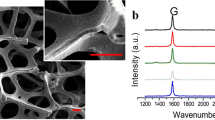
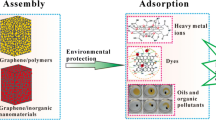
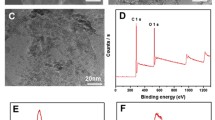
Abstract
Oil spills over seawater and dye pollutants in water cause economic and environmental damage every year. Among various methods to deal oil spill problems, the use of porous materials has been proven as an effective strategy. In recent years, graphene-based porous sorbents have been synthesized to address the shortcomings associated with conventional sorbents such as their low uptake capacity, slow sorption rate, and non-recyclability. This article reviews the research undertaken to control oil spillage using three-dimensional (3D) graphene-based materials. The use of these materials for removal of dyes and miscellaneous environmental pollutants from water is explored and the application of various multifunctional 3D oil sorbents synthesized by surface modification technique is presented. The future prospects and limitations of these materials as sorbents are also discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebajo MO, Frost RL, Kloprogge JT et al (2003) Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J Porous Mater 10:159–170
Al-Majed AA, Adebayo AR, Hossain ME (2012) A sustainable approach to controlling oil spills. J Environ Manag 113:213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.07.034
Al-Majed AA, Adebayo AR, Hossain ME (2014) A novel technology for sustainable oil spills control. Environ Eng Manag J 13:265–274
Ali Tahir A, Ullah H, Sudhagar P, et al (2016) The application of graphene and its derivatives to energy conversion, storage, and environmental and biosensing devices. Chem Rec 1591–1634. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201500279
Bai H, Li C, Wang X, Shi G (2011) On the gelation of graphene oxide. J Phys Chem C 115:5545–5551. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1120299
Bartolomei M, Carmona-Novillo E, Hernández MI et al (2014) Penetration barrier of water through graphynes’ pores: first-principles predictions and force field optimization. J Phys Chem Lett 5:751–755. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz4026563
Bayat A, Aghamiri SF, Moheb A, Vakili-Nezhaad GR (2005) Oil spill cleanup from sea water by sorbent materials. Chem Eng Technol 28:1525–1528. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.200407083
Bhuyan MSA, Uddin MN, Islam MM et al (2016) Synthesis of graphene. Int Nano Lett 6:65–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-015-0176-1
Bi H, Xie X, Yin K et al (2014) Highly enhanced performance of spongy graphene as an oil sorbent. J Mater Chem A 2:1652–1656. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14112H
Bi H, Xie X, Yin K et al (2012) Spongy graphene as a highly efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv Funct Mater 22:4421–4425. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201200888
Bonaccorso F, Lombardo A, Hasan T et al (2012) Production and processing of graphene and 2D crystals. Mater Today 15:564–589
Broje V, Keller AA (2006) Improved mechanical oil spill recovery using an optimized geometry for the skimmer surface. Environ Sci Technol 40:7914–7918. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061842m
Buist I, Potter S, Nedwed T, Mullin J (2011) Herding surfactants to contract and thicken oil spills in pack ice for in situ burning. Cold Reg Sci Technol 67:3–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2011.02.004
Calcagnile P, Fragouli D, Bayer IS et al (2012) Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano 6:5413–5419. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3012948
Cao N, Lyu Q, Li J et al (2017) Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 326:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.117
Cao X, Zeng Z, Shi W et al (2013) Three-dimensional graphene network composites for detection of hydrogen peroxide. Small 9:1703–1707. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200683
Carmalin Sophia A, Lima EC, Allaudeen N, Rajan S (2016) Application of graphene based materials for adsorption of pharmaceutical traces from water and wastewater—a review. Desalin Water Treat 3994:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1172989
Chen Z, Ren W, Liu B et al (2010) Bulk growth of mono- to few-layer graphene on nickel particles by chemical vapor deposition from methane. Carbon 48:3543–3550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.05.052
Chen Z, Ren W, Gao L et al (2011) Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat Mater 10:424–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3001
Chu Y, Pan Q (2012) Three-dimensionally macroporous Fe/C nanocomposites as highly selective oil-absorption materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(5):2420. https://doi.org/10.1021/am3000825
Deng J, Zhang X, Zeng G et al (2013) Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and ionic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite as an adsorbent. Chem Eng J 226:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.045
Falcao EHL, Wudl F (2007) Carbon allotropes: beyond graphite and diamond. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb
Fan X, Chen X, Dai L (2015a) 3D graphene based materials for energy storage. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 20:429–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2015.11.005
Fan Y, Ma W, Han D et al (2015b) Convenient recycling of 3D AgX/graphene aerogels (X = Br, Cl) for efficient photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Adv Mater 27:3767–3773. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500391
Forgacs E, Cserháti T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30:953–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001
Gao X, Jang J, Nagase S (2010) Hydrazine and thermal reduction of graphene oxide: reaction mechanisms and design. J Phys Chem C 114:832–842
Georgakilas V, Perman JA, Tucek J, Zboril R (2015) Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem Rev 115:4744–4822. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500304f
Gui X, Wei J, Wang K et al (2010) Carbon nanotube sponges. Adv Mater 22:617–621. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200902986
Gupta S, Tai N-H (2016) Carbon materials as oil sorbents: a review on the synthesis and performance. J Mater Chem A 4:1550–1565. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA08321D
He Y, Liu Y, Wu T et al (2013) An environmentally friendly method for the fabrication of reduced graphene oxide foam with a super oil absorption capacity. J Hazard Mater 260:796–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.042
Hou C, Zhang Q, Li Y, Wang H (2012) P25-graphene hydrogels: room-temperature synthesis and application for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 205–206:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.071
Hu XJ, Liu YG, Wang H et al (2013) Removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution using sulfonated magnetic graphene oxide composite. Sep Purif Technol 108:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.02.011
Huang S, Shi J (2014) Monolithic macroporous carbon materials as high-performance and ultralow-cost sorbents for efficiently solving organic pollution. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:4888–4893
Huang Y, Li C, Lin Z (2014) EDTA-induced self-assembly of 3D graphene and its superior adsorption ability for paraquat using a teabag. ACS Appl Mater {&} interfaces 6:19766–19773. https://doi.org/10.1021/am504922v
Hummers WS Jr, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Ip AWM, Barford JP, McKay G (2010) Biodegradation of reactive black 5 and bioregeneration in upflow fixed bed bioreactors packed with different adsorbents. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:658–667. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2349
Jang S, Haldorai Y, Lee G, et al (2015) Porous three-dimensional graphene foam/Prussian blue composite for efficient removal of radioactive Cs. Nat Publ Gr 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17510
Jiao T, Liu Y, Wu Y, et al (2015) Facile and scalable preparation of graphene oxide-based magnetic hybrids for fast and highly efficient removal of organic dyes. Sci Rep 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12451
Juuso TK, Kettunen M, Ras RHA, Olli I (2011) Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1813–1816
Kim T, Lee JS, Lee G et al (2016) Autonomous graphene vessel for suctioning and storing liquid body of spilled oil. Sci Rep 6:22339. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22339
Kujawinski EB, Kido Soule MC, Valentine DL et al (2011) Fate of dispersants associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ Sci Technol 45:1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103838p
Lei W, Portehault D, Liu D et al (2013) Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning. Nat Commun 4:1777. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2818
Lessard R, DeMarco G (2000) The significance of oil spill dispersants. Spill Sci Technol Bull 6:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-2561(99)00061-4
Li N, Zhang Q, Gao S et al (2013) Three-dimensional graphene foam as a biocompatible and conductive scaffold for neural stem cells. Sci Rep 3:1604. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01604
Lin Y, Xu S, Li J (2013) Fast and highly efficient tetracyclines removal from environmental waters by graphene oxide functionalized magnetic particles. Chem Eng J 225:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.104
Liu F, Chung S, Oh G, Seo TS (2012) A three-dimensional graphene oxide nanostructure for fast and efficient dye removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1–2
Liu M, Chen C, Hu J et al (2011) Synthesis of magnetite/graphene oxide composite and application for cobalt (II) removal. J Phys Chem C 115:25234–25240
Liu W, Cai J, Li Z (2015a) Self-assembly of semiconductor nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) composite aerogels for enhanced photocatalytic performance and facile recycling in aqueous photocatalysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc5006473
Liu Y, Ma J, Wu T et al (2013) Cost effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as highly efficient and reusable oil absorbent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10018–10026
Liu Z, Wang X, Luo Z, et al (2015b) Removing of disinfection by-product precursors from surface water by using magnetic graphene oxide. PLoS One 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143819
Loeblein M, Bolker A, Tsang SH et al (2015) 3D Graphene-infused polyimide with enhanced electrothermal performance for long-term flexible space applications. Small 11:6425–6434. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201502670
Luo J, Liu J, Zeng Z et al (2013) Three-dimensional graphene foam supported Fe3O4 lithium battery anodes with long cycle life and high rate capability. Nano Lett 13:6136–6143. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl403461n
Ma T, Chang PR, Zheng P et al (2014) Fabrication of ultra-light graphene-based gels and their adsorption of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 240:595–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.077
Marcano DC, Kosynkin DV, Berlin JM et al (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4:4806–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
Mullin JV, Champ M a (2003) Introduction/overview to in situ burning of oil spills. Spill Sci Technol Bull 8:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-2561(03)00076-8
Nguyen DD, Tai N-H, Lee S-B, Kuo W-S (2012) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ Sci 5:7908. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee21848h
Process S, Cong H, Ren X et al (2012) Macroscopic multifunctional graphene-based hydrogels and aerogels by a metal ion induced. ACS Nano 6:2693–2703. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn300082k
Qiu B, Xing M, Zhang J et al (2014) Mesoporous TiO2 nanocrystals grown in-situ on graphene aerogels for high photocatalysis and lithium ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 136:5852–5855. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja500873u
Ratna PBS (2012) Pollution due to synthetic dyes toxicity & carcinogenicity studies and remediation. Int J Environ Sci 3:940–955. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.2012030133002
Ren RP, Li W, Lv YK (2017) A robust, superhydrophobic graphene aerogel as a recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents at various temperatures. J Colloid Interface Sci 500:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.071
Riaz MA, Hadi P, Abidi IH et al (2017) Recyclable 3D graphene aerogel with bimodal pore structure for ultrafast and selective oil sorption from water. RSC Adv 7:29722–29731. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02886E
Rogowska J, Namie J (2010) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology volume 206. Springer, New York
Saleem J, Adil Riaz M, Gordon M (2018) Oil sorbents from plastic wastes and polymers: a review. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.072
Saleem J, Bazargan A, Barford J, McKay G (2014) Super-fast oil uptake using porous ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene sheets. Polym Adv Technol 25:1181–1185. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3376
Saleem J, Ning C, Barford J, McKay G (2015) Combating oil spill problem using plastic waste. Waste Manag 44:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.003
Schulze R (1998) Oil spill response performance review of skimmers, ASTM International Volume 34
Sha J, Gao C, Lee S-K et al (2016) Preparation of three-dimensional graphene foams using powder metallurgy templates. ACS Nano 10:1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b06857
Shen Y, Li L, Xiao K, Xi J (2016) Constructing three-dimensional hierarchical architectures by integrating carbon nanofibers into graphite felts for water purification. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2351–2358. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00030
Sheng K, Xu Y, Li C, Shi G (2011) High-performance self-assembled graphene hydrogels prepared by chemical reduction of graphene oxide. New Carbon Mater 26:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(11)60062-0
Sui Z-Y, Cui Y, Zhu J-H, Han B-H (2013) Preparation of three-dimensional graphene oxide-polyethylenimine porous materials as dye and gas adsorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:9172–9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/am402661t
Sun H, Li A, Qin X et al (2013a) Three-dimensional superwetting mesh film based on graphene assembly for liquid transportation and selective absorption. ChemSusChem 6:2377–2381. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201300319
Sun H, Xu Z, Gao C (2013b) Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv Mater 25:2554–2560. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204576
Tiwari JN, Mahesh K, Le NH et al (2013) Reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogels for the efficient capture of dye pollutants from aqueous solutions. Carbon N Y 56:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.01.001
Wan W b, Yu S, Dong F et al (2016) Efficient C3N4/graphene oxide macroscopic aerogel visible-light photocatalyst. J Mater Chem A 4:7823–7829. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta01804a
Wang C, Lin S (2013) Robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge for effective continuous absorption and expulsion of oil pollutants from. Water 8861–8864
Wang C, Yang S, Ma Q et al (2017a) Preparation of carbon nanotubes/graphene hybrid aerogel and its application for the adsorption of organic compounds. Carbon N Y 118:765–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.04.001
Wang F, Wang Y, Zhan W et al (2017b) Facile synthesis of ultra-light graphene aerogels with super absorption capability for organic solvents and strain-sensitive electrical conductivity. Chem Eng J 320:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.082
Wu C, Huang X, Wu X et al (2013a) Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil–water separators. Adv Mater 25:5658–5662. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302406
Wu SY, An SSA, Hulme J (2015) Current applications of graphene oxide in nanomedicine. Int J Nanomedicine 10:9–24. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S88285
Wu T, Chen M, Zhang L et al (2013b) Three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels prepared by a self-assembly process and its excellent catalytic and absorbing performance. J Mater Chem A 1:7612. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta10989e
Xia X, Chao D, Fan Z et al (2014) A new type of porous graphite foams and their integrated composites with oxide/polymer core/shell nanowires for supercapacitors: structural design, fabrication, and full supercapacitor demonstrations. Nano Lett 14:1651–1658. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5001778
Xu X, Li H, Zhang Q et al (2015) 3D graphene/iron oxide aerogel elastomer deformable in a magnetic field. ACS Nano 9:3969–3977. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn507426u
Xu Y, Wu Q, Sun Y et al (2010) Three-dimensional self-assembly of graphene oxide and DNA into multifunctional hydrogels. ACS Nano 4:7358–7362. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1027104
Yang K, Chen B, Zhu L (2015a) Graphene-coated materials using silica particles as a framework for highly efficient removal of aromatic pollutants in water. Nat Publ Gr 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11641
Yang Z, Chabi S, Xia Y, Zhu Y (2015b) Preparation of 3D graphene-based architectures and their applications in supercapacitors. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 25:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2015.11.010
Ye S, Liu Y, Feng J (2017) Low-density, mechanical compressible, water-induced self-recoverable graphene aerogels for water treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:22456–22464. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04536
Yuan J, Liu X, Akbulut O et al (2008) Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat Nanotechnol 3(6):332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.136
Zahed MA, Aziz HA, Isa MH et al (2010) Optimal conditions for bioremediation of oily seawater. Bioresour Technol 101:9455–9460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.077
Żelechowska K, Kondratowicz I, Sadowski W (2014) 3D porous graphene-based structures—synthesis and applications. Carbon Nanotechnol 4438–4457. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr06858g
Zhang X, Liu D, Yang L et al (2015) Self-assembled three-dimensional graphene-based materials for dye adsorption and catalysis. J Mater Chem A 3:10031–10037. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA00355E
Zhao J, Ren W, Cheng H-M (2012a) Graphene sponge for efficient and repeatable adsorption and desorption of water contaminations. J Mater Chem 22:20197. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34128j
Zhao Y, Hu C, Hu Y et al (2012b) A versatile, ultralight, nitrogen-doped graphene framework. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:11371–11375. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201206554
Zhu H, Chen D, An W et al (2015a) A robust and cost-effective superhydrophobic graphene foam for efficient oil and organic solvent recovery. Small 11:5222–5229. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201501004
Zhu H, Chen D, Li N et al (2015b) Graphene foam with switchable oil wettability for oil and organic solvents recovery. Adv Funct Mater 25:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201403864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riaz, M.A., McKay, G. & Saleem, J. 3D graphene-based nanostructured materials as sorbents for cleaning oil spills and for the removal of dyes and miscellaneous pollutants present in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 27731–27745 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0606-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0606-x