Abstract
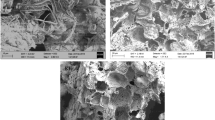
The adsorption mechanism of Cd (II) was investigated by Pennisetum sp. straw biochars (JBC) that were modified by two different methods: KMnO4 impregnation (JMB1) and H2O2 impregnation (JMB2). A scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), and a Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific surface area analysis were employed to examine the physicochemical characteristics of biochars. The Cd(II) adsorption kinetic fit, the Langmuir model well, and the maximum adsorption capacity occurred in the following order: JMB1 (90.32 mg/g) > JMB2 (45.18 mg/g) > JBC (41.79 mg/g), suggesting that JMB1 had an excellent adsorption performance. Finally, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to explore the main adsorption mechanism. Our results showed that JMB1 was an excellent adsorbent in removing Cd(II) from aqueous solution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MB, Zhou JL, Ngo HH, Guo W, Chen M (2016) Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour Technol 214:836–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.057
Biesinger MC, Payne BP, Grosvenor AP, Lau LWM, Gerson AR, Smart RSC (2011) Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl Surf Sci 257:2717–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
Chen H, Zhang W, Yang X, Wang P, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2018) Effective methods to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice grain. Chemosphere 207:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.143
Chengshuai Liu CC, Chang C, Fei Y, Li F, Wang Q, Zhai G, Lei J (2018) Cadmium accumulation in edible flowering cabbages in the Pearl River Delta, China: critical soil factors and enrichment models. Environ Pollut 233:880–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.092
Deng J, Liu Y, Liu S, Zeng G, Tan X, Huang B, Tang X, Wang S, Hua Q, Yan Z (2017) Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto chitosan-pyromellitic dianhydride modified biochar. J Colloid Interface Sci 506:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.07.069
Faheem HY, Liu J, Shen∗ J, Sun X, Li J, Wang L (2016) Preparation of MnOx-loaded biochar for Pb2+ removal: adsorption performance and possible mechanism. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 66:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.07.010
Jefferson WA, Hu C, Liu H, Qu J (2015) Reaction of aqueous Cu-citrate with MnO2 birnessite: characterization of Mn dissolution, oxidation products and surface interactions. Chemosphere 119:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.039
Jung KW, Lee SY, Lee YJ (2018) Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchically structured birnessite-type MnO2/biochar composites for the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous media. Bioresour Technol 260:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.125
Komarek M, Vanek A, Ettler V (2013) Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides--a review. Environ Pollut 172:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.045
Li B, Yang L, Wang CQ, Zhang QP, Liu QC, Li YD, Xiao R (2017) Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derived from different modification processes. Chemosphere 175:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.061
Liang J, Li X, Yu Z, Zeng G, Luo Y, Jiang L, Yang Z, Qian Y, Wu H (2017) Amorphous MnO2 modified biochar derived from aerobically composted swine manure for adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II). ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:5049–5058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00434
Luo HY, Lin QT, Zhang XF, Huang ZF, Liu SS, Jiang JR, Xiao RB, Liao XY (2018) New insights into the formation and transformation of active species in nZVI/BC activated persulfate in alkaline solutions. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.056
Ma Y, Liu WJ, Zhang N, Li YS, Jiang H, Sheng GP (2014) Polyethylenimine modified biochar adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from the aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 169:403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.014
Meng F, Yang B, Wang B, Duan S, Chen Z, Ma W (2017) Novel dendrimerlike magnetic biosorbent based on modified Orange Peel waste: adsorption–reduction behavior of arsenic. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:9692–9700. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01273
Meng J, Tao M, Wang L, Liu X, Xu J (2018) Changes in heavy metal bioavailability and speciation from a Pb-Zn mining soil amended with biochars from co-pyrolysis of rice straw and swine manure. Sci Total Environ 633:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.199
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Das SK (2008) Removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions using clarified sludge. J Colloid Interface Sci 325:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.06.003
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Das SK (2009) Adsorption removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions by rice husk ash. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 28(4):535–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10346
Peng L, Yang Y, Hou Y, Lu G (2014) The biosafety assessment of introduced Pennisetum sp. in Fujian Province, China. Fujian J Agric Sci 29(11):1132–1137 (in Chinese)
Peng H, Gao P, Chu G, Pan B, Peng J, Xing B (2017) Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ Pollut 229:846–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.004
Shengsen Wang BG, Li Y, Ok YS, Shen C, Xue S (2017) Biochar provides a safe and value-added solution for hyperaccumulating plant disposal: a case study of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Chemosphere 178:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.121
Song Z, Lian F, Yu Z, Zhu L, Xing B, Qiu W (2014) Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 242:36–42
Su Y, Sun X, Zhou X, Dai C, Zhang Y, (2015) Zero-valent iron doped carbons readily developed from sewage sludge for lead removal from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 36:1–8
The Ministry of Environmental Protection, The Ministry of Land and Resources (2014) Report on the National Soil Contamination Survey. http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/trhj/201605/t20160526_347133.shtml. Accessed 18 September s2018
Trakal L, Veselská V, Šafařík I, Vítková M, Číhalová S, Komárek M (2016) Lead and cadmium sorption mechanisms on magnetically modified biochars. Bioresour Technol 203:318–324
Trakal L, Michálková Z, Beesley L, Vítková M, Ouředníček P, Barceló AP, Ettler V, Číhalová S, Komárek M (2018) AMOchar: amorphous manganese oxide coating of biochar improves its efficiency at removing metal(loid)s from aqueous solutions. Sci Total Environ 625:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.267
Wang MC, Sheng GD, Qiu YP (2014) A novel manganese-oxide/biochar composite for efficient removal of lead(II) from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1719–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0538-7
Wang H, Gao B, Wang S, Fang J, Xue Y, Yang K (2015a) Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour Technol 197:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.132
Wang S, Gao B, Li Y, Mosa A, Zimmerman AR, Ma LQ, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015b) Manganese oxide-modified biochars: preparation, characterization, and sorption of arsenate and lead. Bioresour Technol 181:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.044
Wang S, Zhou Y, Gao B, Wang X, Yin X, Feng K, Wang J (2017) The sorptive and reductive capacities of biochar supported nanoscaled zero-valent iron (nZVI) in relation to its crystallite size. Chemosphere 186:495–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.014
Wu W, Li J, Niazi NK, Müller K, Chu Y, Zhang L, Yuan G, Lu K, Song Z, Wang H (2016) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on lead immobilization by chemically modified coconut fiber-derived biochars in aqueous environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:22890–22896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7428-0
Xia Y, Meng L, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Dai X, Zhao M (2015) Facile preparation of MnO2 functionalized baker’s yeast composites and their adsorption mechanism for cadmium. Chem Eng J 259:927–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.071
Xia F, Qu L, Wang T, Luo L, Chen H, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M, Mei K, Huang H (2018) Distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollutants in sediments of a rapid developing urban river system. Chemosphere 207:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.090
Xu L, Zhou J, Liang J, Cui H, Tao M, Tao Z, Zhu Z, Huang L (2014) The remediation potential of Pennisetum sp. on cu, cd contaminated soil. Acta Ecol Sin 34(18):5342–5348 (in Chinese)
Xue Y, Gao B, Yao Y, Inyang M, Zhang M, Zimmerman AR, Ro KS (2012) Hydrogen peroxide modification enhances the ability of biochar (hydrochar) produced from hydrothermal carbonization of peanut hull to remove aqueous heavy metals: batch and column tests. Chem Eng J 200-202:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.116
Zhang C, Yu Z, Zeng G, Huang B, Dong H, Huang J, Yang Z, Wei J, Hu L, Zhang Q (2016) Phase transformation of crystalline iron oxides and their adsorption abilities for Pb and Cd. Chem Eng J 284:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.096
Zhao C, Wang J (2014) Fabrication and tensile properties of graphene/copper composites prepared by electroless plating for structrual applications. Phys Status Solidi A 211:2878–2885. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201431478
Zhou Q, Liao B, Lin L, Qiu W, Song Z (2018) Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by ferromanganese binary oxide-biochar composites. Sci Total Environ 615:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.220
Zhu X, Liu Y, Qian F, Zhou C, Zhang S, Chen J (2015) Role of hydrochar properties on the porosity of hydrochar-based porous carbon for their sustainable application. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00153
Zuo X, Liu Z, Chen M (2016) Effect of H2O2 concentrations on copper removal using the modified hydrothermal biochar. Bioresour Technol 207:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.032
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21677041, 41371317), the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (201604030017, 201604020077), and the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2016A04040311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
EDS spectrum with the element ratio: (a) pristine biochar (JBC), (b) KMnO4-impregnated Biochar (JMB1) and (c) H2O2-impregnated Biochar (JMB2). (PDF 2571 kb)
Fig. S2
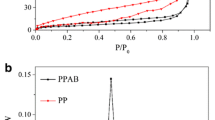
N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distribution of JBC (a, d), JMB1 (b, e) and JMB2 (c, f). (PDF 4740 kb)
Fig. S3
X-ray diffraction pattern of JBC, JMB1, JMB2. Crystallites were detected with peaks labeled G for graphite. (PDF 1262 kb)
Fig. S4
Zeta potentials of JBC (a), JMB1(b) and JMB2 (c) at various pH values. (PDF 177 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, G., Bi, L., Song, X. et al. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by Pennisetum sp. straw biochars derived from different modification methods. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 7024–7032 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04158-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04158-6