Abstract
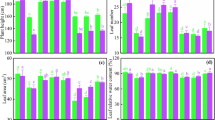
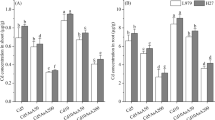
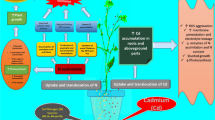
Cadmium (Cd) contamination of farmland soils is a widespread problem around the globe, and rice (Oryza sativa L.) tends to accumulate more Cd and is considered as one of the major sources of Cd intake in humans, especially consuming rice-derived products. The current study investigated the effects of foliar applied aspartic acid (Asp) on growth parameters, biomass, chlorophyll concentration, gas exchange characteristics, Cd uptake, and antioxidative capacity in the shoots and roots of rice seedlings exposed to Cd stress. For this, 30-day-old rice nursery was transferred in the soil with aged Cd contamination (2.86 mg kg−1). After 2 weeks of growth, different concentrations (0, 10, 15, and 20 mg L−1) of Asp were foliar applied four times with a 7-day interval, and the crop was harvested after 10 weeks of transplanting. Foliar applied Asp increased the plant height, shoot and root dry weight, chlorophyll concentration, and gas exchange parameters, while it reduced the Cd concentrations in both shoots and roots as well as shoot to root Cd translocation factor compared to the control. Foliar application of Asp reduced the malondialdehyde content and electrolyte leakage in rice parts compared to the control in a dose-additive manner. The activities of key antioxidant enzymes increased while peroxidase activity decreased by exogenous Asp. The increase in plant weight and photosynthesis might be due to lower Cd concentrations in plants which may reduce the oxidative stress and also help the plants to minimize direct damage caused by Cd to the photosynthetic organs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Abbas F, Hannan F, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2017) Effect of biochar on cadmium bioavailability and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:37–47
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad MK (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou W (2015b) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One 10:1–23
Ali B, Huang CR, Qi ZY, Ali S, Daud MK, Geng XX, Liu HB, Zhou WJ (2013a) 5-Aminolevulinic acid ameliorates cadmium-induced morphological, biochemical, and ultrastructural changes in seedlings of oilseed rape. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7256–7267
Ali B, Qian P, Sun R, Farooq MA, Gill RA, Wang J, Azam M, Zhou W (2015a) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates the aluminum-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by physiochemical and ultrastructural study of plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3068–3081
Ali B, Wang B, Ali S, Ghani MA, Hayat MT, Yang C, Xu L, Zhou WJ (2013b) 5-Aminolevulinic acid ameliorates the growth, photosynthetic gas exchange capacity, and ultrastructural changes under cadmium stress in Brassica napus L. J Plant Growth Regul 32:604–614
Anjum NA, Sharma P, Gill SS, Hasanuzzaman M, Khan EA, Kachhap K, Mohamed AA, Thangavel P, Devi GD, Vasudhevan P, Sofo A (2016) Catalase and ascorbate peroxidase-representative H2O2-detoxifying heme enzymes in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19002–19029
Araujo RP, Almeida AAF, Peeira LS, Mangabeira PAO, Souza JO, Pirovani CP, Ahnert D, Baligar VC (2017) Photosynthetic, antioxidative, molecular and ultrastructural responses of young cacao plants to Cd toxicity in the soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:148–157
Azevedo RA, Lancien M, Lea PJ (2006) The aspartic acid metabolic pathway, an exciting and essential pathway in plants. Amino Acids 30:143–162
Boras M, Zidan R, Halloum W (2011) Effect of amino acids on growth, production and quality of tomato in plastic greenhouse. Tishreen Univ J Res Sci Stud Biol Sci Ser 33:229–238
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agron J 54:464–465
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased level of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
El-Zohiri SSM, Asfour YM (2009) Effect of some organic compounds on growth and productivity of some potato cultivars. Ann Agric Sci Moshtohor 47:403–415
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gill SS, Anjum NA, Gill R, Yadav S, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M, Mishra P, Sabat SC, Tuteja N (2015) Superoxide dismutase-mentor of abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10375–10394
He S, Yang X, He Z, Baligar VC (2017) Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: a review. Pedosphere 27:421–438
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (ed) Methods Enzymol vol 148:350–382
Liu JG, Qu P, Zhang W, Dong Y, Li L, Wang MX (2014) Variations among rice cultivars in subcellular distribution of Cd: the relationship between translocation and grain accumulation. Environ Exp Bot 107:25–31
Liu Xing Q, Chen HY, Qin-xue N, Seung LK (2008) Evaluation of the role of mixed amino acids in nitrate uptake and assimilation in leafy radish by using 15n-labeled nitrate. Agric Sci CHN 7:1196–1202
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62:21–37
Medici LO, Azevedo RA, Smith RJ, Lea PJ (2004) The influence of nitrogen supply on antioxidant enzymes in plant roots. Funct Plant Biol 31:1–9
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis (part 2). Chemical andmicrobiological properties. Agron. 9. SSSA, Madison
Rai VK (2002) Role of amino acids in plant responses to stress. Biol Plant 45:471–478
Rehman MZ, Khalid H, Akmal F, Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Iqbal M, Khalid MU, Azhar M (2017) Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ Pollut 227:560–568
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soils and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, ZRehman MZ, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016b) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Tsang DC, Rehman MZ, Zahir ZA, Rinklebe J, Tack FM, Ok YS (2017) A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 182:90–105
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016a) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17859–17879
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016c) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Jones DJ (2001) Function and mechanism of organic anion exudation from plant roots. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:527–560
Sadak MS, Abdelhamid MT (2015) Influence of amino acids mixture application on some biochemical aspects, antioxidant enzymes and endogenous polyamines of Vicia faba plant grown under seawater salinity stress. Gesunde Pflanzen 67:119–129
Sadak MSH, Abdelhamid MT, Schmidhalter U (2015) Effect of foliar application of aminoacids on plant yield and some physiological parameters in bean plants irrigated with seawater. Acta Biol Colomb 20:141–152
Saeed MR, Kheir AM, Al-Sayed AA (2005) Supperssive effect of some amino acids against Meloidogyne incognita on soybeans. J Agric Sci Mansoura Univ 30:1097–1103
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2006) The significance of amino acids and amino acid-derived molecules in plant responses and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J Exp Bot 57:711–726
Soltanpour PN (1985) Use of AB-DTPA soil test to evaluate elemental availability and toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 16:323–338
Teixeira WF, Fagan EB, Soares LH, Umburanas RC, Reichardt K, Neto DD (2017) Foliar and seed application of amino acids affects the antioxidant metabolism of the soybean crop. Front Plant Sci 8:1–14
US Salinity Laboratory Staff (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agriculture Handbook 60. United States Salinity Laboratory, USDA, Washington DC, p 160
Xie PP, Deng JW, Zhang HM, Ma YH, Cao DJ, Ma RX, Liu RJ, Liu C, Liang YG (2015) Effects of cadmium on bioaccumulation and biochemical stress response in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:392–398
Yu F, Liu K, Li M, Zhou Z, Deng H, Chen B (2013) Effects of cadmium on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative defences of rice (Oryza sativa L.) Int J Phytorem 15:513–521
Yu H, Wang JL, Fang W, Yuan JG, Yang ZY (2006) Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Sci Total Environ 370:302–309
Zhang JX, Kirham MB (1994) Drought stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791
Zhang XZ (1992) Themeasurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. In: Zhang XZ (ed) Research methodology of crop physiology. Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 208–211
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan and Government College University of Faisalabad, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizwan, M., Ali, S., Zaheer Akbar, M. et al. Foliar application of aspartic acid lowers cadmium uptake and Cd-induced oxidative stress in rice under Cd stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 21938–21947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9860-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9860-1