvb+ transferred between the irradiated TiO2 and CuWO4.
• The possible mechanism for synergistic effect of TiO2-CuWO4 and the possible photodegradation pathways of atrazine were proposed.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, D., Yang, Y., Tang, J. et al. Synergistic effect of TiO2-CuWO4 on the photocatalytic degradation of atrazine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 12359–12367 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04686-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04686-1