Abstract
This study aims to investigate the long-run and causal effects of energy consumption, economic growth, urbanization, and trade openness on CO2 emissions in Turkey using newly developed econometric techniques. To our best knowledge, there has been no study examining the relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, trade openness, urbanization, and economic growth in Turkey. Therefore, this study proposes to fill this gap in the literature. In this study, we use time series data covering the years between 1960 and 2015. To capture long-run effects, we used ARDL, FMOLS, and DOLS estimators, while wavelet coherence technique is used to explore causal effects among the variables. Our results reveal that (i) there is a long-run equilibrium relationship between CO2 emissions and energy consumption, economic growth, urbanization, and trade openness; (ii) in the long-run, CO2 emission in Turkey is significantly triggered by energy consumption, economic growth, and urbanization; and (iii) the results of the wavelet coherence–based causality test provide supportive evidence to the long-run estimations of this study.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
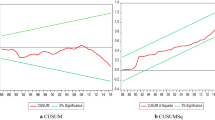
In this study, only three of the five different cases of bounds test are taken into consideration since only these three give reliable results (Katircioglu et al., 2013). Bounds test is applied without deterministic unrestricted intercept and without trend, with deterministic unrestricted intercept and restricted trend, and with unrestricted intercept and restricted trend for case III, case IV, and case V, respectively.
References
Akbostancı E, Türüt-Aşık S, Tunç Gİ (2009) The relationship between income and environment in Turkey: is there an environmental Kuznets curve? Energy Policy 37(3):861–867
Ali HS, Law SH, Zannah TI (2016) Dynamic impact of urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and trade openness on CO2 emissions in Nigeria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):12435–12443
Anatasia V (2015) The causal relationship between GDP, exports, energy consumption, and CO2 in Thailand and Malaysia. Int J Econ Perspect 9(4):37–48
Apergis N, Payne JE (2009) CO2 emissions, energy usage, and output in Central America. Energy Policy 37(8):3282–3286
Ayeche MB, Barhoumi M, Hammas MA (2016) Causal linkage between economic growth, financial development, trade openness and CO2 emissions in European Countries. Am J Environ Engineer 6(4):110–122
Aytun C, Akın CS (2015) Türkiye’de Karbondioksit Emisyonu, Enerji Tüketimi ve Eğitim İlişkisi: Bootstrap Nedensellik Analizi Düzenleme Kurulu, 260
Bilgen S, Keleş S, Kaygusuz A, Sarı A, Kaygusuz K (2008) Global warming and renewable energy sources for sustainable development: a case study in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12(2):372–396
Borhan HB, Ahmed EM (2012) Simultaneous model of pollution and income in Malaysia. Int J Econ Perspect 6(1):50–73
Bozkurt C, Okumuş İ (2015) Türkiye’de ekonomik büyüme, enerji tüketimi, ticari serbestleşme ve nüfus yoğunluğunun Co2 emisyonu üzerindeki etkileri: Yapısal kırılmalı eşbütünleşme analizi/the effects of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness and population density on. Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi 12(32):23–35
Brown RL, Durbin J, Evans JM (1975) Techniques for testing the constancy of regression relationships over time. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 37(2):149–163
Çetin M, Ecevit E (2015) Urbanization, energy consumption and CO 2 emissions in Sub Saharan countries: a panel cointegration and causality analysis. J Econ Dev Stud 3(2):66–76
Cetin M, Ecevit E (2017) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions under the structural breaks: empirical evidence from Turkish economy. Int J Econ Perspect 11(1):64–78
Chang CC (2010) A multivariate causality test of carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China. Appl Energy 87(11):3533–3537
Dinda S, Coondoo D (2006) Income and emission: a panel data-based cointegration analysis. Ecol Econ 57(2):167–181
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO 2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213
Elliott G, Rothenberg TJ, Stock JH (1996) Efficient tests for an autoregressive unit root. Econometrica 64(4):813
Engle RF, Granger CW (1987) Co-integration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica 55:251–276
Goupillaud P, Grossmann A, Morlet J (1984) Cycle-octave and related transforms in seismic signal analysis. Geoexploration 23(1):85–102
Granger CW, Newbold P (1974) Spurious regressions in econometrics. J Econ 2(2):111–120
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Grossman, G. M., Krueger, A. B. (2002). Economic growth and the environment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, CX, May, 353–77. International Library of Critical Writings in Economics 141:105–129.
Halicioglu F (2009) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37(3):1156–1164
Harris R, Sollis R (2003) Applied time series modelling and forecasting. Wiley, Hoboken
Hashem Pesaran M, Shin Y, Smith RP (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Stat Assoc 94(446):621–634
Heidari H, Katircioğlu ST, Saeidpour L (2015) Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and energy consumption in the five ASEAN countries. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 64:785–791
Hossain MS (2011) Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 39(11):6991–6999
Hossain S (2012) An econometric analysis for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, foreign trade and urbanization of Japan. Low Carbon Economy 3(3):92–105
Istaiteyeh R (2016) Electricity consumption and real GDP: are they causal for Jordan? Int J Econ Perspect 10(4):426–540
Kapusuzoglu A (2014) Causality relationships between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: results from a multi-country study. Int J Econ Perspect 8(2):5–15
Kasman A, Duman YS (2015) CO2 emissions, economic growth, energy consumption, trade and urbanization in new EU member and candidate countries: A panel data analysis. Econ Model 44:97–103
Katircioglu S, Katircioglu S (2018) Testing the role of urban development in the conventional environmental Kuznets Curve: evidence from Turkey. Appl Econ Lett 25(11):741–746
Katircioglu S, Caglar D, Kalmaz DB (2013) Trade, energy and growth in G7 countries. Actual Problems of Economics 1:346–358
Katircioglu S, Katircioğlu S, Altinay M (2017) Interactions between energy consumption and imports: empirical evidence from Turkey. Journal of Comparative Asian Development 16(2):161–178
Kraft J, Kraft A (1978) On the relationship between energy and GNP. Journal of Energy Development 3(2):401–403
Kumar Narayan P, Narayan S (2005) Are exports and imports cointegrated? Evidence from 22 least developed countries. Appl Econ Lett 12(6):375–378
Lean HH, Smyth R (2010) CO2 emissions, electricity consumption and output in ASEAN. Appl Energy 87(6):1858–1864
Lee CC, Lee JD (2009) Income and CO2 emissions: evidence from panel unit root and cointegration tests. Energy Policy 37(2):413–423
Masih R, Masih AM (1996) Stock-Watson dynamic OLS (DOLS) and error-correction modelling approaches to estimating long-and short-run elasticities in a demand function: new evidence and methodological implications from an application to the demand for coal in mainland China. Energy Econ 18(4):315–334
Mohapatra G, Giri AK (2015) Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from India. The Empirical Econometrics and Quantitative Economics Letters 4(1):17–32
Narayan S, Narayan PK (2004) Determinants of demand for Fiji's exports: an empirical investigation. Dev Econ 42(1):95–112
Narayan PK, Smyth R (2008) Energy consumption and real GDP in G7 countries: new evidence from panel cointegration with structural breaks. Energy Econ 30(5):2331–2341
Ozcan B, Ari A (2017) Nuclear energy-economic growth nexus in OECD countries: a panel data analysis. Int J Econ Perspect 11(1):138–154
Özer B, Görgün E, İncecik S (2013) The scenario analysis on CO2 emission mitigation potential in the Turkish electricity sector: 2006–2030. Energy 49:395–403
Özmen MT (2009) Sera Gazı-Küresel Isınma ve Kyoto Protokolü. İMO Dergisi 453(1):42–46
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(9):3220–3225
Pal D, Mitra SK (2017) Time-frequency contained co-movement of crude oil and world food prices: a wavelet-based analysis. Energy Econ 62:230–239
Perron P, Ng S (1996) Useful modifications to some unit root tests with dependent errors and their local asymptotic properties. Rev Econ Stud 63(3):435
Pesaran MH, Shin Y (1995) Long-run structural modelling. Cambridge, Department of Applied Economics, University of Cambridge (No. 9419). DAE Working Paper
Pesaran MH, Timmermann A (2005) Small sample properties of forecasts from autoregressive models under structural breaks. J Econ 129(1–2):183–217
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Rogelj J, Den Elzen M, Höhne N, Fransen T, Fekete H, Winkler H, Meinshausen M (2016) Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2 C. Nature 534(7609):631
Shahzad SJH, Kumar RR, Zakaria M, Hurr M (2017) Carbon emission, energy consumption, trade openness and financial development in Pakistan: a revisit. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:185–192
Soytas U, Sari R (2009) Energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon emissions: challenges faced by an EU candidate member. Ecol Econ 68(6):1667–1675
Soytas U, Sari R, Ewing BT (2007) Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecol Econ 62(3–4):482–489
Stock JH, Watson MW (1993) A simple estimator of cointegrating vectors in higher order integrated systems. Econometrica 61:783–820
Tang CF, Tan BW (2015) The impact of energy consumption, income and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 79:447–454
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79(1):61–78
TUIK (2017) Main Statistics. http://www.turkstat.gov.tr. Accessed 05 May 2018
Wang SS, Zhou DQ, Zhou P, Wang QW (2011) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China: a panel data analysis. Energy Policy 39(9):4870–4875
World Bank (2017) World Development Indicators. http://data.worldbank.org/
Yavuz NÇ (2014) CO2 emission, energy consumption, and economic growth for Turkey: evidence from a cointegration test with a structural break. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 9(3):229–235
Yuan J, Zhao C, Yu S, Hu Z (2007) Electricity consumption and economic growth in China: cointegration and co-feature analysis. Energy Econ 29(6):1179–1191
Yuan JH, Kang JG, Zhao CH, Hu ZG (2008) Energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from China at both aggregated and disaggregated levels. Energy Econ 30(6):3077–3094
Zivot E, Andrews D (1992) Further evidence on the great crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J Bus Econ Stat 25:1–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Muhammad Shahbaz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalmaz, D.B., Kirikkaleli, D. Modeling CO2 emissions in an emerging market: empirical finding from ARDL-based bounds and wavelet coherence approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 5210–5220 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3920-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3920-z