Abstract
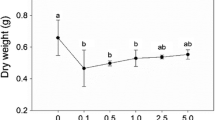
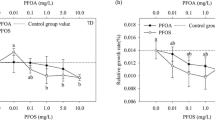
Aquatic plants play an important role in maintaining the health of water environment in nature. Studies have shown that linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS), a type of omnipresent pollutant, can cause toxic damage to aquatic plants. In the present research, we studied the physiological and growth response of submerged plant Potamogeton perfoliatus L. to different concentrations of LAS (0.1, 1.0, 10.0, 20.0, and 50.0 mg l−1). The results showed that LAS is toxic to P. perfoliatus, and the toxicity is dose-dependent. Only slightly reversible oxidative damages were observed in the physiological parameters of P. perfoliatus when P. perfoliatus was exposed to lower LAS doses (< 10 mg l−1): soluble sugar, soluble protein, H2O2, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content in P. perfoliatus increased significantly at 0.1 mg l−1 and then returned to normal levels at 1.0 mg l−1. Antioxidant enzymes were activated before the LAS concentration reached 10 mg l−1, and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and photosynthesis pigment content declined significantly when the concentration of LAS exceeded 10 mg l−1. In addition, at higher concentrations (20–50 mg l−1) of LAS, dry weight and fresh weight of P. perfoliatus showed significant declines. The results indicate that LAS above 10 mg l−1 can cause serious physiological and growth damage to P. perfoliatus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alscher RG, Donahue JL, Cramer CL (1997) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants: relationships in green cells. Physiol Plantarum 100:224–233
Bowler C, Montagu MV, Inze D (2003) Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Phys 43:83–116
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brogan WR 3rd, Relyea RA (2014) A new mechanism of macrophyte mitigation: how submerged plants reduce malathion’s acute toxicity to aquatic animals. Chemosphere 108:405–410
Cunningham JJ, Kemp WM, Lewis MR, Stevenson JC (1984) Temporal responses of the macrophyte, Potamogeton perfoliatus L., and its associated autotrophic community to atrazine exposure in estuarine microcosms. Estuaries 7:519–530
Elavarthi S, Martin B (2010) Spectrophotometric assays for antioxidant enzymes in plants. In: Sunkar R (eds) Plant stress tolerance. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols), vol 639 Humana Press
Farhadian O, Kharamannia R, Soofiani NM, Dorche EE (2009) Antioxidant enzymes activity and phenolic compounds content in red cabbage seedlings exposed to copper stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(2):596
Forgács E, Oros G, Cserháti T (2002) Biological activity and environmental impact of anionic surfactants. Environ Int 28(5):337–348
Garrido-Perez MC, Perales-Vargasmachuca JA, Nebot-Sanz E, Sales-Márquez D (2008) Effect of the test media and toxicity of LAS on the growth of Isochrysis galbana. Ecotoxicology 17(8):738–746
Guo YH, Sun XZ, Wang HQ (1985) Studies on the classification of Potamogeton in Shaanxi Province. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occident 4:291–304
Guo W, Gong X, Deng X, Wang Z, Li Z (2016) Community succession of macrophytes in the middle and lower reaches of the Hanjiang River. Chin Bull Bot 51(6):782–789
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Station Circ 347(5406):357–359
Hodges G, Roberts DW, Marshall SJ, Dearden JC (2006) The aquatic toxicity of anionic surfactants to Daphnia magna-a comparative QSAR study of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates and ester sulphonates. Chemosphere 63:1443–1450
Jardak K, Drogui P, Daghrir R (2016) Surfactants in aquatic and terrestrial environment: occurrence, behavior, and treatment processes. Environ Sci Pollut R Int 23(4):3195–3216
Jaschinski S, Brepohl DC, Sommer U (2011) The trophic importance of epiphytic algae in a freshwater macrophyte system (Potamogeton perfoliatus L.): stable isotope and fatty acid analyses. Aquat Sci 73(1):91–101
Jones TW, Estes PS (1984) Uptake and phytotoxicity of soil-sorbed atrazine for the submerged aquatic plant, Potamogeton perfoliatus L. Arch Environ Con Tox 13(2):237–241
Jones TW, Kemp WM, Estes PS, Stevenson JC (1986) Atrazine uptake, photosynthetic inhibition, and shortterm recovery for the submersed vascular plant, Potamogeton perfoliatus L. Arch Environ Con Tox 15(3):277–283
Jonsson CM, Paraiba LC, Aoyama H (2009) Metals and linear alkylbenzene sulphonate as inhibitors of the algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata acid phosphatase activity. Ecotoxicology 18(5):610–619
Kráľová K, Šeršeň F, Ľudmila M, Devínsky F, Krempaská E (1992) Effect of surfactants on growth, chlorophyll content and hill reaction activity. Photosynthetica 29(3):440–475
Lechuga M, Fernándezserrano M, Jurado E, Núñezolea J, Ríos F (2016) Acute toxicity of anionic and non-ionic surfactants to aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:1–8
Lewis MA (1991) Chronic and sublethal toxicities of surfactants to aquatic animals: a review and risk assessment. Water Res 25:101–113
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvent. Biochem Soc Trans 11:1982–1983
Liu N, Wu ZH (2018) Toxic effects of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate on chara vulgaris L. Environ Sci Pollut R 25(5):4934–4941
Liu HY, Zhou PH, Yang RB, Liao BH, Lu SQ, Yu PZ (2001) Effect of anionic surfactant linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) on physiological and biochemical characteristics of aquatic plants. Agro-environmental Protection 20(5):341–344
Liu HY, Liao BH, Zhou PH, Yu PZ (2004) Toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and alkylethoxylate to aquatic plants. B Environ Contam Tox 72(4):866–872
Merta J, Stenius P (1999) Interactions between cationic starch and anionic surfactants. Colloids Surf 149:367–377
Mishra V, Srivastava G, Prasad SM (2009) Antioxidant response of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) seedlings to interactive effect of dimethoate and UV-B irradiation. Sci Hortic-amsterdam 120(3):373–378
Misra V, Chawla G, Kumar V, Lal H, Viswanathan PN (1987) Effect of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate in skin of fish fingerlings (Cirrhina mrigala): observations with scanning electron microscope. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 13(2):164–168
Prasad MNV, Malec P, Waloszek A, Bojko M, Strzałka K (2001) Physiological responses of lemna trisulca, L. (duckweed) to cadmium and copper bioaccumulation. Plant Sci 161(5):881–889
Rosen MJ (1989) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Salin ML (1991) Chloroplast and mitochondrial mechanisms for protection against oxygen toxicity. Free Radical Res Com 13(1):851–858
Sandalio LM, Dalurzo HC, Gómez MC, Romero-Puertas MC, Río LA (2001) Cadmium induces changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J Exp Bot 52:2115–2126
Shi HT (2016) Experimental guidance on plant stress physiology. Science Press, Beijing
Singh J, Chawla G, Naqvi SHN, Viswanathan PN (1994) Combined effects of cadmium and linear alkyl benzene sulfonate on Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicology 3(1):59–67
Singh S, Eapen S, Dsouza SF (2006) Cadmium accumulation and its influence on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative system in an aquatic plant, Bacopa monnieri L. Chemosphere 62(2):233–246
Song GA (2000) Prospects of surfactants used in home scour. Chem Industry Times 2:5–9
Temmink H, Klapwijk B (2004) Fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) in activated sludge plants. Water Res 38(4):903–912
Venhuis SH, Mehrvar M (2004) Health effects, environmental impacts, and photochemical degradation of selected surfactants in water. Int J Photoenergy 6:115–125
Verge C, Moreno A, Bravo J, Berna JL (2001) Influence of water hardness on the bioavailability and toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate (LAS). Chemosphere 44(8):1749–1757
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164(4):645–655
Waloszek A, Stanisław W (1994) Chloroplast pigment photobleaching and its effect on low temperature fluorescence spectra of chlorophyll in greening cucumber cotyledons. Photosynthetica 29(4):509–520
Wang Z, Xiao BD, Song LR, Wu XQ, Zhang JQ, Wang CB (2011) Effects of microcystin-LR, linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and their mixture on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) seeds and seedlings. Ecotoxicology 20(4):803–814
Wang Z, Xiao B, Song L, Wang C, Zhang J (2012) Responses and toxin bioaccumulation in duckweed (lemna minor) under microcystin-LR, linear alkybenzene sulfonate and their joint stress. J Hazard Mater 229-230:137–144
Wu ZH, Yu D, Wang D, Xia SL (2003) Structure and quantitative features of aquatic plant communities in the Hanjiang River. Acta Phytoecol Sinica 27(1):118–124
Wu ZH, Yu D, Li JL, Wu GG, Niu XN (2010) Growth and antioxidant response in hydrocharis dubis (bl.) backer exposed to linear alkylbenzene sulfonate. Ecotoxicology 19(4):761–769
Wu KH, Xiao SQ, Chen Q, Wang QF, Zhang YN, Li KZ, Yu Y, Chen L (2013) Changes in the activity and transcription of antioxidant enzymes in response to Al stress in black soybeans. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31(1):141–150
Xu F, Yang ZF, Chen B, Zhao YW (2013) Impact of submerged plants on ecosystem health of the plant-dominated Baiyangdian Lake, China. Ecol Model 252(1):167–175
Yamasaki H, Sakihama Y, Ikehara N (1997) Flavonoid-peroxidase reaction as a detoxification mechanism of plant cells against H2O2. Plant Physiol 115(4):1405–1412
Yu XZ, Stefan T, Zhou PH, Peng XY, Cao X (2006) Response of weeping willows to linear alkylbenzene sulfonate. Chemosphere 64(1):43–48
Zhao SJ, Xu CC, Zou Q, Meng QW (1991) Improvements of method for measurement of malondialdehvde in plant tissues. Plant Physiol Commun 30(3):207–210
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31270410, No. 30970303), the Special Foundation of National Science and Technology Basic Research (2013FY112300), and the Scientific Research Project of Hubei Province Environmental Protection Department (2014HB07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wu, Z., Yu, D. et al. Toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate to aquatic plant Potamogeton perfoliatus L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 32303–32311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3204-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3204-7