Abstract
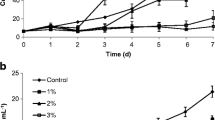
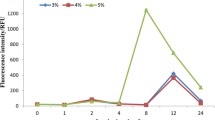
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) induced by Prorocentrum donghaiense occur frequently and cause a serious threat to the marine ecosystem. In this study, antialgal effects of α-linolenic acid (ALA) that is generally extracted from diverse macroalga on P. donghaiense were investigated. Specifically, the growth, cellular morphology and ultrastructure, reactive oxygen species (ROS) content, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), cytochrome C (Cyt-C), and caspase-9,3 activity of untreated and treated P. donghaiense were investigated. The results showed that ALA significantly inhibited the growth of P. donghaiense. Under ALA exposure, the cellular morphology and ultrastructure were damaged. ALA also induced ROS overproduction in the algal cells, decreased MMP, induced Cyt-C release, and activated caspase-9,3, which strongly relates to algal apoptosis. In summary, this study revealed the responses of morphology and physiology of P. donghaiense when exposed under ALA, and shows the potential of biotechnology on controlling P. donghaiense.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamsjah MA, Hirao S, Ishibashi F, Oda T, Fujita Y (2008) Algicidal activity of polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from Ulva fasciata and U. pertusa (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta) on phytoplankton. J Appl Phycol 20(5):713–720
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JAM (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25(4):704–726
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (2002) Defining hormesis. Hum Exp Toxicol 21(2):91–97
Das S, Ward LR, Burke C (2008) Prospects of using marine actinobacteria as probiotics in aquaculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(3):419–429
El-Kassas HY, Ghobrial MG (2017) Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles using three marine plant species: anti-algal efficiencies against “ Oscillatoria simplicissima ”. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(8):1–13
Fleury C, Mignotte B, Vayssière JL (2002) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie 84(2–3):131–141
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York, pp 29–60
He YY, Häder DP (2002) UV-B-induced formation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp.: protective effects of ascorbic acid and N-acetyl-l-cysteine. J Photochem Photobiol B 66(2):115–124
Hoko Z, Makado PK (2011) Optimization of algal removal process at Morton Jaffray water works, Harare, Zimbabwe. Phys Chem Earth Pt A/B/C 36(14–15):1141–1150
Ikawa M (2004) Algal polyunsaturated fatty acids and effects on plankton ecology and other organisms. UNH Center Freshwat Biol Res 6(2):17–44
Kuida K (2000) Caspase-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32(2):121–124
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/Caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91(4):479–489
Liu L, Yan H, Li C, Zhou Y, Zhang TT (2014) Interactions between heavy metal lead and two freshwater algae. Acta Ecol Sin 34(7):1690–1697
Lopes VM, Rita LA, Pedro C, Rui R (2013) Cephalopods as vectors of harmful algal bloom toxins in marine food webs. Marine Drugs 11(9):3381–3409
Lou I, Gong S, Huang X, Liu Y, Mok KM (2013) Coagulation optimization using ferric and aluminum salts for treating high algae and high alkalinity source water in a typical North-China plant. Desalin Water Treat 51(16–18):3361–3370
Lu DD, Goebel J (2001) Five red tide species in genus Prorocentrum including the description of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu SP. nov. from the East China Sea. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 19(4):337–344
Lu X, Zhou B, Xu L, Liu L, Wang G, Liu X, Tang X (2016) A marine algicidal Thalassospira and its active substance against the harmful algal bloom species Karenia mikimotoi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(11):5131–5139
Ly JD, Grubb DR, Lawen A (2003) The mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 8(2):115–128
Ma Z, Wu M, Lin L, Thring RW, Yu H, Zhang X, Zhao M (2017) Allelopathic interactions between the macroalga Hizikia fusiformis (Harvey) and the harmful blooms-forming dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. Harmful Algae 65:19–26
Muller-Feuga A (2000) The role of microalgae in aquaculture: situation and trends. J Appl Phycol 12(3–5):527–534
Park J, Lee J, Choi C (2012) Mitochondrial network determines intracellular ROS dynamics and sensitivity to oxidative stress through switching inter-mitochondrial messengers. PLoS One 6(1):e23211–e23283
Pichierri S, Accoroni S, Pezzolesi L, Guerrini F, Romagnoli T, Pistocchi R, Totti C (2017) Allelopathic effects of diatom filtrates on the toxic benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. Mar Environ Res:131
Pokrzywinski KL, Tilney CL, Modla S, Caplan JL, Ross J, Warner ME, Coyne KJ (2017) Effects of the bacterial algicide IRI-160AA on cellular morphology of harmful dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 62:127–135
Rice EL (1984) Natural ecosystems: ecological effects of algal allelopathy. In: Elroy LR (ed) Allelopathy, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 189–205
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, Sil PC (2013) Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1157–1180
Tang DL, Di BP, Wei G, Ni IH, Oh IS, Wang SF (2006) Spatial, seasonal and species variations of harmful algal blooms in the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Hydrobiologia 568(1):245–253
Wang R, Xiao H, Wang Y, Zhou W, Tang X (2007a) Effects of three macroalgae, Ulva linza (Chlorophyta), Corallina pilulifera (Rhodophyta) and Sargassum thunbergii (Phaeophyta) on the growth of the red tide microalga Prorocentrum donghaiense under laboratory conditions. J Sea Res 58(3):189–197
Wang R, Xiao H, Zhang P, Qu L, Cai H, Tang X (2007b) Allelopathic effects of Ulva pertusa, Corallina pilulifera and Sargassum thunbergii on the growth of the dinoflagellates Heterosigma akashiwo and Alexandrium tamarense. J Appl Phycol 19(2):109–121
Wang R, Wang Y, Tang X (2012) Identification of the toxic compounds produced by Sargassum thunbergii to red tide microalgae. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 30(5):778–785
Wang HQ, Zhu HJ, Zhang LY, Xue WJ, Yuan B (2014) Identification of antialgal compounds from the aquatic plant Elodea nuttallii. Allelopath J 34(2):207–213
Xiao X, Huang H, Ge Z, Rounge TB, Shi J, Xu X, Li R, Chen Y (2014) A pair of chiral flavonolignans as novel anti-cyanobacterial allelochemicals derived from barley straw (Hordeum vulgare): characterization and comparison of their anti-cyanobacterial activities. Environ Microbiol 16(5):1238–1251
Yu H, Hu HY, Xing X, Sakoda A, Sagehashi M, Li FM (2009) Gramine-induced growth inhibition, oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 91(3):262–269
Yu X, Cai G, Wang H, Hu Z, Zheng W, Lei X, Zhu X, Chen Y, Chen Q, Din H (2017) Fast-growing algicidal Streptomyces sp. U3 and its potential in harmful algal bloom controls. J Hazard Mater 341:138
Zhang XF, Liu YJ (2007) Advances in the biological study of Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu. Ecol Environ 16(3):1053–1057
Zhang X, Tang X, Wang M, Zhang W, Zhou B, Wang Y (2017) ROS and calcium signaling mediated pathways involved in stress responses of the marine microalgae Dunaliella salina to enhanced UV-B radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 173:360–367
Zhou M, Zhu M, Zhang J (2001) Status of harmful algal blooms and related research activities in China. Chin Bull Life Sci 13:54–59,53
Zhou M, Yan T, Zhou J (2003) Preliminary analysis of the characteristics of red tide areas in Changjiang River estuary and its adjacent sea. Chin J Appl Ecol 14(7):1031–1038
Zhou W, Yin K, Dedi Z (2006) Phytoplankton biomass and high frequency of Prorocentrum donghaiense harmful algal bloom in Zhoushan sea area in spring. Chin J Appl Ecol 17(5):887–893
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31500414 and 31200400), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Nos. ZR2015CL015 and ZR2017MC037), Foundation for Outstanding Young Scientist in Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2016CB27), and Project of Science and Technology in Qufu Normal University (Grant No. xkj201608).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vitor Manuel Oliveira Vasconcelos
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Chen, J., Ding, N. et al. Antialgal effects of α-linolenic acid on harmful bloom-forming Prorocentrum donghaiense and the antialgal mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 24798–24806 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2536-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2536-7