Abstract
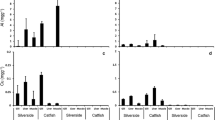
Although the impacts of large dams on freshwater biota are relatively well known, the effects of small hydropower plants (SHP) are not well investigated. In this work, we studied if mercury (Hg) concentrations in fish rise in two tropical SHP reservoirs, and whether similar effects take place during impoundment. Total Hg concentrations in several fish species were determined at two SHP in the Upper Guaporé River basin floodplain, Brazil. In total, 185 specimens were analysed for Hg content in dorsal muscle and none of them reported levels above the safety limit (500 μg kg−1) for fish consumption recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The highest levels of Hg (231 and 447 μg kg−1) were found in carnivorous species in both reservoirs. Mercury increased as a function of standard length in most of the fish populations in the reservoirs, and higher Hg concentrations were found in fish at the reservoir compared with fish downstream. The high dissolved oxygen concentrations and high transparency of the water column (i.e. oligotrophic reservoir) together with the absence of thermal stratification may explain low Hg methylation and low MeHg levels found in fish after flooding. Overall, according to limnological characteristics of water, we may hypothesise that reservoir conditions are not favourable to high net Hg methylation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastos WR, Malm O, Pfeiffer WC, Cleary D (1998) Establishment and analytical quality control of laboratories for Hg determination in biological and geological samples in the Amazon. Brazil Ciência Cultura 50:255–260
Belger L, Forsberg BR (2006) Factors controlling Hg levels in two predatory fish species in the Negro river basin, Brazilian Amazon. Sci Total Environ 367:451–459
Bloom NS, Watras, CJ, Hurley JP (1991) Impact of acidification on the methylmercury cycle of remote seepage lakes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 56:477–491
Bodaly RA, Jansen WA, Majewski AR, Fudge RJP, Strange NE, Derksen AJ, Green DJ (2007) Postimpoundment time course of increased mercury concentrations in fish in hydroelectric reservoirs of Northern Manitoba, Canada. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:379–389. doi:10.1007/s00244-006-0113-4
Britski HA, Silimon KZ, Lopes BS (1999) Peixes do Pantanal: manual de identificação. Embrapa-SPI, Brasília/Embrapa Pantanal, Corumbá: 184
Canavan CM, Caldwell CA, Bloom NS (2000) Discharge of methylmercury enriched hypolimnetic water from a stratified reservoir. Sci Total Environ 260:159–170
Ceccatto APS, Testoni MC, ARA I, Santos-Filho M, Malm O, Díez S (2016) Mercury distribution in organs of fish species and the associated risk in traditional subsistence villagers of the Pantanal wetland. Environ Geochem Health 38:713–722. doi:10.1007/s10653-015-9754-4
Chen CY, Folt C (2005) High plankton densities reduce mercury biomagnification. Environ Sci Technol 39:115–121
Clayden M, Kidd K, Wyn B, Kirk J, Muir D, O'Driscoll N (2014) Response to comment on “Mercury biomagnification through food webs is affected by physical and chemical characteristics of lakes”. Environ Sci Technol 48:10526–10527
Corrêa CE, Petry AC, Hahn NS (2009) Influência do ciclo hidrológico na dieta e estrutura trófica da ictiofauna do rio Cuiabá, Pantanal Mato-Grossense. Iheringia Sér Zool 99:456–463
Da Silva CJ, Girard P (2004) New challenges in the management of the Brazilian Pantanal and catchment area. Wet Eco Man 12:553–561
Díez S (2009) Human health effects of methylmercury exposure. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 198:111–132
Dominique Y, Maury-Brachet R, Muresan B, Vigouroux R, Richard S, Cossa D, Mariotti A, Boudou A (2007) Biofilm and mercury availability as key factors for mercury accumulation in fish (Curimata cyprinoids) from a disturbed Amazonian freshwater system. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:45–52
Giora J, Fialho CB, Dufech APS (2005) Feeding habit of Eigenmannia trilineata Lopez Castello, 1966 (Teleostei: Sternopygidae) of Parque Estadual de Itapuã, RS, Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 3:291–298
Guimarães JRD, Meili M, Malm O, Brito EMS (1998) Hg methylation in sediments and floating meadows of a tropical lake in the Pantanal floodplain, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 213:165–175
Hahn NS, Agostinho AA, Gomes LC, Bini LM (1998) Estrutura trófica da ictiofauna do reservatório de Itaipu (Paraná – Brasil) nos primeiros anos de sua formação. Interciência 23(5):229–235
Hammerschmidt CR, Fitzgerald WF (2006) Photodecomposition of methylmercury in an arctic Alaskan lake. Environ Sci Technol 40:1212–1216
Hylander LD, Pinto FN, Guimarães JRD, Meili M, Oliveira LJ, Castro e Silva E (2000) Fish mercury concentration in the Alto Pantanal, Brazil: influence of season and water parameters. Sci Total Environ 261:9–20
Hylander LD, Gröhn J, Tropp M, Vikström A, Wolpher H, Castro e Silva E, Meili M, Oliveira LJ (2006) Fish mercury increase in Lago Manso, a new hydroelectric reservoir in tropical Brazil. J Environ Manag 81:155–166
Ikingura JR, Akagi H (2003) Total mercury and methylmercury levels in fish from hydroelectric reservoirs in Tanzania. Sci Total Environ 304:355–368
Ioris AAR (2013) Rethinking Brazil’s Pantanal wetland: beyond narrow development and conservation debates. J Environ Develop 22:239–260
IPCS (1990). International Programme on Chemical Safety (Environmental Health Criteria 101: Methylmercury, World Health Organization, Geneva) http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc101.htm
Kasper D, Palermo EFA, Dias ACMI, Ferreira GL, Leitão RP, Branco CWC, Malm O (2009) Mercury distribution in different tissues and trophic levels of fish from a tropical reservoir, Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 7:751–758
Kasper D, Palermo EFA, Branco CWC, Malm O (2012) Evidence of elevated mercury levels in carnivorous and omnivorous fishes downstream from an Amazon Reservoir. Hydrobiologia 694:87–98
Kasper D, Forsberg BR, Amaral JH, Leitão RP, Py-Daniel SS, Bastos WR, Malm O (2014) Reservoir stratification affects methylmercury levels in river water, plankton, and fish downstream from Balbina hydroelectric dam, Amazonas, Brazil. Environ Sci Technol 48:1032–1040
Kehrig HA, Howard BM, Malm O (2008) Methylmercury in a predatory fish (Cichla spp.) inhabiting the Brazilian Amazon. Environ Pollut 154:68–76
Lázaro WL, Guimarães JRD, Ignácio ARA, da Silva CJ, Díez S (2013) Cyanobacteria enhance methylmercury production: a hypothesis tested in the periphytonn of two lakes in the Pantanal floodplain, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 456-457:231–238
Lázaro WL, de Oliveira RF, dos Santos-Filho M, da Silva CJ, Malm O, Ignácio ARA, Díez S (2015) Non-lethal sampling for mercury evaluation in crocodilians. Chemosphere 138:25–32
Malm O, Palermo EFA, Santos HSB, Rebelo MF, Kehrig HA, Oliveira RB, Meire RO, Pinto FN, Moreira LPA, Guimarães JRD, Torres JPM, Pfeiffer WC (2004) Transport and cycling of mercury in Tucuruí reservoir, Amazon, Brazil: 20 years after fulfillment. RMZ Mater Geoenviron 51:1195–1198
Mazzoni R, Nery L, Iglesias RI (2010) Ecologia e ontogenia da alimentação de Astyanax janeiroensis (Osteichthyes, Characidae) de um riacho costeiro do Sudeste do Brasil. Biota Neotrop 10:53–60
Mirlean N, Larned ST, Nikora V, Kütter VT (2005) Mercury in lakes and lake fishes on a conservation-industry gradient in Brazil. Chemosphere 60:226–236
Palermo EFA, Kasper D, Reis TS, Nogueira S, Branco CWC, Malm O (2004) Mercury level increase in fish tissues downstream the Tucuruí Reservoir, Brazil. RMZ Mater Geoenviron 51:1292–1294
Pereira RAC, Resende EK (2006) Alimentação de Gymnotus cf. carapo (Pisces: Gymnotidae) e suas relações com a Fauna Associada às Macrófitas Aquáticas no Pantanal, Brasil. EMBRAPA-CPAP, Corumbá: 21
Pickhardt PC, Folt CL, Chen CY, Klaue B, Blum JD (2002) Algal blooms reduce the uptake of toxic methylmercury in freshwater food webs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:4419–4423
Porvari P (1995) Mercury levels of fish in Tucurui hydroelectric reservoir and in River Mojti in Amazonia, in the state of Para brazil. Sci Total Environ 175:109–117
Pouilly M, Rejas D, Pérez T, Duprey JL, Molina CI, Hubas C, Guimarães JRD (2013) Trophic structure and mercury biomagnification in tropical fish assemblages, Iténez River, Bolivia. PLoS One 8(5):e65054. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065054
Resende EK, Pereira RAC, Almeida VLL, Silva AG (1996) Alimentação de peixes carnívoros da planície inundável do rio Miranda, Pantanal, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brasil. EMBRAPA-CPAP, Corumbá: 36
Resende EK, Pereira RAC, Almeida VLL, Silva AG (1998) Peixes onívoros da planície inundável do rio Miranda, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brasil. EMBRAPA-CPA,Corumbá: 28
Schetagne R, Verdon R (1999) Post-impoundment evolution of fish mercury levels at the La Grande complex, Québec, Canada from 1978 to 1996. In: Lucotte M, Schetagne R, Thérien N, Langlois C, Tremblay A (eds) Mercury in the biogeochemical cycle: natural environments and hydroelectric reservoirs of northern Québec, Environmental science series. Springer, Berlin, pp 235–258
Schetagne R, Doyo JF, Fournier JJ (2000) Export of mercury downstream from reservoirs. Sci Total Environ 260(1–3):135–145
SEMA/MT (2015) Accessed January 2017. http://sema.mt.gov.br
Tuomola L, Niklasson T, Castro e Silva E, Hylander LD (2008) Fish mercury development in relation to abiotic characteristics and carbon sources in a six-year-old, Brazilian reservoir. Sci Total Environ 390:177–187
Verburg P (2014) Lack of evidence for lower mercury biomagnification by biomass dilution in more productive lakes: comment on mercury biomagnification through food webs is affected by physical and chemical characteristics of lakes. Environ Sci Technol 48:10524
Verburg P, Hickey C, Phillips N (2014) Mercury biomganification in three geothermally influenced lakes differing in chemistry and algal biomass. Sci Total Environ 493:342
Yao H, Feng XB, Guo YN, Yan HY, Fu XW, Li ZG, Meng B (2011) Mercury and methylmercury concentrations in 2 newly constructed reservoir in the Wujiang River, Guizhou, China. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:530–537
Acknowledgements
Financial support was obtained from the Fundación BBVA (BIOCON06/113; Project EMECO). One of the authors acknowledges the FAPEMAT for a Graduate Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cebalho, E.C., Díez, S., dos Santos Filho, M. et al. Effects of small hydropower plants on mercury concentrations in fish. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 22709–22716 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9747-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9747-1