Abstract
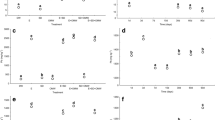
The in situ stabilization has been widely used to remediate metal-contaminated soil. However, the long-term retaining performance of heavy metals and the associated risk after in situ stabilization remains unclear and has evoked amounting concerns. Here, Pb- or As-contaminated soil was stabilized by a commercial amendment. The availability of Pb and As after in situ stabilization were estimated by ten different in vitro chemical extractions and DGT technique. After amendment application, a significant decline in extractable Pb or As was observed in treatments of Milli-Q water, 0.01 M CaCl2, 0.1 M NaNO3, 0.05 M (NH4)2SO4, and 0.43 M HOAc. Potential available metal(loid)s determined by DGT also showed remarkable reduction. Meanwhile, the results of in vivo uptake assays demonstrated that Pb concentrations in shoots of ryegrass Lolium perenne L. declined to 12% of the control samples, comparable to the extraction ratio of 0.1 M NaNO3 (15.8%) and 0.05 M (NH4)2SO4 (17.3%). For As-contaminated soil, 0.43 M HOAC provided a better estimation of relative phytoavailability (64.6 vs. 65.4% in ryegrass) compared to other extraction methods. We propose that 0.1 M NaNO3 or 0.05 M (NH4)2SO4 for Pb and 0.43 M HOAc for As may serve as surrogate measures to estimate the lability of metal(loid)s after soil remediation of the tested contaminated soils. Further studies over a wider range of soil types and amendments are necessary to validate extraction methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouwman LA, Vangronsveld J (2004) Rehabilitation of the nematode fauna in a phytostabilized, heavily zinc-contaminated, sandy soil. J Soils Sediments 4:17–23
Bouwman LA, Bloem J, Romkens P, Boon GT, Vangronsveld J (2001) Beneficial effects of the growth of metal tolerant grass on biological and chemical parameters in copper- and zinc-contaminated sandy soils. Minerva Biotecnologica 13:19–26
Chapman EEV, Dave G, Murimboh JD (2012) Bioavailability as a factor in risk assessment of metal-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2907–2922
Degryse F, Smolders E (2012) Cadmium and nickel uptake by tomato and spinach seedlings: plant or transport control. Environ Chem 9:48–54
Degryse F, Shahbazi A, Verheyen L, Smolders E (2012) Diffusion limitations in root uptake of cadmium and zinc, but not nickel, and resulting bias in the Michaelis constant. Plant Physiol 160:1097–1109
Fitz WJ et al (2003) Rhizosphere characteristics of the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and monitoring of phytoremoval efficiency. Environ Sci Technol 37:5008–5014
Fu QL, He JZ, Gong H, Blaney L, Zhou DM (2016) Extraction and speciation analysis of roxarsone and its metabolites from soils with different physicochemical properties. J Soils Sediments 16:1557–1568
Garrabrants AC, Kosson DS (2000) Use of a chelating agent to determine the metal availability for leaching from soils and wastes. Waste Manag 20:155–165
Kim RY, Yoon JK, Kim TS, Yang JE, Owens G, Kim KR (2015) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: definitions and practical implementation—a critical review. Environ Geochem Health 37:1041–1061
Lakanen E, Erviö R (1971) A comparison of eight extractants for the determination of plant available micronutrients in soils. Suomen Maataloustieteellinen Seura 123:223–232
Lee SS, Lim JE, Abd El-Azeem SAM, Choi B, Oh S-E, Moon DH, Ok YS (2013) Heavy metal immobilization in soil near abandoned mines using eggshell waste and rapeseed residue. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1719–1726
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Liu JL, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Anderson CWN, Yao H (2012) Prediction of methyl mercury uptake by rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) using the diffusive gradient in thin films technique. Environ Sci Technol 46:11013–11020
Luo J, Cheng H, Ren J, Davison W, Zhang H (2014) Mechanistic insights from DGT and soil solution measurements on the uptake of Ni and Cd by radish. Environ Sci Technol 48:7305–7313
McLaughlin MJ, Zarcinas BA, Stevens DP, Cook N (2000) Soil testing for heavy metals. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1661–1700
Menzies NW, Donn MJ, Kopittke PM (2007) Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phytoavailable trace metals in soils. Environ Pollut 145:121–130
Moon DH, Cheong KH, Koutsospyros A, Chang YY, Hyun S, Ok YS, Park JH (2016) Assessment of waste oyster shells and coal mine drainage sludge for the stabilization of As-, Pb-, and Cu-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2362–2370
Ngo LK, Pinch BM, Bennett WW, Teasdale PR, Jolley DF (2016) Assessing the uptake of arsenic and antimony from contaminated soil by radish (Raphanus sativus) using DGT and selective extractions. Environ Pollut 216:104–114
Peijnenburg WJGM, Zablotskaja M, Vijver MG (2007) Monitoring metals in terrestrial environments within a bioavailability framework and a focus on soil extraction. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:163–179
Ruttens A, Mench M, Colpaert JV, Boisson J, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2006) Phytostabilization of a metal contaminated sandy soil. I: influence of compost and/or inorganic metal immobilizing soil amendments on phytotoxicity and plant availability of metals. Environ Pollut 144:524–532
Sanka M, Dolezal M (1992) Prediction of plant contamination by cadmium and zinc based on soil extraction method and contents in seedlings. Int J Environ Anal Chem 46:87–96
Sneath HE, Hutchings TR, de Leij F (2013) Assessment of biochar and iron filing amendments for the remediation of a metal, arsenic and phenanthrene co-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 178:361–366
Sun B, Zhao FJ, Lombi E, McGrath SP (2001) Leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soils using EDTA. Environ Pollut 113:111–120
Sun YB, Sun GH, Xu YM, Liu WT, Liang XF, Wang L (2016) Evaluation of the effectiveness of sepiolite, bentonite, and phosphate amendments on the stabilization remediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. J Environ Manag 166:204–210
Szakova J, Tlustos P, Goessler W, Frkova Z, Najmanova J (2009) Mobility of arsenic and its compounds in soil and soil solution: the effect of soil pretreatment and extraction methods. J Hazard Mater 172:1244–1251
USEPA (1994a) Method 1312: synthetic precipitation leaching procedure. In Test methods for evaluating solid waste (SW-846)
USEPA (1994b) Method 1311: toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. In Test methods for evaluating solid waste (SW-846)
Voegelin A, Weber F-A, Kretzschmar R (2007) Distribution and speciation of arsenic around roots in a contaminated riparian floodplain soil: micro-XRF element mapping and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:5804–5820
Wang P, Zhou D, Weng N, Wang D, Peijnenburg WJGM (2011) Calcium and magnesium enhance arsenate rhizotoxicity and uptake in Triticum aestivum. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:1642–1648
Wang JJ, Bai LY, Zeng XB, Su SM, Wang YN, Wu CX (2014) Assessment of arsenic availability in soils using the diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) technique—a comparison study of DGT and classic extraction methods. Environ Sci: Processes Impacts 16:2355–2361
Wenzel WW, Kirchbaumer N, Prohaska T, Stingeder G, Lombi E, Adriano DC (2001) Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure. Anal Chim Acta 436:309–323
Zhang H, Davison W (2015) Use of diffusive gradients in thin-films for studies of chemical speciation and bioavailability. Environ Chem 12:85–101
Zhang H, Davison W, Knight B, McGrath S (1998) In situ measurements of solution concentrations and fluxes of trace metals in soils using DGT. Environ Sci Technol 32:704–710
Zhang H, Zhao FJ, Sun B, Davison W, McGrath SP (2001) A new method to measure effective soil solution concentration predicts copper availability to plants. Environ Sci Technol 35:2602–2607
Zhang H, Davison W, Mortimer RJG, Krom MD, Hayes PJ, Davies IM (2002) Localised remobilization of metals in a marine sediment. Sci Total Environ 296:175–187
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Research Projects of Environmental Protection Public Welfare Industry in China (201509035) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41671484) for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Yang, J., Li, Z. et al. Assessment of the availability of As and Pb in soils after in situ stabilization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 23153–23160 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9877-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9877-5