Abstract
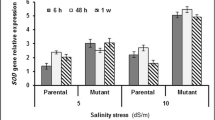
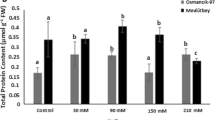
Salinity stress is the most important and common environmental stresses throughout the world, including Iran. The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of several important genes involved in the salinity tolerance of the rice cultivars differing in salt sensitivity. In this research, the expression of four mitochondrial genes, H2O2, malondialdehyde (MDA), proline, sodium, potassium and superoxide dismutase (SOD), was measured in Iranian rice cultivars and two well-known international varieties as checks in response to 100 mM salt stress. The results show that the activity of SOD in the tolerant cultivars is much higher than in the susceptible ones under saline conditions (100 mM NaCl). The study of the gene expression in the tolerant and sensitive cultivars also showed that the expression of the genes increased in the early hours of the stress, with the exception of the OsGR1. Moreover, the amount of the expression in the tolerant cultivars was far more than the susceptible ones. The result of this study showed that the function of a set of antioxidant enzymes can lead to detoxification of the reactive oxygen species, so in order to better understand ROS scavengers, a comprehensive study on the antioxidant system should be conducted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi FM, Komatsu S (2004) A proteomic approach to analyze salt-responsive proteins in rice sheath. Proteomics 4:2072–2081
Abdel Latef AA, Tran LSP (2016) Impacts of priming with silicon on the growth and tolerance of maize plants to alkaline stress. Front Plant Sci 7:243. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00243
Ashraf M, McNeilly T (2004) Salinity tolerance in Brassica oilseeds. Crit Rev Plant Sci 23:157–174
Azuma R, Ito N, Nakayama N, Suwa R, Nguyen NT, Larrinaga-Mayoral JÁ, Esaka M, Fujiyama H, Saneoka H (2010) Fruits are more sensitive to salinity than leaves and stems in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci Hort 125:171–178
Bates LS, Wladren PR, Tear DT (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Choukr AR (1996) The potential halophytes in the development and rehabilitation of arid and semiarid zones halophytes and Biosalin. Agriculture 5:3–13
Ciarmiello LF, Woodrow P, Fuggi A, Pontecorvo G, Carillo P (2011) Plant genes for abiotic stress. In: Shanker A, Venkateswarlu B (ed) Abiotic stress in plants: mechanisms and adaptations. InTech, pp 284–308
Cramer GR, Urano K, Delrot S, Pezzotti M, Shinozaki K (2011) Effects of abiotic stress on plants: a systems biology perspective. BMC Plant Biol 11:163
Desingh R, Kanagaraj G (2007) Influence of salinity stress on photosynthesis and antioxidative systems in two cotton varieties. General Appl Plant Physiol 33:221–234
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
FAO (2007) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Desertification
Fry IV, Huflejt M, Erber WWA, Peschek GA, Packer L (1986) The role of respiration during adaptation of the freshwater Cyanobacterium synechococcus 6311 to salinity. Arch Biochem Biophys 244:686–691
Ghomi K, Rabiei B, Sabouri H, Sabouri A (2013) Mapping QTLs for traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage of rice (Oryza sativa L.): an agrigenomics study of an Iranian rice population. OMICS J Integr Biol 17:242–251
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases. I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Herbette S, Lenne C, Leblanc N, Julien JL, Drevet JR, Roeckel Drevet P (2002) Two GPX-like proteins from Lycopersicon esculentum and Helianthus annuus are antioxidant enzymes with phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin peroxidase activities. Eur J Biochem 269:2414–2420
Hernandez JA, Aguilar AB, Portillo B, Lopez-Gomez E, Beneyto JM, Garcia-Legaz MF (2003) The effect of calcium on the antioxidant enzymes from salt-treated loquat and anger plants. Funct Plant Biol 30:1127–1137
Jana S, Choudhuri M (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperms during aging. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Jeanjean R, Matthijs HCP, Onana B, Havaux M, Joset F (1993) Exposure of the Cyanobacterium synechocystis PCC6803 to salt stress induces concerted changes in respiration and photosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 34:1073–1079
Joseph EA, Mohanan KV, Radhakrishnan VV (2015) Effect of salinity variation on the quantity of antioxidant enzymes in some rice cultivars of North Kerala, India. Univers J Agric Res 3:89–105
Jung BG, Lee KO, Lee SS, Chi YH, Jang HH, Kang SS (2002) A Chinese cabbage cDNA with high sequence identity to phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidases encodes a novel isoform of thioredoxindependent peroxidase. J Biol Chem 277:12572–12578
Kamali E, Shahmohammadi Heydari Z, Heydari M, Feyzi M (2011) Effects of irrigation water salinity and leaching fraction on soil chemical characteristic, grain yield, yield components and cation accumulation in safflower in Esfehan. Iran J Field Crops Sci 6:339–545
Kaouther Z, Nina H, Rezwan A, Cherif H (2013) Evaluation of salt tolerance (NaCl) in Tunisian chili pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.) on growth, mineral analysis and solutes synthesis. J Stress Physiol Biochem 9:209–228
Kordrostami M, Rabiei B, Hassani Kumleh H (2016) Association analysis, genetic diversity and haplotyping of rice plants under salt stress using SSR markers linked to SalTol and morpho-physiological characteristics. Plant Syst Evol 7:871–890. doi:10.1007/s00606-016-1304-8
Lin CC, Kao CH (2001) Cell wall peroxidase activity, hydrogen peroxide level and NaCl-inhibited root growth of rice seedlings. Plant Soil 230:135–143
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
López-Aguilar R, Medina-Hernández D, Ascencio-Valle F, Troyo-Dieguez E, Nieto-Garibay A, Arce-Montoya M, Larrinaga-Mayoral JA, Gómez-Anduro GA (2012) Differential responses of Chiltepin (Capsicum annuum var. glabriusculum) and Poblano (Capsicum annuum var. annuum) hot peppers to salinity at the plantlet stage. Afric J Biotechnol 11:2642–2653
Meloni DA, Oliva MA, Martinez CA, Cambraia J (2003) Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 49:69–76
Mishra P, Bhoomika K, Dubey RS (2013) Differential responses of antioxidative defense system to prolonged salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 250:3–19
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Mittova V, Tal M, Volokita M, Guy M (2002) Salt stress induces up-regulation of an efficient chloroplast antioxidant system in the salt-tolerant wild tomato species Lycopersicon pennellii but not in the cultivated species. Physiol Plant 115:393–400
Mohammadi-Nejad G, Singh RK, Arzani A, Rezaie AM, Sabouri H, Gregorio GB (2010) Evaluation of salinity tolerance in rice genotypes. Int J Pl Prod 4:199–208
Momeni A (2010) The geographic distribution of soil salinity levels in Iran. Iran J Soil Res 24:203–215
Moser D, Nicholls P, Wastyn M, Peschek GA (1991) Acidic cytochrome c6 of unicellular cyanobacteria is an indispensable and kinetically competent electron donor to cytochrome oxidase in plasma and thylakoid membranes. Int J Biochem 24:757–768
Mousa MA, Al-Qurashi AD, Bakhashwain AA (2013) Response of tomato genotypes at early growing stages to irrigation water salinity. J Food Agric Environ 11:501–507
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Eenviron 25:239–250
Navrot N, Collin V, Gualberto J, Gelhaye E, Hirasawa M, Rey P, Knaff DB, Issakidis E, Jacquot JP, Rouhier N (2006) Plant glutathione peroxidases are functional peroxiredoxins distributed in several subcellular compartments and regulated during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol 142:1364–1379
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
Orcutt DM, Nilsen ET (2000) Physiology of plants under stress: soil and biotic factors. Wiley, New York
Paul M, Hasegava A (1996) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Polidoros AN, Mylona PV, Arnholdt-Schmitt B (2009) AOX gene structure, transcript variation and expression in plants. Physiol Plant 137:342–353
Puri YP, Williams WA (1985) Evaluation of yield components as selection criteria in barley breeding. Crop Sci 22:927–931
Sabouri H, Rezai AM, Moumeni A (2008) Evaluation of salt tolerance in Iranian landrace and improved rice cultivars. J Sci Tech Agric Nat Reso (In Persian, Abs. in English)
Shalata A, Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M, Tal M (2001) Response of cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennelli to salt-dependent oxidative stress: the root antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 122:487–494
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:35–52
Sakhno LO, Slyvets MS, Korol NA, Karbovska NV, Ostapchuk AM, Sheludko YV, Kuchuk MV (2014) Changes in fatty acid composition in leaf lipids of canola biotech plants under short-time heat stress. J Stress Physiol Biochem 10:24–34
Slesak I, Miszalski Z, Karpinska B, Niewiadomska E, Ratajczak R, Karpinski S (2002) Redox control of oxidative stress responses in the C-3-CAM intermediate plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:669–677
Solomon A, Beer S (1994) Effect of NaCl on the carboxylating activity of rubisco and absence of proline related compatible solutes plant. Physiol 108:1387–1394
Stepien P, Klobus G (2005) Antioxidant defense in the leaves of C3 and C4 plants under salinity stress. Physiol Plant 125:31–40
Sudhakar C, Lakshmi A, Giridarakumar S (2001) Changes in the antioxidant enzyme efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Sci 161:613–619
Tsai YC, Hong C-Y, Liu L-F, Kao H (2004) Relative importance of Na+ and Cl− in NaCl-induced antioxidant systems in roots of rice seedlings. Physiol Plant 122:86–94
Van Weert F, Van der Gun J, Reckman J (2009) Global overview of saline groundwater occurrence and genesis. International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre 105 pp
Wopereis MCS, Defoer T, Idinoba P, Diack S, Dugué MJ (2009) PLAR–IRM Curriculum: Technical Manual
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The authors declare that the present study does not involve any human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
The authors declare that the present study does not involve any informed consent.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yi-ping Chen
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Fig. 1
(DOCX 474 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 2
(DOCX 48 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 3
(DOCX 48 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 4
(DOCX 34 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 5
(DOCX 24 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 6
(DOCX 18 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 7
(DOCX 25 kb)
Supplemental Table 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kordrostami, M., Rabiei, B. & Kumleh, H.H. Different physiobiochemical and transcriptomic reactions of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in terms of salt sensitivity under salinity stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 7184–7196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8411-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8411-0