Abstract
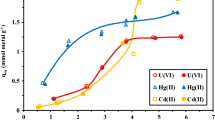
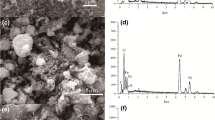
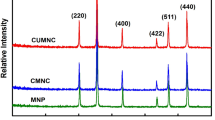
This comparative study investigates pre-concentration/separation procedure for the magnetic solid phase extraction of Hg(II) species by a new green materials: naked magnetic chitosan flakes coated Fe3O4 micro-particles (NMCFs) and magnetic chitosan flakes coated Fe3O4 micro-particles embedded ethylenediaminetetraacetic-disodium (MCFs-EDTA-Na2) in a batch process. The sorption procedure was optimized by using model solutions containing mercury(II) ions in chloride medium. The influence of experimental parameters like pH, time reaction, initial Hg(II) concentration, and ionic strength was investigated. The SEM micrograph indicates a good dispersion of magnetite micro-particles onto chitosan flakes. The FTIR spectrum reveals that EDTA-Na2 moieties have been successfully cross-linked onto magnetic chitosan flakes. Vibration magneto-metric measurements confirm the paramagnetic (without remanence) behavior of NMCFs and MCFs-EDTA-Na2. The experimental sorption data show that Hg(II) ions extraction yield decreases in acidic medium in both NMCFs and MCFs-EDTA-Na2. The found optimum pH values are near 4.5 using NMCFs and 4.7 when the Hg(II) ion sorption occurs onto MCFs-EDTA-Na2 micro-particles. The results also showed that Hg(II) ion sorption kinetic was very fast at the initial stage of contact time. The maximal sorption capacity was found to be 454 ± 13 mg g−1, under optimum conditions, using NMCFs and 495 ± 14 mg g−1 when MCFs-EDTA-Na2 was used.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh B, Delnavaz M, Shakeri A (2018) Removal of Cd(ӀӀ) and phenol using novel cross-linked magnetic EDTA/chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite. Carbohydr Polym 181:675–683
Allouche FN, Guibal E, Mameri N (2014) Preparation of a new chitosan-based material andits application for mercury sorption. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 446:224–232
Awwad NS, Gad HMH, Ahmad MI, Aly HF (2010) Sorption of lanthanum and erbium from aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared from rice husk. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 81:593–599
Bansal M, Ram B, Chauhan GS, Kaushik A (2018) l-Cysteine functionalized bagasse cellulose nanofibers for mercury(II) ions adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 112:728–736
Behjati M, Baghdadi M, Karbassi A (2018) Removal of mercury from contaminated saline wasters using dithiocarbamate functionalized-magnetic nanocomposite. J Environ Manag 213:66–78
Chakrabarty K, Saha P, Ghoshal AK (2010) Simultaneous separation of mercury and lignosulfonate from aqueous solution using supported liquid membrane. J Membr Sci 346:37–44
Chmielniak T, Słowik K, Sajdak M (2017) Mercury removal by mild thermal treatment of coal. Fuel 195:290–298
Cui H, Li D, Zhang Z (2015) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified by perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid surfactant. Mater Lett 143:38–40
Dąbrowski A, Hubicki Z, Podkościelny P, Robens E (2004) Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 56:91–106
Donia AM, Atia AA, Elwakeel KZ (2008) Selective separation of mercury(II) using magnetic chitosan resin modified with Schiff’s base derived from thiourea and glutaraldehyde. J Hazard Mater 151:372–379
Elkady MF, Mahmoud MM, Abd-El-Rahman HM (2011) Kinetic approach for cadmium sorption using microwave synthesized nano-hydroxyapatite. J Non-Cryst Solids 357:1118–1129
Elwakeel KZ (2010) Removal of Cr (VI) from alkaline aqueous solutions using chemically modified magnetic chitosan resins. Desalin Water Treat 250:105–112
Elwakeel KZ, Al-Bogami AS, Elgarahy AM (2018) Efficient retention of chromate from industrial wastewater onto a green magnetic polymer based on shrimp peels. J Polym Environ 26:2018–2029
Fan L, Luo C, Lv Z, Lu F, Qiu H (2011) Removal of Ag+ from water environment using a novel magnetic thiourea-chitosan imprinted Ag+. J Hazard Mater 194:193–201
Fan FL, Qin Z, Bai J, Rong WD, Fan FY, Tian W, Wu XL, Wang Y, Zhao L (2012) Rapid removal of uranium from aqueous solutions using magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 composite particles. J Environ Radioact 106:40–46
Figueira P, Lopes CB, Daniel ALD, Pereira E, Duarte AC, Trindade T (2011) Removal of mercury (II) by dithiocarbamate surface functionalized magnetite particles: application to synthetic and natural spiked waters. Water Res 45:5773–5784
Gavilan KC, Pestov AV, Maldonado HG, Yatluk Y, Roussy J, Guibal E (2009) Mercury sorption on a thiocarbamoyl derivative of chitosan. J Hazard Mater 165:415–426
Gode F, Pehlivan E (2003) A comparative study of two chelating ion-exchange resins for the removal of chromium(III) from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater B 100:231–243
Guibal E (2004) Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: a review. Sep Purif Technol 38:43–74
Hennion MC (1999) Solid-phase extraction: method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 856:3–54
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Jeon C, Park KH (2005) Adsorption and desorption characteristics of mercury(II) ions using aminated chitosan bead. Water Res 39:3938–3944
Kong X (2012) Simultaneous determination of degree of deacetylation, degree of substitution and distribution fraction of –COONa in carboxymethyl chitosan by potentiometric titration. Carbohydr Polym 88:336–341
Kumari M, Pittman CU, Mohan D (2015) Heavy metals [chromium (VI) and lead (II)] removal from water using mesoporous magnetite (Fe3O4) nanospheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 442:120–132
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelosterstoffe. K Sven Vetensk Akad Handl 24:1–39
Li H, Dl X, He H, Lin R, Pl Z (2013) Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 23:2657−2665
Mamani JB, Costa-Filho AJ, Cornejo DR, Vieira ED, Gamarra LF (2013) Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated with lauric acid. Mater Charact 81:28–36
Marczak M, Budzyń S, Szczurowski J, Kogut K, Burmistrz P (2018) Active methods of mercury removal from flue gases. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1772-1
Mohapatra S, Panda N, Pramanik P (2009) Boronic acid functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle as a novel tool for adsorption of sugar. Mater Sci Eng 292:254–2260
Nasiri moghaddam S, Zeinali S, Sabbaghi S (2015) Chitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbent for efficient removal of mercury contents from industrial aqueous and oily samples. J Ind Eng Chem 27:79–87
Papageorgiou SK, Kouvelos EP, Katsaros FK (2008) Calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata for the removal of Cu+2 and Cd+2 from dilute aqueous metal solutions. Desalin Water Treat 224:293–306
Peng H, Xiong H, Li J, Xie M, Liu Y, Bai C, Chen L (2010) Vanillin cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled release of resveratrol. Food Chem 121:23–28
Pestov A, Bratskaya S (2016) Chitosan and its derivatives as highly efficient polymer ligands. Molecules 21:330
Raji F, Pakizeh M (2014) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Hg(II) adsorption onto MCM-41 modified by ZnCl2. Appl Surf Sci 301:568–575
Rao KS, Chaudhury GR, Mishra BK (2010) Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions using Duolite ES 467 resin. Int J Miner Process 97:68–73
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 201-202:68–93
Şahan T, Erol F, Yılmaz Ş (2018) Mercury(II) adsorption by a novel adsorbent mercapto-modified bentonite using ICP-OES and use of response surface methodology for optimization. Microchem J 138:360–368
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sari A (2018) Polyamide magnetic palygorskite for the simultaneous removal of Hg(II) and methyl mercury; with factorial design analysis. J Environ Manag 211:323–333
Sgarlata C, Zito V, Arena G, Consoli GML, Galante E, Geraci C (2009) A sinapic acid–calix[4]arene hybrid selectively binds Pb2+ over Hg2+ and Cd2+. Polyhedron 28:343–348
Shehzad H, Zhou L, Li Z, Chen Q, Wang Y, Liu Z, Adesina AA (2017) Effective adsorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution using magnetic chitosan nanoparticles grafted with maleic anhydride: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 315:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5647-6
Shibata S (1961) Solvent extraction and spectrophotometric determination of metals with 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphtol. Anal Chim Acta 25:348–359
Sobahi TRA, Abdelaal MY, Makki MSI (2014) Chemical modification of chitosan for metal ion removal. Arab J Chem 7:741–746
Tan Y, Chen M, Hao Y (2012) High efficient removal of Pb (II) by amino-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nano-particles. Chem Eng J 191:104–111
Tan L, Zhang X, Liu Q, Jing X, Liu J, Song D, Hu S, Liu L, Wang J (2015) Synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2core–shell magnetic composites for highly efficient sorption of uranium (VI). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 469:279–286
Tang Y, Chen L, Wei X, Yao Q, Li T (2013) Removal of lead ions from aqueous solution by the dried aquatic plant, Lemna perpusilla Torr. J Hazard Mater 244– 245:603–612
Wang J, Xu W, Chen L, Huang X, Liu J (2014) Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles impregnated chitosan beads for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J 251:25–34
Wang Y, Dang F, Zhong H, Wei Z, Li P (2016) Effects of sulfate and selenite on mercury methylation in a mercury-contaminated rice paddy soil under anoxic conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4602–4608
Zhang S, Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu Q, Xiao H, Wang X, Xu H, Zhou J (2013) Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chem Eng J 226:30–38
Zhenchuan N, Zhang X, Wang S, Ci Z, Kong X, Wang Z (2013) The linear accumulation of atmospheric mercury by vegetable and grass leaves: Potential biomonitors for atmospheric mercury pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20: 6337–6343
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express his sincere thanks to Dr. Eric GUIBAL (Ecole des Mines d’Alès, Centre des matériaux et des mines C2MA, 6 Avenue de Clavières, F-30319 Ales Cedex, France) for his keen interest in the work. Also, a sincere thanks for Prof. Alexandru STANCU (University of Iași, Faculty of Physics, Department of Physics & CARPATH, Iași, 700506, Romania).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrah, N. Comparative study of mercury(II) species removal onto naked and modified magnetic chitosan flakes coated ethylenediaminetetraacetic-disodium: kinetic and thermodynamic modeling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 24923–24938 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2553-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2553-6