Abstract
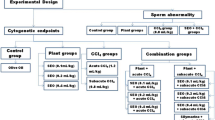
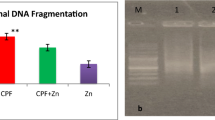
Nigella sativa is a well-known dietary antioxidant and a valuable inhibitor of clastogenesis and carcinogenesis. The purpose of the present work was to investigate the effects of N. sativa seeds against chromosomal aberrations in primary spermatocytes and early embryonic lethality induced by CCl4 hepatotoxin in Swiss albino mice. One hundred male Swiss albino mice were randomly divided into five groups. Groups I, II, and III received only normal saline, olive oil, and aqueous suspension of N. sativa seeds (50 mg/kg b.w.), while groups IV and V were orally given CCl4 dissolved in olive oil at a dose level of 1.9 (¼ LD50) alone and with aqueous suspension of N. sativa seeds (50 mg/kg b.w.) alternately. Aqueous extract of N. sativa significantly reduced the elevated frequency of chromosomal aberrations induced by CCl4 in mouse primary spermatocytes. For the male-dominant lethal test, four males from each group (control and experimental) were used and each male was mated for 13 days to two untreated virgin females. On days 14–16 after breeding, all the females were evaluated for incidence of pregnancy, live implants, and fetal deaths. Treatment with 1/4 LD50 of CCl4 induced positive dominant lethal mutation, reflecting a high rate of deformations in male germ cells. Interestingly, no dominant lethal mutations were recorded in females mated to male mice treated with CCl4 plus N. sativa. Under the experimental conditions of this study, our results highlight the beneficial role of N. sativa against CCl4-induced mutagenicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmeguid NE, Fakhoury R, Kamal SM, Al Wafai RJ (2010) Effects of Nigella sativa and thymoquinone on biochemical and subcellular changes in pancreatic β-cells of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes 2(4):256–266
Abdel-Moneim AM, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Kersh MA, Al-Omair MA (2015) Free radical-scavenging, anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic and hepatoprotective actions of taurine and silymarin against CCl4 induced rat liver damage. PLoS One 10(12):e0144509
Ahmad A, Husain A, Mujeeb M, Khan SA, Najmi AK, Siddique NA, Damanhouri ZA, Anwar F (2013) A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: a miracle herb. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:337–352
Akour A, Kasabri V, Afifi FU, Bulatova N (2016) The use of medicinal herbs in gynecological and pregnancy-related disorders by Jordanian women: a review of folkloric practice vs. evidence-based pharmacology. Pharm Biol 209:1–18
Alchinbayev MK, Aralbayeva AN, Tuleyeva LN, Duysenbayeva SM, Makazhanov MA (2016) Aneuploidies level in sperm nuclei in patients with infertility. Mutagenesis 31(5):559–565
Al-Enazi MM (2007) Effect of thymoquinone on malformations and oxidative stress-induced diabetic mice. Pak J Biol Sci 10:3115–3119
Al-Olayan EM, El-Khadragy MF, Metwally DM, Abdel Moneim AE (2014) Protective effects of pomegranate (Punica granatum) juice on testes against carbon tetrachloride intoxication in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:164
Alyoussef A, Al-Gayyar MM (2016) Thymoquinone ameliorated elevated inflammatory cytokines in testicular tissue and sex hormones imbalance induced by oral chronic toxicity with sodium nitrite. Cytokine 83:64–74
Awadalla EA (2012) Ameliorative effect of the crude oil of the Nigella sativa on oxidative stress induced in rat testes by cisplatin treatment. Biomed Preventive Nutr 2(4):265–268
Babazadeh B, Sadeghnia HR, Safarpour Kapurchal E, Parsaee H, Nasri S, Tayarani-Najaran Z (2012) Protective effect of Nigella sativa and thymoquinone on serum/glucose deprivation-induced DNA damage in PC12 cells. Avicenna J Phytomedicine 2:125–132
Badary OA, Al-Shabanah OA, Nagi MN, Al-Bekairi AM, Elmazar MMA (1998) Acute and subchronic toxicity of thymoquinone in mice. Drug Dev Res 44:56–61
Badary OA, Abd-Ellah MF, El-Mahdy MA, Salama SA, Hamada FM (2007) Anticlastogenic activity of thymoquinone against benzo(a)pyrene in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 45(1):88–92
Cho Ping N, Hashim NH, Hasan Adli DS (2014) Effects of Nigella sativa (Habbatus sauda) oil and nicotine chronic treatments on sperm parameters and testis histological features of rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014:218293
Ehling UH, Machemer L, Buselmaier W, Dýcka J, Frohberg H, Kratochvilova J et al (1978) Standard protocol for the dominant lethal test on male mice set up by the work group “Dominant Lethal Mutations of the ad hoc Committe Chemogenetics”. Arch Toxicol 39(3):173–185
El Shenawy NS, Soliman MF, Reyad SI (2008) The effect of antioxidant properties of aqueous garlic extract and Nigella sativa as anti-schistosomiasis agents in mice. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 50(1):29–36
Emeka LB, Emeka PM, Khan TM (2015) Antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa L. seed oil against multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from diabetic wounds. Pak J Pharm Sci 28(6):1985–1990
Epstein SS, Arnold E, Andrea J, Bass W, Bishop Y (1972) Detection of chemical mutagens by the dominant lethal assay in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 23(2):288–325
Essawy AE, Hamed SS, Abdel-Moneim AM, Abou-Gabal AA, Alzergy AA (2010) Role of black seeds (Nigella sativa) in ameliorating carbon tetrachloride induced haematotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. J Med Plant Res 4(19):1977–1986
Essawy AE, Abdel-Moneim AM, Khayyat LI, Alzergy AA (2012) Nigella sativa seeds protect against hepatotoxicity and dyslipidemia induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. J Appl Pharm Sci 2(10):021–025
Farooqui Z, Ahmed F, Rizwan S, Shahid F, Khan AA, Khan F (2017) Protective effect of Nigella sativa oil on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Biomed Pharmacother 85:7–15
Gholamnezhad Z, Havakhah S, Boskabady MH (2016) Preclinical and clinical effects of Nigella sativa and its constituent, thymoquinone: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 190:372–386
Hadi V, Kheirouri S, Alizadeh M, Khabbazi A, Hosseini H (2016) Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Avicenna J Phytomed 6(1):34–43
Hosseinzadeh H, Tafaghodi M, Mosav MJ, Taghiabadi E (2013) Effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Nigella sativa seeds on milk production in rats. JAMS J Acupunct Meridian Stud 6:18–23
Ibraheim Z (2002) Effect of Nigella sativa seeds and total oil on some blood parameters in female volunteers. Saudi Pharm J 10:54–59
Jha AM, Singh AC, Sinha U, Kumar M (2007) Genotoxicity of crotonaldehyde in the bone marrow and germ cells of laboratory mice. Mutat Res 632(1–2):69–77
Kamarzaman S, Shaban M, AbdulRahman S (2014) The prophylactic effect of Nigella sativa against cyclophosphamide in the ovarian follicles of matured adult mice: a preliminary study. J Animal Plant Sci 24:81–88
Khader M, Bresgen N, Eckl PM (2009) In vitro toxicological properties of thymoquinone. Food Chem Toxicol 47:129–133
Khan MR, Ahmed D (2009) Protective effects of Digera muricata (L.) Mart. on testis against oxidative stress of carbon tetrachloride in rat. Food Chem Toxicol 47(6):1393–1399
Khattak KF, Simpson TJ, Ihasnullah (2008) Effect of gamma irradiation on the extraction yield, total phenolic content and free radical-scavenging activity of Nigella staiva seed. Food Chem 110(4):967–972
Kim SH, Lee IC, Baek HS, Moon C, Kim SH, Yu JC, Shin IS, Kim JC (2014) Induction of cytochrome P450 3A1 expression by diallyl disulfide: protective effects against cyclophosphamide-induced embryo-fetal developmental toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 69:312–319
Kolahdooz M, Nasri S, Modarres SZ, Kianbakht S, Huseini HF (2014) Effects of Nigella sativa L. seed oil on abnormal semen quality in infertile men: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 21:901–905
Kooti W, Hasanzadeh-Noohi Z, Sharafi-Ahvazi N, Asadi-Samani M, Ashtary-Larky D (2016) Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of black seed (Nigella sativa). Chin J Nat Med 14:732–745
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L, Liu CM (2014) Ursolic acid protects mouse liver against CCl4-induced oxidative stress and inflammation by the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(3):975–983
Mabrouk A, Cheikh HB (2014) Thymoquinone supplementation ameliorates lead-induced testis function impairment in adult rats. Toxicol Ind Health. doi:10.1177/0748233714548474
Machev N, Gosset P, Viville S (2005) Chromosome abnormalities in sperm from infertile men with normal somatic karyotypes: teratozoospermia. Cytogenet Genome Res 111(3–4):352–357
Malashenko AM, Beskova TB, Vasileva SV (1997) Mutagenic effect of dimethylnitrosourea in male mice: induction of dominant lethal mutations and chromosome aberrations in germ cells; genotype influence on the clastogenic effect in bone marrow cells. Genetika 33:524–531
Mosbah R, Yousef MI, Maranghi F, Mantovani A (2016) Protective role of Nigella sativa oil against reproductive toxicity, hormonal alterations, and oxidative damage induced by chlorpyrifos in male rats. Toxicol Ind Health 32(7):1266–1277
Oud JL, de Jong JH, de Rooij DG (1979) A sequential analysis of meiosis in the male mouse using a restricted spermatocyte population obtained by a hydroxyurea/triaziquone treatment. Chromosoma 71(2):237–248
Parandin R, Yousofvand N, Ghorbani R (2012) The enhancing effects of alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa seed on fertility potential, plasma gonadotropins and testosterone in male rats. Iran J Reprod Med 10:355–362
Reddy YP, Chandrasekhar KB, Sadiq MJ (2015) A study of Nigella sativa induced growth inhibition of MCF and HepG2 cell lines: an anti-neoplastic study along with its mechanism of action. Pharm Res 7(2):193–197
Sheikhbahaei F, Khazaei M, Rabzia A, Mansouri K, Ghanbari A (2015) Protective effects of thymoquinone against methotrexate-induced germ cell apoptosis in male mice. Int J Fertil Steril 9:541–547
Türk G, Çeribaşı S, Sönmez M, Çiftçi M, Yüce A, Güvenç M et al (2016) Ameliorating effect of pomegranate juice consumption on carbon tetrachloride-induced sperm damages, lipid peroxidation, and testicular apoptosis. Toxicol Ind Health 32(1):126–137
Vahdati-Mashhadian N, Rakhshandeh H, Omidi A (2005) An investigation on LD50 and subacute hepatic toxicity of Nigella sativa seed extracts in mice. Pharmazie 60:544–547
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experimental design was conducted in accord with NIH guidelines of animal care and all procedures were approved by a local committee at Alexandria University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Moneim, A.M., Essawy, A.E., Hamed, S.S. et al. Protective effect of Nigella sativa seeds against spermatocyte chromosomal aberrations and genotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 11677–11682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8806-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8806-y