Abstract
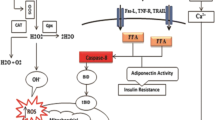
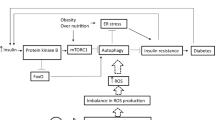
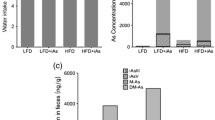
Arsenic (As) is a toxic and hazardous metalloid. Unfortunately, its presence in drinking water together with wrong nutritional patterns is associated with an increase in the occurrence of metabolic disorders in young people. Degradation of mitochondria is presented by a specific form of autophagy called mitophagy which is an important landmark leading to apoptosis during lipotoxicity. Lipotoxicity and cellular toxicity due to arsenic intake can lead to changes in mitophagy and apoptosis. The protein derived from SQSTM1 gene, also called p62, plays an important role in energy homeostasis in the liver, and it can contribute to the regulation of autophagic responses given its effect on signaling of mTOR, MAPK, and NF-KB. Consequently, changes in Sqstm1, mitophagy (BNIP3), and apoptotic (caspase 3) genes in the livers of NMRI mice were examined with the use of real-time RT-PCR Array followed by exposure to an environmentally relevant and negligible cytotoxic concentration of arsenite (50 ppm) in drinking water while being fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) or low-fat diet (LFD) for 20 weeks (LFD-As and HFD-As groups). While LFD-As and HFD groups showed a decrease in BNIP3 expression, a significant increase was observed in the HFD-As group. P62 gene showed downregulation in LFD-As and HFD groups, and upregeneration was observed in the HFD-As group. Caspase 3 showed increased expression as the key factor associated with apoptotic liver cell death in the three groups, with the highest value in HFD-As group. Overall, the changes observed in the expression of Sqstm1, BNIP3, and caspase 3 in this study can be related to the level of liver damage caused by exposure to arsenic and HFD and probably, BNIP3 pro-apoptotic protein is associated with an increased cell death due to HFD and As.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy CO, Thomas DJ, Calderon RL (2003) Health effects and risk assessment of arsenic. J Nutr 133:1536S–1538S
Ahangarpour A, Oroojan AA, Rezae M, Khodayar MJ, Alboghobeish S, Zeinvand M (2017) Effects of butyric acid and arsenic on isolated pancreatic islets and liver mitochondria of male mouse. Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench 10:44–53
Ahangarpour A, Alboghobeish S, Rezaei M, Khodayar MJ, Oroojan AA, Zainvand M (2018) Evaluation of diabetogenic mechanism of high fat diet in combination with arsenic exposure in male mice. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 17
Bai J, Yao X, Jiang L, Zhang Q, Guan H, Liu S, Wu W, Qiu T, Gao N, Yang L, Yang G, Sun X (2016) Taurine protects against As2O3-induced autophagy in livers of rat offsprings through PPARγ pathway. Sci Rep 6:27733. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27733
Bhowmick S, Pramanik S, Singh P, Mondal P, Chatterjee D, Nriagu J (2018) Arsenic in groundwater of West Bengal, India: a review of human health risks and assessment of possible intervention options. Sci Total Environ 612:148–169
Biswas A, Das A, Deb D, Ghose A, Mazumder DNG (2018) Cancer risk estimation from dietary arsenic, a new approach from longitudinal cohort study. Stoch Env Res Risk A 32:1035–1050
Brown KG, Ross GL (2002) Arsenic, drinking water, and health: a position paper of the American Council on Science and Health. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 36:162–174
Bülow MH et al (2018) Unbalanced lipolysis results in lipotoxicity and mitochondrial damage in peroxisome-deficient Pex19 mutants. Mol Biol Cell 29:396–407
Cavaliere V, Lombardo T, Costantino SN, Kornblihtt L, Alvarez EM, Blanco GA (2014) Synergism of arsenic trioxide and MG132 in Raji cells attained by targeting BNIP3, autophagy, and mitochondria with low doses of valproic acid and vincristine. Eur J Cancer 50:3243–3261
Chilakapati J, Wallace K, Hernandez-Zavala A, Moore T, Ren H, Kitchin KT (2015) Pharmacokinetic and genomic effects of arsenite in drinking water on mouse lung in a 30-day exposure. Dose-Response 13:1559325815592392. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559325815592392
Choudhury S, Ghosh S, Mukherjee S, Gupta P, Bhattacharya S, Adhikary A, Chattopadhyay S (2016) Pomegranate protects against arsenic-induced p53-dependent ROS-mediated inflammation and apoptosis in liver cells. J Nutr Biochem 38:25–40
Del Razo LM et al (2011) Exposure to arsenic in drinking water is associated with increased prevalence of diabetes: a cross-sectional study in the Zimapan and Lagunera regions in Mexico. Environ Health 10:73
Duchen MR (2004) Mitochondria in health and disease: perspectives on a new mitochondrial biology. Mol Asp Med 25:365–451
Dutta M et al (2014) High fat diet aggravates arsenic induced oxidative stress in rat heart and liver. Food Chem Toxicol 66:262–277
Engel RR, Receveur O (1993) Re:“Arsenic ingestion and internal cancers: a review”. Am J Epidemiol 138:896–897
Graier WF, Malli R, Kostner GM (2009) Mitochondrial protein phosphorylation: instigator or target of lipotoxicity? Trends Endocrinol Metab 20:186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2009.01.004
Grau-Perez M et al (2018) Arsenic exposure, diabetes-related genes and diabetes prevalence in a general population from Spain. Environ Pollut 235:948–955
Guo Z et al (2017) The optimal dose of arsenic trioxide induced opposite efficacy in autophagy between K562 cells and their initiating cells to eradicate human myelogenous leukemia. J Ethnopharmacol 196:29–38
Hou H, Yu Y, Shen Z, Liu S, Wu B (2017) Hepatic transcriptomic responses in mice exposed to arsenic and different fat diet. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10621–10629
Hsueh Y-M, Cheng G, Wu M, Yu H, Kuo T, Chen CJ (1995) Multiple risk factors associated with arsenic-induced skin cancer: effects of chronic liver disease and malnutritional status. Br J Cancer 71:109
Huang C-F et al (2015) Arsenic exposure and glucose intolerance/insulin resistance in estrogen-deficient female mice. Environ Health Perspect 123:1138
Hughes MF, Beck BD, Chen Y, Lewis AS, Thomas DJ (2011) Arsenic exposure and toxicology: a historical perspective. Toxicol Sci 123:305–332
Islam MR et al (2012) Association between type 2 diabetes and chronic arsenic exposure in drinking water: a cross sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health 11:38
Jain A et al (2010) p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem 285:22576–22591. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.118976
Katsuragi Y, Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2016) Regulation of the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway by p62/SQSTM1. Curr Opin Toxicol 1:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2016.09.005
Law BA, Roddy P, Liao X, Schulze P, Cowart L (2015) Lipid oversupply to cardiomyocytes induces sphingolipid-dependent oxidative stress and induction of mitophagy through ceramide synthase 2. Am Heart Assoc,
Li S et al (2016) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates apoptosis and autophagy in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by inhibiting BNIP3 Drug design. Dev Ther 10:631
Li Y, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Zhang W, Cui X, Liu J, Wei Y (2018) Arsenic induces Thioredoxin 1 and apoptosis in human liver HHL-5 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 181:234–241
Liu X et al (2016) MicroRNA-21 activation of ERK signaling via PTEN is involved in arsenite-induced autophagy in human hepatic L-02 cells. Toxicol Lett 252:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.04.015
Manley S, Williams JA, Ding W-X (2013) The role of p62/SQSTM1 in liver physiology and pathogenesis. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, NJ) 238:525–538 https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370213489446
Meliker JR, Wahl RL, Cameron LL, Nriagu JO (2007) Arsenic in drinking water and cerebrovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease in Michigan: a standardized mortality ratio analysis. Environ Health 6:4
Mitra SR et al (2004) Nutritional factors and susceptibility to arsenic-caused skin lesions in West Bengal, India. Environ Health Perspect 112:1104
Nakamura Y et al (2012) BNIP3 and NIX mediate Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosomal proteins within mitochondria. PLoS One 7:e30767. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030767
Navas-Acien A, Silbergeld EK, Streeter RA, Clark JM, Burke TA, Guallar E (2006) Arsenic exposure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of the experimental and epidemiologic evidence. Environ Health Perspect 114:641
Nesha M, Islam M, Ferdous N, Nazrul FB, Rasker JJ (2018) Chronic arsenic exposure through drinking water and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a study from Bangladesh. J Family Med Prim Care Open Acc: JFOA-113 DOI 10
Niu Z, Zhang W, Gu X, Zhang X, Qi Y, Zhang Y (2016) Mitophagy inhibits proliferation by decreasing cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in arsenic trioxide-treated HepG2 cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 45:212–221
Pan J-A et al (2016) TRIM21 ubiquitylates SQSTM1/p62 and suppresses protein sequestration to regulate redox homeostasis. Mol Cell 61:720–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.007
Pang L et al (2018) Differential effects of reticulophagy and mitophagy on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Death Dis 9:90
Paul DS, Walton FS, Saunders RJ, Stýblo M (2011) Characterization of the impaired glucose homeostasis produced in C57BL/6 mice by chronic exposure to arsenic and high-fat diet. Environ Health Perspect 119:1104–1109. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1003324
Perluigi M, Di Domenico F, Butterfield DA (2015) mTOR signaling in aging and neurodegeneration: at the crossroad between metabolism dysfunction and impairment of autophagy. Neurobiol Dis 84:39–49
Pickles S, Vigié P, Youle RJ (2018) Mitophagy and quality control mechanisms in mitochondrial maintenance. Curr Biol 28:R170–R185
Rana T, Bera AK, Das S, Bhattacharya D, Pan D, Das SK (2016) Inhibition of oxidative stress and enhancement of cellular activity by mushroom lectins in arsenic induced carcinogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17:4185–4197
Rautou P-E, Mansouri A, Lebrec D, Durand F, Valla D, Moreau R (2010) Autophagy in liver diseases. J Hepatol 53:1123–1134
Sahani MH, Itakura E, Mizushima N (2014) Expression of the autophagy substrate SQSTM1/p62 is restored during prolonged starvation depending on transcriptional upregulation and autophagy-derived amino acids. Autophagy 10:431–441. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.27344
Santra A (2015) Arsenic-induced liver injury. In: Handbook of arsenic toxicology. Elsevier, pp 315–334
Schaffer JE (2003) Lipotoxicity: when tissues overeat. Curr Opin Lipidol 14:281–287
Schneider JL, Cuervo AM (2014) Autophagy and human disease: emerging themes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 26:16–23
Schrauwen P (2004) The role of uncoupling protein 3 in fatty acid metabolism: protection against lipotoxicity? Proc Nutr Soc 63:287–292
Schrauwen P, Hesselink MK (2004) Oxidative capacity, lipotoxicity, and mitochondrial damage in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53:1412–1417
Schrauwen P, Hesselink MK, Vaartjes I, Kornips E, Saris WH, Giacobino J-P, Russell A (2002) Effect of acute exercise on uncoupling protein 3 is a fat metabolism-mediated effect. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282:E11–E17
Schrauwen P et al (2003) Uncoupling protein 3 as a mitochondrial fatty acid anion exporter. FASEB J 17:2272–2274
Shi RY, Zhu SH, Li V, Gibson SB, Xu XS, Kong JM (2014) BNIP3 interacting with LC3 triggers excessive mitophagy in delayed neuronal death in stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 20:1045–1055
Sun X et al (2018) Synergistic effect of copper and arsenic upon oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy alterations in brain tissues of Gallus gallus. J Inorg Biochem 178:54–62
Tseng C-H et al (2000) Long-term arsenic exposure and incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a cohort study in arseniasis-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Environ Health Perspect 108:847
Tsuji JS, Alexander DD, Perez V, Mink PJ (2014) Arsenic exposure and bladder cancer: quantitative assessment of studies in human populations to detect risks at low doses. Toxicology 317:17–30
Turner N, Heilbronn LK (2008) Is mitochondrial dysfunction a cause of insulin resistance? Trends Endocrinol Metab 19:324–330
Unger RH (2002) Lipotoxic diseases. Annu Rev Med 53:319–336
Unger RH (2003) Minireview: weapons of lean body mass destruction: the role of ectopic lipids in the metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology 144:5159–5165
Vahter M, Concha G (2001) Role of metabolism in arsenic toxicity Pharmacology & Toxicology. MiniReview 89:1–5
Van Herpen N, Schrauwen-Hinderling V (2008) Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol Behav 94:231–241
Varga ZV, Giricz Z, Liaudet L, Haskó G, Ferdinandy P, Pacher P (2015) Interplay of oxidative, nitrosative/nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis 1852:232–242
Walton FS, Harmon AW, Paul DS, Drobná Z, Patel YM, Styblo M (2004) Inhibition of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by trivalent arsenicals: possible mechanism of arsenic-induced diabetes. Tox Appl Pharmacol 198:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2003.10.026
Wang S-F, Wu M-Y, Cai C-Z, Li M, Lu J-H (2016a) Autophagy modulators from traditional Chinese medicine: mechanisms and therapeutic potentials for cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. J Ethnopharmacol 194:861–876
Wang S, Pacher P, De Lisle RC, Huang H, Ding WX (2016b) A mechanistic review of cell death in alcohol-induced liver injury. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40:1215–1223
Wang G et al (2017) Arsenic sulfide induces apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of ROS/JNK and suppression of Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in osteosarcoma. Free Radic Biol Med 106:24–37
Wu W et al (2018) Pancreatic islet-autonomous effect of arsenic on insulin secretion through endoplasmic reticulum stress-autophagy pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 111:19–26
Xia Y, Liu X, Liu B, Zhang X, Tian G (2018) Enhanced antitumor activity of combined megestrol acetate and arsenic trioxide treatment in liver cancer cells. Exp Ther Med 15:4047–4055
Yang T, Blackwell R (1961) Nutritional and environmental conditions in the endemic blackfoot area. Formos Sci 15:101–129 Find this article online
Yang L, Li P, Fu S, Calay ES, Hotamisligil GS (2010) Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab 11:467–478
Yousefsani BS, Pourahmad J, Hosseinzadeh H (2018) The mechanism of protective effect of crocin against liver mitochondrial toxicity caused by arsenic III. Toxicol Mech Methods 28:105–114
Zeinvand-Lorestani M et al (2018) Autophagy upregulation as a possible mechanism of arsenic induced diabetes. Sci Rep 8:11960
Zhu X-X et al (2014) Sodium arsenite induces ROS-dependent autophagic cell death in pancreatic β-cells. Food Chem Toxicol 70:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.05.006
Acknowledgements
This paper is issued from Ph.D. thesis of Marzieh Zeinvand-Lorestani.
Funding
This paper was financially supported by Toxicology Research Center (Grant number TRC-9505) of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeinvand-Lorestani, M., Kalantari, H., Khodayar, M.J. et al. Dysregulation of Sqstm1, mitophagy, and apoptotic genes in chronic exposure to arsenic and high-fat diet (HFD). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 34351–34359 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3349-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3349-4