Abstract
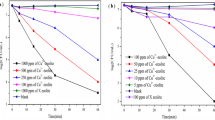
Two types of zeolites—natural clinoptilolite (NZ) and synthetic zeolite A (A)—were enriched with approx. 0.25 mmol of Cu(II), Zn(II), or Ag(I) ions, and the obtained materials (M-Z) were tested against three different isolates of Escherichia coli. Two isolates were environmental isolates from waters in Serbia whereas the third one was DSM 498. Antibacterial activity was studied in different water media—nutrient-rich media (peptone water), water from Sava Lake, and commercially available spring water. The Ag-containing zeolites showed bactericidal activity in the nutrient-rich peptone water after 1 h of contact. Cu- and Zn-containing zeolites showed bactericidal activity in real water samples. Antibacterial activity of the M-Z decreases in all three examined water media in the following order: Ag-NZ ≈ Ag-A > Cu-NZ ≈ Cu-A > Zn-NZ >>> Zn-A, suggesting that mainly the metal type and not the zeolite type have a role in the antibacterial activity. Leaching experiments showed small amounts of the leached Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions, indicating that the antibacterial activity is not due to the metal ions but should be attributed to the M-Z itself. However, leached amounts of Ag(I) from Ag-NZ and Ag-A in peptone water indicate that the released Ag(I) could be mainly responsible for the bactericidal effect of the Ag(I)-containing zeolites. Since no loss of cellular material was found, the antibacterial activity is not attributed to cytoplasmic membrane damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhigbe L, Ouki S, Saroj D, Min Lim X (2014) Silver-modified clinoptilolite for the removal of Escherichia coli and heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:10940–10948. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-2888-6
Bovenkamp GL, Zanzen U, Krishna KS, Hormes J, Prange A (2013) X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy study of the interaction of silver ions with Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6385–6390. doi:10.1128/AEM.01688-13
Carson C, Mee B, Riley T (2002) Mechanism of action of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil on Staphylococcus aureus determined by time-kill, lysis, leakage, and salt tolerance assays and electron microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Ch 46:1914–1920. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.6.1914-1920.2002
Cox SD, Mann CM, Markham JL, Gustafson JE, Warmington JR, Wyllie SG (2001) Determining the antimicrobial actions of tea tree oil. Molecules 6:87–91. doi:10.3390/60100087
De la Rosa-Gomez I, Olguin MT, Alcantara D (2008a) Bactericides of coliform microorganisms from wastewater using silver-clinoptilolite rich tuffs. Appl Clay Sci 40:45–53. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2007.07.001
De la Rosa-Gomez I, Olguin MT, Garcia-Sosa I, Alcantara D, Rodriguez-Fuentes G (2008b) Silver supported on natural Mexican zeolite as an antibacterial material. Micropor Mesopor Mater 39:431–444. doi:10.1016/S1387-1811(00)00217-1
Demirci S, Ustaoğlu Z, Yılmazer GA, Sahin F, Baç N (2014) Antimicrobial properties of zeolite-X and zeolite-A ion-exchanged with silver, copper and zinc against a broad range of microorganisms. Appl Biochem Biotech 172:1652–1662. doi:10.1007/s12010-013-0647-7
de Souza EL, de Barros JC, Eduardo C, de Oliveira V, da Conceição ML (2010) Influence of Origanum vulgare L. essential oil on enterotoxin production, membrane permeability and surface characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Food Microbiol 137:308–311. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.11.025
EUCAST (2014) European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Reading guide. Version 4.0 available at http://www.Eucast.Org/clinical_breakpoints/ (online December 2, 2016)
Feng QL, Wu J, Chen GQ, Cui FZ, Kim TN, Kim JO (2000) A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Mater Res 52:662–668. doi:10.1002/1097-4636(20001215)52:4<662::AID-JBM10>3.0.CO;2-3
Ferreira L, Fonseca AM, Botelho G, Almeida-Aguiar C, Neves IC (2012) Antimicrobial activity of faujasite zeolites doped with silver. Micropor Mesopor Mater 160:126–132. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.05.006
Guerra R, Lima E, Viniegra M, Guzman A, Lara V (2012) Growth of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi inhibited by fractal silver nanoparticles supported on zeolite. Micropor Mesopor Mater 147:267–273. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.06.031
Hong R, Kang TY, Michels CA, Gadura N (2012) Membrane lipid peroxidation in copper alloy-mediated contact killing of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1776–1784. doi:10.1128/AEM.07068-11
Hrenovic J, Milenkovic J, Ivankovic T, Rajic N (2012) Antibacterial activity of heavy metal-loaded natural zeolite. J Hazard Mater 201-202:260–264. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.079
Hrenovic J, Milenkovic J, Goic-Barisic I, Rajic N (2013) Antibacterial activity of containing natural zeolite against clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Micropor Mesopor Mater 169:148–152. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.10.026
Jiraroj D, Tungasmita S, Tungasmita DN (2014) Silver ions and silver nanoparticles in zeolite A composites for antibacterial activity. Powder Technol 264:418–422. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2014.05.049
Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, Shin S, Kim SH, Park YH (2008) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2171–2178. doi:10.1128/AEM.02001-07
Kawahara K, Tsuruda K, Morishita M, Uchida M (2000) Antibacterial effect of silver-zeolite on oral bateria under anaerobic conditions. Dent Mater 16:452–455. doi:10.1016/S0109-5641(00)00050-6
Kwakye-Awuah B, Williams C, Kenward MA, Radecka I (2008) Antimicrobial action and efficiency of silver-loaded zeolite X. J Appl Microbiol 104:1516–1524. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03673.x
Lemire J, Harrison J, Turner R (2013) Antimicrobial activity of metals: mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:371–384. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3028
Le Ouay B, Stellacci F (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: a surface science insight. Nano Today 10:339–354. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2015.04.002
Macomber L, Rensing C, Imlay JA (2007) Intracellular copper does not catalyze the formation of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 189:1616–1626. doi:10.1128/JB.01357-06
Mulley G, Jenkins AT, Waterfield N (2014) Inactivation of the antibacterial and cytotoxic properties of silver ions by biologically relevant compounds. PLoS One 9(4):e94409. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0094409
Navarro CA, von Bernath D, Jerez CA (2013) Heavy metal resistance strategies of acidophilic bacteria and their acquisition: Importance for biomining and bioremediation. Biol Res 46:363–371. doi:10.4067/S0716-97602013000400008
Pathak SP, Gopal K (2012) Evaluation of bactericidal efficacy of silver ions on Escherichia coli for drinking water disinfection. Environ Sci Pollut R 19:2285–2290. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0735-6
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:4020–4028. doi:10.1021/la104825u
Rivera-Garza M, Olguin MT, Garcia-Sosa I, Alcantara D, Rodriguez-Fuentes G (2000) Silver supported on natural Mexican zeolite as an antibacterial material. Micropor Mesopor Mater 39:431–444. doi:10.1016/S1387-1811(00)00217-1
Rossainz-Castro LG, De la Rosa-Gomez I, Olguín MT, Alcantara-Díaz D (2016) Comparison between silver- and copper-modified zeolite-rich tuffs as microbicidal agents for Escherichia coli and Candida albicans. J Environ Manag 183:763–770. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.09.034
Top A, Ulku S (2004) Silver, zinc, and copper exchange in Na-clinoptilolite and resulting effect on antibacterial activity. Appl Clay Sci 27:13–19. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2003.12.002
WHO (2003a) Zinc in drinking-water. Background document for preparation of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/17) Available at http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/zinc.pdf (Online December 2, 2016)
WHO (2003b) Copper in drinking-water. Background document for preparation of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/88) Available at http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/copper.pdf (Online December 2, 2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development (project nos. 172018 and III 46010) and partly by the Croatian Science Foundation (project no. IP-2014-09-5656). The authors are grateful to Dr. Milan Radović and Dr. Zorica Zrnić from the Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr Milan Jovanović Batut” for providing the bacterial isolates and for help in determining the antibiotic resistance profiles of the isolates, to Prof. Maja Vukasinovic Sekulic from the Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy of University of Belgrade for useful advices and discussions during the laboratory experiments, and to the Company Zeodigest from Iran for providing the zeolite samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milenkovic, J., Hrenovic, J., Matijasevic, D. et al. Bactericidal activity of Cu-, Zn-, and Ag-containing zeolites toward Escherichia coli isolates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 20273–20281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9643-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9643-8