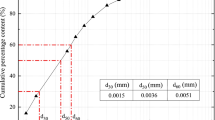
Abstract
Municipal sludge, composed of numerous types of organic matter with a gel structure, has high water content, low permeability coefficient, and poor mechanical properties. Fenton oxidation-assisted vacuum preloading method for municipal sludge treatment was proposed. First, the municipal sludge was oxidized and treated with Fenton’s reagent; then, drainage consolidation was performed on the sludge with the vacuum preloading method. The optimal dosage of Fenton’s reagent for municipal sludge was determined. Comparative experiments of the one-dimensional consolidation of municipal sludge treated with Fenton’s reagent and the drainage consolidation by Fenton oxidation-assisted vacuum preloading were conducted. The results reveal that the specific resistance of municipal sludge decreases upon Fenton oxidation by approximately 98.6% at the optimal dosage of 22%, sludge water content decreases from 82.14 to 66.67%, volume reduces by ~ 40%, and unconfined compressive strength increases to 55 kPa.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amudha V, Kavitha S, Fernandez C et al (2016) Effect of deflocculation on the efficiency of sludge reduction by Fenton process. Environ Sci Pollut Res :1–11
Chai JC, Carter JP, Hayashi S (2005) Ground deformation induced by vacuum consolidation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 131:1552–1561
Chai JC, Ong CY, Carter JP et al (2013) Lateral displacement under combined vacuum pressure and embankment loading. Geotechnique 63:842–856
Dewil R, Baeyens J, Neyens E (2005) Fenton peroxidation improves the drying performance of waste activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 117:161–170
Ealias AM, Jose JV, Saravanakumar MP (2016) Biosynthesised magnetic iron nanoparticles for sludge dewatering via Fenton process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1–15
Feng Y, Luo XY, Lin WA et al (2013) Geotechnical properties measurement of sewage sludge at a disposal site. Rock Soil Mech 34:115–122 (in Chinese)
Guezennec AG, Michel C, Bru K et al (2015) Transfer and degradation of polyacrylamide-based flocculants in hydrosystems: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:6390–6406
Imc L, Lai KC, Chen GH (2001) Salinity effect on mechanical dewatering of sludge with and without chemical conditioning. Environ Sci Technol 35:4691–4696
Lee SS, Shah HS, Awad YM, Kumar S, Ok YS (2015) Synergy effects of biochar and polyacrylamide on plants growth and soil erosion control. Environ Earth Sci 74:2463–2473
Lentz RD (2015) Polyacrylamide and biopolymer effects on flocculation, aggregate stability, and water seepage in a silt loam. Geoderma 241-242:289–294
Li F-H, Wang A-P (2016) Interaction effects of polyacrylamide application and slope gradient on potassium and nitrogen losses under simulated rainfall. Catena 136:162–174
Lin WA, Zhan XJ, Zhan TL et al (2014) Effect of FeCl3-conditioning on consolidation property of sewage sludge and vacuum preloading test with integrated PVDs at the Changan landfill, China. Geotext Geomembr 42:181–190
Lu MC, Lin CJ, Liao CH et al (2001) Influence of pH on the dewatering of activated sludge by Fenton’s reagent. Wat Sci Technol 44:327–332
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Department of the People’s Republic of China (2012) The technical guidelines of sludge treatment in urban sewage treatment plant (trial). China Construction Industry Press, pp:54–65 (in Chinese)
Nanjing Institute of Hydraulic Engineering Geotechnical Research Institute (2003) Geotechnical test technology manual. People’s Transportation Press, Nanjing (in Chinese)
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J Hazard Mater 98:33–50
Neyens E, Baeyens J, Dewil R, Heyder BD (2004) Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. J Hazard Mater 106:83–92
O’Kelly BC (2006) Geotechnical properties of municipal sewage sludge. Geotech Geol Eng 24:833–850
Ribeiro MC, Starling MC, Leão MM et al (2016) Textile wastewater reuse after additional treatment by Fenton’s reagent. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:1–11
Ruiz T, Kaosol T, Wisniewski C (2010) Dewatering of urban residual sludges: filterability and hydro-textural characteristics of conditioned sludge. Sep Purif Technol 72:275–281
Taylor DW (1948) Fundamentals of soil mechanics. John Wiley & Sons
Thapa KB, Qi Y, Clayton SA, Hoadley AFA (2009) Lignite aided dewatering of digested sewage sludge. Water Res 43:623–634
Wu YJ, Kong GQ, Lu YT, Sun DA (2015) Ground deformation induced by vacuum loading-unloading. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–8
Wu YJ, Xu F, Yuan M, Sun DA (2017) Experimental study on vacuum preloading with flocculation for solid-liquid separation in waste slurry. Geomech Eng 13:319–331
Zhan LT, Zhang P, Zhan X, Lin W (2016) Experimental study on inhibition effect of chemical conditioning on low permeability sewage sludge layer under conditions of vacuum preloading. J Southeast Univ 46:7–13 (in Chinese)
Zhou Z, Qiao WM, Xing C et al (2014) Sludge reduction and performance analysis of a modified sludge reduction process. Water Sci Technol 69:934–940
Zhu H, Sun HY, Wang FH, Zou J, Fan JT (2012) Preparation of chitosan-based flocculant for high density waste drilling mud solid-liquid separation. J Appl Polym Sci 125(4):2646–2651
Funding
The research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41772303) and Shanghai Natural Science Foundation, China (17ZR1410100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Lin, Z., Kong, G. et al. Treatment of municipal sludge by Fenton oxidation combined vacuum preloading. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 15990–15997 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1736-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1736-5