Abstract
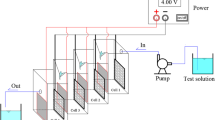
The performance of cathode on H2O2 electrogeneration is a critical factor that limits the practical application of electro-Fenton (EF) process. Herein, we report a simple but effective electrochemical modification of reticulated vitreous carbon foam (RVC foam) electrode for enhanced H2O2 electrogeneration. Cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectrum were used to characterize the modified electrode. Oxygen-containing groups (72.5–184.0 μmol/g) were introduced to RVC foam surface, thus resulting in a 59.8–258.2% higher H2O2 yield. The modified electrodes showed much higher electrocatalytic activity toward O2 reduction and good stability. Moreover, aimed at weakening the extent of electroreduction of H2O2 in porous RVC foam, the strategy of pulsed current was proposed. H2O2 concentration was 582.3 and 114.0% higher than the unmodified and modified electrodes, respectively. To test the feasibility of modification, as well as pulsed current, EF process was operated for removal of Reactive Blue 19 (RB19). The fluorescence intensity of hydroxybenzoic acid in EF with modified electrode is 3.2 times higher than EF with unmodified electrode, illustrating more hydroxyl radicals were generated. The removal efficiency of RB 19 in EF with unmodified electrode, modified electrode, and unmodified electrode assisted by pulsed current was 53.9, 68.9, and 81.1%, respectively, demonstrating that the green modification approach, as well as pulsed current, is applicable in EF system for pollutant removal.

ᅟ











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton SS, Evans MJB, Halliop E, MacDonald JAF (1997) Anodic oxidation of porous carbon. Langmuir 13(5):1332–1336. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9509413
Basova YV, Hatori H, Yamada Y, Miyashita K (1999) Effect of oxidation–reduction surface treatment on the electrochemical behavior of PAN-based carbon fibers. Electrochem Commun 1(11):540–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2481(99)00112-5
Berenguer R, Marco-Lozar JP, Quijada C, Cazorla-Amorós D, Morallón E (2009) Effect of electrochemical treatments on the surface chemistry of activated carbon. Carbon 47(4):1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.12.022
Brillas E, Mur E, Casado J (1996) Iron(II) catalysis of the mineralization of aniline using a carbon-PTFE O2-fed cathode. J Electrochem Soc 143(3):L49–L53. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1836528
Chen L, Ma J, Li X, Zhang J, Fang J, Guan Y, Xie P (2011) Strong enhancement on Fenton oxidation by addition of hydroxylamine to accelerate the ferric and ferrous iron cycles. Environ Sci Technol 45(9):3925–3930. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2002748
Daneshvar N, Aber S, Vatanpour V, Rasoulifard MH (2008) Electro-Fenton treatment of dye solution containing Orange II: influence of operational parameters. J Electroanal Chem 615(2):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2007.12.005
Drogui P, Elmaleh S, Rumeau M, Bernard C, Rambaud A (2001) Oxidising and disinfecting by hydrogen peroxide produced in a two-electrode cell. Water Res 35(13):3235–3241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00021-5
Es’haghzade Z, Pajootan E, Bahrami H, Arami M (2017) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles via aqueous based electro chemical route for heterogeneous electro-Fenton removal of azo dyes. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 71:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.11.015
Flores N, Thiam A, Rodriguez RM et al (2017) Electrochemical destruction of trans-cinnamic acid by advanced oxidation processes: kinetics, mineralization, and degradation route. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(7):6071–6082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6035-9
Gao C, Wang N, Peng S et al (2013) Influence of Fenton’s reagent treatment on electrochemical properties of graphite felt for all vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochim Acta 88:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.021
Gazi S, Ananthakrishnan R (2012) Semi-quantitative determination of hydroxyl radicals by benzoic acid hydroxylation: an analytical methodology for photo-Fenton systems. Curr Anal Chem 8(1):143–149. https://doi.org/10.2174/157341112798472297
Gong Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Tian X, Wang A (2016) Partial degradation of levofloxacin for biodegradability improvement by electro-Fenton process using an activated carbon fiber felt cathode. J Hazard Mater 304:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.064
Hickling a, Wilson WH (1951) The anodic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. J Electrochem Soc 98(11):425. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2778020
Hou B, Han H, Jia S et al (2015) Three-dimensional heterogeneous electro-Fenton oxidation of biologically pretreated coal gasification wastewater using sludge derived carbon as catalytic particle electrodes and catalyst. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 60:352–360
Jiang J, Pang SY, Ma J, Liu H (2012) Oxidation of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals by potassium permanganate in synthetic and real waters. Environ Sci Technol 46(3):1774–1781. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2035587
Khataee AR, Safarpour M, Zarei M, Aber S (2011) Electrochemical generation of H2O2 using immobilized carbon nanotubes on graphite electrode fed with air: investigation of operational parameters. J Electroanal Chem 659(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.05.002
Li Q, Batchelor-Mcauley C, Lawrence NS et al (2014) A flow system for hydrogen peroxide production at reticulated vitreous carbon via electroreduction of oxygen. J Solid State Electrochem 18(5):1215–1221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2250-9
Li W, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Sun M, Cheng R, Xu X, Chen Y, Mo Y (2005) Effect of hydroxyl radical on the structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Synth Met 155(3):509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2005.07.346
Li XG, Huang KL, Liu SQ et al (2007) Characteristics of graphite felt electrode electrochemically oxidized for vanadium redox battery application. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China (English Edition) 17(1):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(07)60071-5
Liang C, Su HW (2009) Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(11):5558–5562. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9002848
Liu Y, Chen S, Quan X, Yu H, Zhao H, Zhang Y (2015) Efficient mineralization of perfluorooctanoate by electro-Fenton with H2O2 electro-generated on hierarchically porous carbon. Environ Sci Technol 49(22):13528–13533. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03147
Miao J, Zhu H, Tang Y, Chen Y, Wan P (2014) Graphite felt electrochemically modified in H2SO4 solution used as a cathode to produce H2O2 for pre-oxidation of drinking water. Chem Eng J 250:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.043
Nava JL, Recéndiz A, González LG, Carreňo G, Martínez F (2009) Mass transport and potential studies in a flow-through porous electrode reactor: a comparative study of reticulated vitreous carbon and graphite felt used as cathode. Port Electrochim Acta 27(3):381–396. https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.200903381
Navalon S, Alvaro M, Garcia H (2008) Reaction of chlorine dioxide with emergent water pollutants: product study of the reaction of three β-lactam antibiotics with ClO2. Water Res 42(8-9):1935–1942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.11.023
Neta P, Madhavan V, Zemel H, Fessenden RW (1977) Rate constants and mechanism of reaction of sulfate radical anion with aromatic compounds. J Am Chem Soc 99(1):163–164. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00443a030
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R (2012) Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: an overview. Desalination 299:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.05.011
Oturan MA, Peiroten J, Chartrin P, Acher AJ (2000) Complete destruction of p-Nitrophenol in aqueous medium by electro-Fenton method. Environ Sci Technol 34(16):3474–3479. https://doi.org/10.1021/es990901b
Pimentel M, Oturan N, Dezotti M, Oturan MA (2008) Phenol degradation by advanced electrochemical oxidation process electro-Fenton using a carbon felt cathode. Appl Catal B Environ 83(1-2):140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.02.011
Pittman CU, Jiang W, Yue ZR et al (1999) Surface properties of electrochemically oxidized carbon fibers. Carbon 37(11):1797–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00048-2
Qiang ZM, Chang JH, Huang CP (2002) Electrochemical generation of hydrogen peroxide from dissolved oxygen in acidic solutions. Water Res 36(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00235-4
Sánchez-Sánchez CM, Bard AJ (2009) Hydrogen peroxide production in the oxygen reduction reaction at different electrocatalysts as quantified by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Anal Chem 81(19):8094–8100. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac901291v
Scialdone O, Guarisco C, Galia A, Filardo G, Silvestri G, Amatore C, Sella C, Thouin L (2010) Anodic abatement of organic pollutants in water in micro reactors. J Electroanal Chem 638(2):293–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2009.10.031
Sheng Y, Zhao Y, Wang X, Wang R, Tang T (2014) Electrogeneration of H2O2 on a composite acetylene black-PTFE cathode consisting of a sheet active core and a dampproof coating. Electrochim Acta 133:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.04.071
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Strelko VV, Kartel NT, Dukhno IN, Kuts VS, Clarkson RB, Odintsov BM (2004) Mechanism of reductive oxygen adsorption on active carbons with various surface chemistry. Surf Sci 548(1-3):281–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2003.11.012
Tabti Z, Ruiz-Rosas R, Quijada C, Cazorla-Amorós D, Morallón E (2014) Tailoring the surface chemistry of activated carbon cloth by electrochemical methods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(14):11682–11691. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502475v
Tang X, Guo K, Li H, Du Z, Tian J (2011) Electrochemical treatment of graphite to enhance electron transfer from bacteria to electrodes. Bioresour Technol 102(3):3558–3560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.022
Walsh FC, Arenas LF, Ponce de Leon C et al (2016) The continued development of reticulated vitreous carbon as a versatile electrode material: structure, properties and applications. Electrochim Acta 215:566–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.103
Yoon C-M, Long D, Jang S-M, Qiao W, Ling L, Miyawaki J, Rhee CK, Mochida I, Yoon SH (2011) Electrochemical surface oxidation of carbon nanofibers. Carbon 49(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.08.047
Yu F, Zhou M, Yu X (2015) Cost-effective electro-Fenton using modified graphite felt that dramatically enhanced on H2O2 electro-generation without external aeration. Electrochim Acta 163:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.02.166
Yu M, Teel AL, Watts RJ (2016) Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by subsurface minerals. J Contam Hydrol 191:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2016.05.001
Yuan S, Fan Y, Zhang Y, Tong M, Liao P (2011) Pd-catalytic in situ generation of H2O2 from H2 and O2 produced by water electrolysis for the efficient electro-Fenton degradation of rhodamine B. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8514–8520. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2022939
Yuan S, Liao P, Alshawabkeh AN (2014) Electrolytic manipulation of persulfate reactivity by iron electrodes for trichloroethylene degradation in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 48(1):656–663. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404535q
Yue ZR, Jiang W, Wang L, Gardner SD, Pittman CU Jr (1999) Surface characterization of electrochemically oxidized carbon fibers. Carbon 37(11):1785–1796. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00047-0
Zhang H, Yamada H, Tsuno H (2008a) Removal of endocrine-disrupting chemicals during ozonation of municipal sewage with brominated byproducts control. Environ Sci Technol 42(9):3375–3380. https://doi.org/10.1021/es702714e
Zhang L, Li P, Gong Z, Li X (2008b) Photocatalytic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on soil surfaces using TiO2 under UV light. J Hazard Mater 158(2-3):478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.119
Zhang W, Xi J, Li Z, Zhou H, Liu L, Wu Z, Qiu X (2013) Electrochemical activation of graphite felt electrode for VO2+/VO2+ redox couple application. Electrochim Acta 89:429–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.11.072
Zhou L, Zhou M, Hu Z, Bi Z, Serrano KG (2014) Chemically modified graphite felt as an efficient cathode in electro-Fenton for p-nitrophenol degradation. Electrochim Acta 140:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.04.090
Zhou L, Zhou M, Zhang C, Jiang Y, Bi Z, Yang J (2013) Electro-Fenton degradation of p-nitrophenol using the anodized graphite felts. Chem Eng J 233:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.08.044
Zhou W, Zhao H, Gao J, Meng X, Wu S, Qin Y (2016) Influence of reagents addition strategy on Fenton oxidation of rhodamine B: control of competitive reaction of ·OH. RSC Adv 6(110):108791–108800. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20242J
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Highlights
(1) Green electrochemical modification of RVC foam in acid-free, low conductivity electrolyte was reported.
(2) By applying pulsed current, the H2O2 concentration was 582.3 and 114.0% higher than the unmodified and modified RVC foam electrodes, respectively.
(3) CV, CA, NaOH uptake method, and XPS were used to characterize the modified electrodes.
(4) Performance on model pollutant removal in electro-Fenton process, as well as enhanced hydroxyl radical generation, was analyzed.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 10020 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Ding, Y., Gao, J. et al. Green electrochemical modification of RVC foam electrode and improved H2O2 electrogeneration by applying pulsed current for pollutant removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 6015–6025 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0810-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0810-8