Abstract
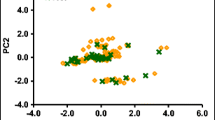
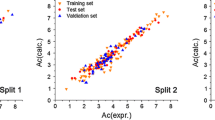
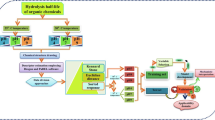
In advanced water treatment processes, the degradation efficiency of contaminants depends on the reactivity of the hydroxyl radical toward a target micropollutant. The present study predicts the hydroxyl radical rate constant in water (k OH) for 118 emerging micropollutants, by means of quantitative structure-property relationships (QSPR). The conformation-independent QSPR approach is employed, together with a large number of 15,251 molecular descriptors derived with the PaDEL, Epi Suite, and Mold2 freewares. The best multivariable linear regression (MLR) models are found with the replacement method variable subset selection technique. The proposed five-descriptor model has the following statistics for the training set: \( {R}_{\mathrm{train}}^2=0.88 \), RMS train = 0.21, while for the test set is \( {R}_{\mathrm{test}}^2=0.87 \), RMS test = 0.11. This QSPR serves as a rational guide for predicting oxidation processes of micropollutants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACD/ChemSketch (2016) http://www.acdlabs.com
Aranda JF, Garro Martinez JC, Castro EA, Duchowicz PR (2016) Conformation-independent QSPR approach for the soil sorption coefficient of heterogeneous compounds. Int J Mol Sci 17:1247–1255
Bagheri M, Mohseni M (2015) A study of enhanced performance of VUV/UV process for the degradation of micropollutants from contaminated water. J Hazard Mater 294:1–8
Benfenati, E. (2013) Theory, guidance and applications on QSAR and REACH, Orchestra, http://ebook.insilico.eu/insilico-ebook-orchestra-benfenati-ed1_rev-June2013.pdf
Borhani TNG, Saniedanesh M, Bagheri M, Lim JS (2016) QSPR prediction of the hydroxyl radical rate constant of water contaminants. Water Res 98:344–353
Buxton GV, Greenstock CL, Helman WP, Ross AB (1988) Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen-atoms and hydroxyl radicals (OH/O−) in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Ref Data 17:513–886
Delgado LF, Charles P, Glucina K, Morlay C (2012) QSAR-like models: a potential tool for the selection of PhACs and EDCs for monitoring purposes in drinking water treatment systems—a review. Water Res 46:6196–6209
Diudea MVE (2001) QSPR/QSAR studies by molecular descriptors. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Draper NR, Smith H (1981) Applied regression analysis. John Wiley&Sons, New York
Duchowicz PR, Castro EA, Fernández FM (2006) Alternative algorithm for the search of an optimal set of descriptors in QSAR-QSPR studies. MATCH Commun Math Comput Chem 55:179–192
Duchowicz PR, Comelli NC, Ortiz EV, Castro EA (2012) QSAR study for carcinogenicity in a large set of organic compounds. Curr Drug Safe 7:282–288
Duchowicz PR, Bennardi DO, Baselo DE, Bonifazi EL, Rios-Luci C, Padrón JM, Burton G, Misico RI (2014) QSAR on antiproliferative naphthoquinones based on a conformation-independent approach. Eur J Med Chem 77:176–184
Duchowicz PR, Fioressi SE, Bacelo DE, Saavedra LM, Toropova AP, Toropov AA (2015) QSPR studies on refractive indices of structurally heterogeneous polymers. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 140:86–91
Elovitz MS, von Gunten U (1999) Hydroxyl radical ozone ratios during ozonation processes. I The Rct concept. Ozone Sci Eng 21:239–260
Epi Suite 4.11 (2016) U.S. EPA: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-screening-tools/epi-suitetm-estimation-program-interface
Eriksson L, Jaworska J, Worth AP, Cronin MT, McDowell RM, Gramatica P (2003) Methods for reliability and uncertainty assessment and for applicability evaluations of classification- and regression-based QSARs. Environ Health Perspect 111:1361–1375
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2! J Mol Graph Model 20:269–276
Gramatica P (2007) Principles of QSAR models validation: internal and external. QSAR Comb Sci 26:694–701
Hansch C, Leo A (1995) Exploring QSAR. fundamentals and applications in chemistry and biology. American Chemical Society, Washington, D. C
Hong H, Xie Q, Ge W, Qian F, Fang H, Shi L, Su Z, Perkins R, Tong W (2008) Mold2, molecular descriptors from 2D structures for chemoinformatics and toxicoinformatics. J Chem Inf Model 48:1337–1344
Open Babel for Windows (2016) http://openbabel.org/wiki/Category:Installation
Jagiello K, Grzonkowska M, Swirog M, Ahmed L, Rasulev B, Avramopoulos A, Papadopoulos MG, Leszczynski J, Puzyn T (2016) Advantages and limitations of classic and 3D QSAR approaches in nano-QSAR studies based on biological activity of fullerene derivatives. J Nanopart Res 18:256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3564-1
Jaworska J, Nikolova-Jeliazkova N, Aldenberg T (2005) QSAR applicability domain estimation by projection of the training set in descriptor space: a review. ATLA Altern Lab Anim 18:256
Jin X, Peldszus S, Huck PM (2012) Reaction kinetics of selected micropollutants in ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. Water Res 46:6519–6530
Jin X, Peldszus S, Huck PM (2015) Predicting the reaction rate constants of micropollutants with hydroxyl radicals in water using QSPR modeling. Chemosphere 138:1–9
Katritzky AR, Goordeva EV (1993) Traditional topological indices vs. electronic, geometrical, and combined molecular descriptors in QSAR/QSPR research. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 33:835–857
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ (2005) Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis. Wiley, New York
Kusic H, Rasulev B, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J, Koprivanac N (2009) Prediction of rate constants for radical degradation of aromatic pollutants in water matrix: a QSAR study. Chemosphere 75:1128–1134
Lee Y, Gunten U v (2012) Quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) for the transformation of organic micropollutants during oxidative water treatment. Water Res 46:6177–6195
Lee Y, von Gunten U (2012) Quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSARs) for the transformation of organic micropollutants during oxidative water treatment. Water Res 46:6177–6195
Leonard JT, Roy K (2006) On selection of training and test sets for the development of predictive QSAR models. QSAR Comb Sci 25:235–251
Luo Y, Guo W, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD, Hai FI, Zhang J, Liang S, Wang XC (2014) A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 473-474:619–641
Matlab 7.0. (2008) The MathWorks Inc., Masachussetts, USA. http://www.mathworks.com
Minakata D, Li K, Westerhoff P, Crittenden J (2009) Development of a group contribution method to predict aqueous phase hydroxyl radical (OH) reaction rate constants. Environ Sci Technol 43:6220–6227
Monod A, Doussin JF (2008) Structure-activity relationship for the estimation of OH-oxidation rate constants of aliphatic organic compounds in the aqueous phase: alkanes, alcohols, organic acids and bases. Atmos Environ 42:7611–7622
Morales AH, Duchowicz PR, Cabrera Pérez MA, Castro EA, Cordeiro MNDS, González MP (2006) Application of the replacement method as a novel variable selection strategy in QSAR. 1. Carcinogenic potential. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 81:180–187
PaDEL (2016). http://www.yapcwsoft.com
Peres JA, Dominguez JR, Beltran-Heredia J (2010) Reaction of phenolic acids with fenton-generated hydroxyl radicals: Hammett correlation. Desalination 252:167–171
Puzyn T, Leszczynski J, Cronin MTD (2010) Recent advances in QSAR studies: methods and applications: challenges and advances in computational chemistry and physics. Springer Science&Business Media B.V, Netherlands
Rojas C, Duchowicz PR, Tripaldi P, Pis Diez R (2015) Quantitative structure-property relationship analysis for the retention index of fragrance-like compounds on a polar stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1422:277–288
Rosenfeldt EJ, Linden KG (2007) The ROH, UV concept to characterize and the model UV/H2O2 process in natural waters. Environ Sci Technol 41:2548–2553
Roy K (2015) Quantitative structure-activity relationships in drug design, predictive toxicology, and risk assessment. IGI Global, New York
Roy K, Roy PP (2009) Comparative chemometric modeling of cytochrome 3A4 inhibitory activity of structurally diverse compounds using stepwise MLR, FAMLR, PLS, GFA, G/PLS and ANN techniques. Eur J Med Chem 44:2913–2922
Roy K, Kar S, Ambure P (2015) On a simple approach for determining applicability domain of QSAR models. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 145:22–29
Roy K, Das RN, Ambure P, Aher RB (2016) Be aware of error measures. Further studies on validation of predictive QSAR models. Chemom Intel Lab Syst 152:18–33
Rücker C, Rücker G, Meringer M (2007) Y-randomization and its variants in QSPR/QSAR. J Chem Inf Model 47:2345–2357
Sudhakaran S, Amy GL (2013) QSAR models for oxidation of organic micropollutants in water based on ozone and hydroxyl radical rate constants and their chemical classification. Water Res 47:1111–1122
Sudhakaran S, Calvin J, Amy GL (2012) QSAR models for the removal of organic micropollutants in four different river water matrices. Chemosphere 87(2):144–150
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2009) Molecular descriptors for chemoinformatics (methods and principles in medicinal chemistry). Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Toropov AA, Toropova AP, Rasulev BF, Benfenati E, Gini G, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) Coral: QSPR modeling of rate constants of reactions between organic aromatic pollutants and hydroxyl radical. J Comput Chem 33:1902–1906
Yap CW (2011) PaDEL-descriptor: an open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J Comput Chem 32:1466–1474
Zimbron JA, Reardon KF (2005) Hydroxyl free radical reactivity toward aqueous chlorinated phenols. Water Res 39:865–869
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the reviewers’ comments, which have helped to improve this work. EVO, DEB, SEF, and PRD are members of the scientific researcher career of CONICET.
Funding
We thank the financial support provided by the National Research Council of Argentina (CONICET) PIP11220130100311 project and to Ministerio de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación Productiva for the electronic library facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz, E.V., Bennardi, D.O., Bacelo, D.E. et al. The conformation-independent QSPR approach for predicting the oxidation rate constant of water micropollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 27366–27375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0315-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0315-5