Abstract
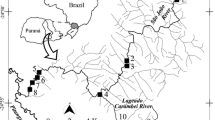
The present study focuses on the evaluation of metal (chromium, copper, and lead), arsenic, and pesticide (atrazine and endosulfan) contamination in freshwater streams of one of the most important agricultural and industrial areas of central-eastern Argentina, which has not been reported earlier. The environmental fate of inorganic microcontaminants and pesticides was assessed. Samples were collected monthly for a year. Pesticide concentrations were measured in water; metal and arsenic concentrations were measured in water and sediments, and physicochemical variables were analyzed. In most cases, metals and arsenic in water exceeded the established guideline levels for the protection of aquatic biota: 98 and 56.25% of the samples showed higher levels of Cr and Pb, while 81.25 and 85% of the samples presented higher values for Cu and As, respectively. Cr, Pb, Cu, and As exceeded 181.5 times, 41.6 times, 57.5 times, and 12.9 times, respectively, the guideline level values. In sediment samples, permitted levels were also surpassed by 40% for Pb, 15% for As, 4% for Cu, and 2% for Cr. Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) demonstrated that most of the sediment samples were highly polluted by Cr and Cu and very seriously polluted by Pb, which indicates progressive deterioration of the sediment quality. Atrazine never exceeded them, but 27% of the 48 water samples contained total endosulfan that surpassed the guidelines. The findings of this study suggest risk to the freshwater biota over prolong periods and possible risk to humans if such type of contaminated water is employed for recreation or human use. Improper disposal of industrial effluents and agricultural runoffs need to be controlled, and proper treatment should be done before disposal to avoid further deterioration of the aquifers of this area.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEQGs:
-
Argentine Environmental Quality Guidelines
- As:
-
Arsenic
- Atr:
-
Atrazine
- BOD:
-
Biological oxygen demand
- CEQGs:
-
Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- Cr:
-
Chromium
- Cu:
-
Copper
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- EEA:
-
European Environment Agency
- End:
-
Endosulfan
- EPA:
-
Environmental Protection Agency
- EQGs:
-
Environmental quality guidelines
- FD:
-
Frequency of detection
- IC:
-
Inorganic carbon
- Igeo :
-
Geoaccumulation Index
- INIDEP:
-
Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo Pesquero
- LAQUIGE:
-
Laboratorio de Química Geológica y Edafológica
- MAC:
-
Maximum allowable concentration
- MC:
-
Maximum concentration
- NA:
-
Not available
- ND:
-
No data
- Pb:
-
Lead
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- S1:
-
Site one
- S2:
-
Site two
- S3:
-
Site three
- S4:
-
Site four
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- Sed.:
-
Sediment
- SRP:
-
Soluble reactive phosphorus
- T. End:
-
Total endosulfan (α END, β END and END. SULFATO)
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Aparicio V, De Gerónimo E, Hernández Guijarro K, Pérez D, Portocarrero R, Vidal C (2015) Pesticides added to the soil and their fate into the environment Buenos Aires; Eds INTA, 2015. 73 p. (in Spanish)
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1975a) Method 160.3. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 14th (ed) P. 91, Method 208A, (1975). American public health association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1975b) Method 410.1. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 1975, 45th (ed) Amer Public Health Assoc, Americ Water Works Association, Water Poll. Control Federation, Washington D.C. pp 550
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1975c) Method 415.1. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 1975, 14th (ed) Amer. Public. Health Assoc., Americ Water Works Association, Water Poll. Control Federation, Washington D.C., pp 532
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1980) Method 405.1. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 1980. 15th (ed) Amer. Public. Health Assoc., Americ Water Works Association, Water Poll. Control Federation, Washington D.C. pp 83
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) SM 4500-P-E, SM 4500- NO2-B y SM 4500- NO3-D. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 1998, 20th (ed). Amer. Publ. Health Assoc. (Environmental Protection Agency 1999)
APHA (American Public Health Association), AWWA (American Water Works Association), WEF (Water Environment Federation) (1976) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn, Washington DC
Arribére MA, Cohen IM, Ferpozzi LH, Kestelman AJ, Casa VA, Guevara SR (1997) Neutron activation analysis of soils and loess deposits, for the investigation of the origin of the natural arsenic-contamination in the Argentine Pampa. Radiochim Acta 78:187–191
Bajguz A (2011) Suppression of Chlorella vulgaris growth by cadmium, lead, and copper stress and its restoration by endogenous Brassinolide. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60(3):406–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9551-0
Bonansea RI, Amé MV, Wunderlin DA (2012) Determination of priority pesticides in water samples combining SPE and SPME coupled to GC–MS. A case study: Suquía River basin (Argentina). Chemosphere 90:1860–1869
Canadian Environmetal Quality Guidelines (2003) Canadian council of ministers of the environment. Ottawa, Ontario
Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (2008) Water quality guidelines of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the environment. Ottawa, Ontario
CASAFE (Chamber of Agricultural and Fertilizer Health) (2013) Argentine market for phytosanitary products. http://www.casafe.org/. Accessed 20 October 2015
Castañé PM, Topalián ML, Cordero RR, Salibián A (2003) Influence of the speciation of heavy metals in aquatic environment as a determinant of their toxicity. J Toxicol 20:13–18 (in Spanish)
Castelao G, Glur G (2012) Morpho-biogeographic aspects in a sector of the a Corralito-Colastiné basin province of Santa Fe, Argentina. Notes of the Biogeography lecture. Faculty of Humanities and Sciences. Universidad Nacional del Litoral (in Spanish)
Chen B, Liu J, Hu L, Liu M, Wang L, Zhang X, Fan D (2017) Spatio-temporal distribution and sources of Pb identified by stable isotopic ratios in sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent áreas. Sci Total Environ 580:936–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.042
Christopher SV, Bird KT (1992) The effects of herbicides on development of Myriophyllum spicatum L. cultured in vitro. J Environ Qual 21(2):203–207. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1992.00472425002100020008x
Coria S, Devia L, Lamas A, Nonna S, Villanueva C (1998) The environmental direction in Argentina. City Argentina (ed) Bs As. ISBN 978-987-507-038-7 (in Spanish)
Davis PE, Cook LSJ, Goenarso D (1994) Sublethal responses to pesticides of several species of Australian freshwater fish and crustaceans and rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 13(8):1341–1354. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620130816
de Gerónimo E, Aparicio VC, Barbaro S et al (2014) Presence of pesticides in surface water from four sub-basins in Argentina. Chemosphere 107:423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.039
De Lorenzo ME, Scott GI, Ross PE (2001) Toxicity of pesticides to aquatic microorganisms: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(1):84–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200108
De Noyelles F, Kettle WD, Sinn DN (1982) The responses of plankton communities in experimental ponds to atrazine, the most heavily used pesticide in the United States. Ecology 63(5):1285–1293. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938856
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81(2):163–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1464793105006950
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (1994) Methods for the determination of metals in environmental samples - Supplement I - EPA/600/R-94-111 - T.D. Martin et. al. - Method 200.2 - Sample preparation procedure for spectrochemical determination of total recoverable elements. - J.T. Creed et. al - Method 200.9, Revision 2.2 - Determination of trace elements by stabilized temperature graphite furnacle atomic absorption. Cincinatti, Ohio. EEUU
Epstein E, Grant WJ (1968) Chlorinated insecticides in run-off water as affected by crop rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am 32:423–426. In: International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS )1984. doi:https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1968.03615995003200030042x
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics Division. (FAO) (2015) http://faostat3.fao.org/home/E. Accessed 1 Oct 2017
Forney DR, Davis DE (1981) Effects of low concentrations of herbicides on submersed aquatic plants. Weed Sci 29:677–685. In: Solomon KR, Baker DB, Richards RP, Dixon KR, Klaine SJ, La Point TW, Kendall RJ, Weisskopf CP, Giddings JM, Giesy JP (1996) Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15(1):31–76
Gagneten AM, Ceresoli N (2004) Effect of tannery effluent on the abundance and richness of zooplankton species in the Prusianas Arroyo (Santa Fe, Argentina). Interciencia 29(12):702–708 (in Spanish)
Gagneten AM, Gervasio S, Paggi JC (2007) Heavy metal pollution and eutrophication in the lower Salado River basin (Argentine Republic). Water Air Soil Pollut 178(1-4):335–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9202-2
Gagneten AM, Paggi JC (2009) Effects of heavy metal contamination (Cr, Cu, Pb, Cd) and eutrophication on zooplankton in the lower basin of the Salado River (Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 204(1-4):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0032-x
Gallo M, Trento A, Alvarez A (2006) Dissolved and particulate heavy metals in the Salado River (Santa Fe, Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 174:67–384
Giraut M, Ludueña S, Postiglioni A, Rey C, Dente M, Sol I (2000) Digital surface water mapping of the Argentine Republic, National Water Information System, Undersecretariat of Water Resources Water and Environment Institute,X National Congress of Cartography (in Spanish)
Giunta R, Zalesky M, Sona G (2005) Changes registered in the Santa Fe agropecuarian sector between 1988 and 2002: analysis of the most significant variables. Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Natural Resources, Ministry of Production, Government Santa Fe Province (in Spanish)
Gonzalez M, Miglioranza KSB, Shimabukuro VM, Quiroz Londoño OM, Martinez DE, Aizpún JE, Moreno VJ (2012) Surface and groundwater pollution by organochlorine compounds in a typical soybean system from the south Pampa, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 65(2):481–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1328-x
Graymore M, Stagnitti F, Allinson G (2001) Impacts of atrazine in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Int 26(7-8):483–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00031-9
Gutiérrez MF, Gagneten AM (2011) Effect of metals on freshwater microcrustaceans. Methodological advances and potential of cladocerans. Rev Perú Biol 18(3):389–396 (in Spanish)
Gutiérrez MF, Gagneten AM, Paggi JC (2010) Copper and chromium alter life cycle variables and the equiproportional development of the freshwater copepod Notodiaptomus conifer (SARS). Water Air Soil Pollut 213(1-4):275–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0383-3
Gutiérrez MF, Gagneten AM, Paggi JC (2012) Exposure to sublethal chromium and endosulfan alter the diel vertical migration (DVM) in freshwater zooplankton crustaceans. Ecotoxicology 21(1):37–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0761-7
Hamilton PB, Jacksonb GS, Kaushik NK et al (1988) The impact of two applications of atrazine on the plankton communities of in situ enclosures. Aquat Toxicol 13(2):123–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(88)90038-0
Huggins DG, Anderson J (2005) Dissolved oxygen fluctuation regimes in streams of the Western Corn Belt Plains Ecoregion. Kansas Biological Survey. Central Plains Center for BioAssessment. Kansas: University of Kansas, prepared in fulfillment of USEPA award X7-99790401, report no. 130
Hunt L, Bonetto C, Marrochi N, Scalise A, Fanelli S, Liess M, Lydy MJ, Chiu MC, Resh VH (2017) Species at Risk (SPEAR) index indicates effects of insecticides on stream invertebrate communities in soy production regions of the Argentine Pampas. Sci Total Environ 580:699–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.016
Hunt L, Bonetto C, Resh VH, Buss DF, Fanelli S, Marrochi N, Lydy MJ (2016) Insecticide concentrations in stream sediments of soy production regions of South America. Sci Total Environ 547:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.140
Industrial Chamber of Leather Manufactures and Allied (ICLA) (2017) Argentina in the world leather market. Magazine 52 (in Spanish). http://www.cuerocima.com.ar/ Accessed 1 Oct 2017
Iriondo M, Kröhling D (2007) Geomorphology and sedimentology of the upper basin of the Salado River (Southern Santa Fe and Buenos Aires provinces; Argentina). Latin Am J Sedimentol Basin Anal 14(1):65–87
Jergentz S, Mugni H, Bonetto C, Schulz R (2005) Assessment of insecticide contamination in runoff and stream water of small agricultural streams in the main soybean area of Argentina. Chemosphere 61(6):817–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.036
José de Paggi S, Devercelli M (2011) Land use and basin characteristics determine the composition and abundance of the microzooplankton. Water Air Soil Pollut 218(1-4):93–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0626-3
Kabdasli I, Tunay O, Cetin MS, Olmez T (2002) Assessment of magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation for the treatment of leather tanning industry wastewaters. Water Sci Technol 46(4-5):231–239
Lakshminarayana JSS, O'Neill HJ, Jonnavithula SD, Leger DA, Milburn PH (1992) Impact of atrazine-bearing agricultural tile drainage discharge on planktonic drift of a natural stream. Environ Pollut 76(3):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(92)90138-Z
Luoma SN, Rainbow P (2005) Why is metal bioaccumulation so variable? Biodynamics as a unifying concept. Environ Sci Technol 38(7):1921–1931
Maguire RJ, Tkacz RJ (1993) Occurrence of pesticides in the Yamaska River, Québec. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25(2):220–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212133
Manzi R, Gallardo M. (1970) Geography of Santa Fe. Spadoni S.A. Mendoza, pp. 192 (in Spanish)
Margalef R (1983) Limnology. Omega, Barcelona, p 1010 (in Spanish)
Marino D, Ronco A (2005) Cypermethrin and chlorpyrifos concentration levels in surface water bodies of the Pampa Ondulada, Argentina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75(4):820–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-005-0824-7
Min G, Wang S, Zhu H, Fang G, Zhang Y (2008) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction adsorbents for determination of atrazine and its principal metabolites in water and soil samples by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ 396(1):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.016
Montes C, Martino P (1987) The Spanish saline lagoonsin. Royal Academy of Exact, Physical and Natural Sciences: Scientific bases for the protection of wetlands in Spain, pp 95–145 (in Spanish)
Moreno VJ (2012) Surface and groundwater pollution by organochlorine compounds in a typical soybean system from the south Pampa, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 65:481–491
Müller G (1981) Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimente des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse: Cine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemiker-Zeitung 105:157–164
Muniz P, Venturini N, Gómez-Erache N (2004) Spatial distribution of chromium and lead in the benthic environmental coastal areas of the Río de la Plata estuary (Montevideo, Uruguay). Braz J Biol 64(1):103–116
Nakano Y, Miyazaki A, Yoshida T, Ono K, Inoue T (2004) A study on pesticide runoff from paddy fields to a river in rural region: field survey of pesticide runoff in the Kozakura River, Japan. Water Res 38(13):3017–3022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.02.013
Novo M (2006) Sustainable development. Environmental and educational dimension. Pearson education (3 ed), Madrid ISBN 9789568302672 (in Spanish)
Ouyang Y, Higman J, Thompson J, Toole OT, Campbell D (2002) Characterization and spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediment from Cedar and Ortega Rivers sub-basin. J Contam Hydrol 54(1-2):19–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(01)00162-0
Palma P, Köck-Schulmeyer M, Alvarenga P, Ledo L, Barbosa IR, López de Alda M, Barceló D (2014) Risk assessment of pesticides detected in surface water of the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana basin, southern of Portugal). Sci Total Environ 488–489:208–2191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.088
Palma P, Palma VL, Matos C, Fernandes RM, Bohn A, Soares AMVM, Barbosa IR (2009) Effects of atrazine and endosulfan sulfate on the ecdysteroid system of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 74(5):676–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.021
Portal of the Government of the Santa Fe Province (2013a) http://www.santa-fe.gov.ar/gbrn/regpluv/. Accessed 1 Jan 2013
Portal of the Government of the Santa Fe Province (2013b) https://www.santafe.gov.ar/index.php/web/content/view/full/120719/(subtema)/93824. Accessed 1 Oct 2013
Primost J, Marino D, Aparicio V, Costa JL, Carriquiriborde P (2017) Glyphosate and AMPA, “pseudo-persistent” pollutants under real world agricultural management practices in the Mesopotamic Pampas agroecosystem, Argentina. Environ Poll:1–9
Regaldo L, Gagneten AM, Troiani H (2009) Accumulation of chromium and interaction with other elements in Chlorella sp. (Cloroficeae) and Daphnia magna (Crustacea, Cladocera). J Environ Biol 30(2):213–216
Regaldo L, Gervasio S, Gagneten AM, Troiani H (2013) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of copper and lead in Chlorella vulgaris. J Algal Biomass Utln 4:59–66
Regaldo L, Reno U, Gervasio S, Troiani H, Gagneten AM (2014) Effect of metals on Daphnia magna and cladocerans representatives of the Argentinean fluvial littoral. J Environ Biol 35(4):689–697
Romero DM, Ríos de Molina MC, Juárez AB (2011) Oxidative stress induced by a commercial glyphosate formulation in a tolerant strain of Chlorella kessleri. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74(4):741–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.10.034
Ronco AE, Marino DJG, Abelando M, Almada P, Apartin CD (2016) Water quality of the main tributaries of the Paraná Basin: glyphosate and AMPA in surface water and bottom sediments. Environ Monit Assess 188(8):458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5467-0
Siegfried K, Hahn-Tomer S, Koelsch A, Osterwalder E, Mattusch J, Staerk HJ, Meichtry J, de Seta G, Reina F, Panigatti C, Litter M, Harms H (2015) Introducing simple detection of bioavailable arsenic at Rafaela (Santa Fe Province, Argentina) using the ARSOlux biosensor. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(5):5465–5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120505465
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1969) Biometry. Principles and statistical methods in biological research. Madrid, pp 852
Solomon KR, Baker RP, Richards KR et al (1996) Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:31–76
Stratton GW (1984) Effects of the herbicide atrazine and its degradation products alone and in combination, on phototropic microorganisms. Arch Env Contam Toxicol 13(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055644
Trevors JT, Saier MH Jr (2010) Manage humans, not the environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 205(1):93–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0008-x
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2003a) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to chromium (in Spanish)
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2003b) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to atrazine (in Spanish)
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2004a) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to arsenic (in Spanish)
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2004b) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to endosulfan (in Spanish)
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2005a) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to lead (in Spanish)
Undersecretariat of Hydric Resources of Argentina for the protection of aquatic biota (2005b) (applicable to fresh water) Development of National Guidelines of Environmental Water Quality corresponding to copper (in Spanish)
Visviki K, Rashlin JW (1991) The toxic action and interaction of copper and cadmium to the marine algae Dunalliela minuta in both acute and chronic exposures. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20(2):271–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055915
Weber J, Halsall CJ, Muir DCG, Teixeira C, Burniston DA, Strachan WMJ, Hung H, Mackay N, Arnold D, Kylin H (2006) Endosulfan and γ-HCH in the Arctic: an assessment of surface seawater concentrations and airsurface exchange. Environ Sci Technol 40(24):7570–7576. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061591h
Wilcock RJ, McBride GB, Nagels JW, Northcott GL (1995) Water quality in a polluted lowland stream with chronically depressed dissolved oxygen: causes and effects. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 29(2):277–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.1995.9516661
Winkelmann DA, Klaine SJ (1991) Degradation and bound residue formation of four atrazine metabolites deethylatrazine, deisopropylatrazine, and hidroxyatrazine in a western Tennessee. Soil Environ Toxicol Chem 10(3):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620100307
Wong CK, Pak AP (2004) Acute and subchronic toxicity of the heavy metals copper, chromium, nickel and zinc, individually and in mixture, to the freshwater copepod Mesocyclops pehpeiensis. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 73:190–196
Woolhouse HW (1981) Aspects of the carbon and energy requirements of photosynthesis considered in relation to environmental constrains. In: Ecological risk assessment of atrazine in North American surface waters. Solomon KR, Baker DB, Richards RP et al (ed). Environ Toxicol Chem15:31–76
World Bank (2015) Performance of the cereals (Kg per hectare) http://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/AG.YLD.CREL.KG. Accessed 1 Nov 2015
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Universidad Nacional del Litoral, Project CAI +D No. 501 201101 00215 LI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Severine Le Faucheur
Highlights
- Metals, arsenic, and pesticides in surface waters and sediments of central-eastern Argentina were monitored for 1 year. The status of pollution in relation to standard levels was considered in conjunction with other assessment methods.
- Similarly, to physicochemical variables, microcontaminant concentrations in sediments between sites were more informative about the impairment of the system than those between months.
- In water samples, findings suggest a serious level of metal pollution—mainly Cr, Pb, Cu and As, and pesticides mostly by endosulfan. In sediment samples, Pb, As, Cu, and Cr also surpassed the established international guideline levels.
- Proper measures in terms of technological innovations or improvements of public and private policies must be taken immediately in order to protect aquatic resources and human health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Regaldo, L., Gutierrez, M.F., Reno, U. et al. Water and sediment quality assessment in the Colastiné-Corralito stream system (Santa Fe, Argentina): impact of industry and agriculture on aquatic ecosystems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 6951–6968 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0911-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0911-4