Abstract
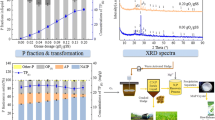
The release rule of phosphorus from sewage sludge during ozonation and removal by the magnesium ammonium phosphate (MAP) method were investigated. The results showed that the concentrations of total phosphorus in aqueous phase (TP(A)) and orthophosphate (PO4 3−-P) in ozonized sludge supernatant rose obviously with increasing ozone dose when ozone dose was below 61.2 mg O3/gSS then almost kept constant. The TP(A) and PO4 3−-P contents in the ozonized sludge supernatant were 70.9 and 63.3 mg/L when ozone dose was 61.2 mg O3/gSS, respectively. Total phosphorus in the sludge solid (TP(S)) was mostly distributed in inorganic phosphorus (IP) (more than 81.5% of TP(S)), and non-apatite inorganic phosphorus (NAIP) was the major component of IP in the sludge (more than 78.7% of IP) during ozonation. The release contribution (RC) of IP to TP(A) accounted for over 73.9%. The optimized conditions for the removal of phosphorus from ozonized sludge supernatant were set at an initial Mg2+/PO4 3−-P molar ratio of 1.8, pH 9.5, and reaction time of 5 min, under which the removal efficiencies of TP(A) and PO4 3−-P were 43.1 and 52.2%, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjum M, Al-Makishah N, Barakat M (2016) Wastewater sludge stabilization using pre-treatment methods. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:615–632
de-Bashan L, Bashan Y (2004) Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997-2003). Water Res 38:4222–4246
Bertanza G, Pedrazzani R, Manili L, Menoni L (2013) Bio-P release in the final clarifiers of a large WWTP with co-precipitation: key factors and troubleshooting. Chem Eng J 230:195–201
Bertanza G, Papa M, Canato M, Collivignarelli M, Pedrazzani R (2014) How can sludge dewatering devices be assessed? Development of a new DSS and its application to real case studies. J Environ Manag 137:86–92
Bi W, Li Y, Hu Y (2014) Recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from alkaline hydrolysis supernatant of excess sludge by magnesium ammonium phosphate. Bioresour Technol 166:1–8
Bouropoulos N, Koutsoukos P (2000) Spontaneous precipitation of struvite from aqueous solutions. J Cryst Growth 213:381–388
CEPB (2002) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, Fourth edn. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Cesbron D, Deleris S, Debellefontaine H, Roustan M, Paul E (2003) Study of competition for ozone between soluble and particulate matter during activated sludge ozonation. Chem Eng Res Des 81:1165–1170
Chu L, Yan S, Xing X, Sun X, Jurcik B (2009) Progress and perspectives of sludge ozonation as a powerful pretreatment method for minimization of excess sludge production. Water Res 43:1811–1822
Cui R, Jahng D (2004) Nitrogen control in AO process with recirculation of solubilized excess sludge. Water Res 38:1159–1172
Demirer S, Othman M (2009) Removal of ammonium and phosphate from the supernatant of an aerobically digested waste activated sludge by chemical precipitation. Bioresour Technol 100:3236–3244
Dytczak M, Londry K, Siegrist H, Oleszkiewicz J (2007) Ozonation reduces sludge production and improves denitrification. Water Res 41:543–550
Hao X, Wang C, Lan L, Loosdrecht M (2008) Struvite formation, analytical methods and effects of pH and Ca2+. Water Sci Technol 58:1687–1692
He S, Xue G, Wang B (2006) Activated sludge ozonation to reduce sludge productionin membrane bioreactor (MBR). J Hazard Mater B135:406–411
He Z, Liu W, Wang L, Yang C, Guo Z, Zhou A, Liu J, Wang A (2016) Role of extracellular polymeric substances in enhancement of phosphorus release from waste activated sludge by rhamnolipid addition. Bioresour Technol 202:59–66
Huang H, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Ding L (2014) Treatment of swine wastewater combined with MgO-saponification wastewater by struvite precipitation technology. Chem Eng J 254:418–425
Jorge R, Carlos A, Tânia S, Dionysios D, Gianluca L, Marco S, José A (2017) Treatment of winery wastewater by sulphate radicals: HSO5 −/transition metal/UV-A LEDs. Chem Eng J 310:473–483
Kamiya T, Hirotsui J (1998) New combined system of biological process and intermittent ozonation for advanced wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 38:145–153
Latif M, Mehta C, Batstone D (2015) Low pH anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge for enhanced phosphorous release. Water Res 81:288–293
Lee S, Weon S, Lee C, Koopman B (2003) Removal of nitrogen and phosphate from wastewater by addition of bittern. Chemosphere 51:265–271
Manterola G, Uriarte I, Sancho L (2008) The effect of operational parameters of the process of sludge ozonation on the solubilisation of organic andnitrogenous compounds. Water Res 42:3191–3197
Moed N, Lee D, Chang J (2015) Struvite as alternative nutrient source for cultivation of microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 56:73–76
Nelson N, Mikkelsen R, Hesterberg D (2003) Struvite precipitation in anaerobic swine lagoon liquid: effect of pH and Mg:P ratio and determination of rate constant. Bioresour Technol 89:229–236
Pardo P, Rauret G, López-sánchez J (2004) Shortened screening method for phosphorus fractionation in sediments: a complementary approach to the standards, measurements and testing harmonized protocol. Anal Chim Acta 508:201–206
Park K, Ahn K, Maeng S, Hwang J, Kwon J (2003) Feasibility of sludge ozonation for stabilization and conditioning. Ozone Sci Eng 25:73–80
Song Y, Yuan P, Zheng B, Peng J, Yuan F, Gao Y (2007) Nutrients removal and recovery by crystallization of magnesium ammonium phosphate from synthetic swine wastewater. Chemosphere 69:319–324
Tong J, Chen Y (2007) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal driven by short-chain fatty acids produced from waste activated sludge alkaline fermentation. Environ Sci Technol 41:7126–7130
Wang C, Hao X, Guo G, Loosdrecht M (2010) Formation of pure struvite at neutral pH by electrochemical deposition. Chem Eng J 159:280–283
Wei Y, Van Houten R, Borger A, Eikelboom D, Fan Y (2003) Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Water Res 37:4453–4467
Xie C, Zhao J, Tang J, Xu J, Lin X, Xu X (2011) The phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activities in sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:2455–2461
Xu Y, Hu H, Liu J, Luo J, Qian G, Wang A (2015) pH dependent phosphorus release from waste activated sludge: contributions of phosphorus speciation. Chem Eng J 267:260–265
Yan S, Chu L, Xing X, Yu A, Sun X, Jurcik B (2009a) Analysis of the mechanism of sludge ozonation by a combination of biological and chemical approaches. Water Res 43:195–203
Yan S, Zheng H, Li A, Zhang X, Xing X, Chu L, Ding G, Sun X, Jurcik B (2009b) Systematic analysis of biochemical performance and the microbial community of an activated sludge process using ozone-treated sludge for sludge reduction. Bioresour Technol 100:5002–5009
Yang S, Guo W, Cao G, Zheng H, Ren N (2012) Simultaneous waste activated sludge disintegration and biological hydrogen production using an ozone/ultrasound pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 124:347–354
Zhang G, Yang J, Liu H, Zhang J (2009) Sludge ozonation: disintegration, supernatant changes and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 100:1505–1509
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Pan B (2015) Struvite-based phosphorus recovery from the concentrated bioeffluent by using HFO nanocomposite adsorption: effect of solution chemistry. Chemosphere 141:227–234
Zhang J, Zhang J, Tian Y, Li N, Kong L, Sun L, Yu M, Zuo W (2016) Changes of physicochemical properties of sewage sludge during ozonation treatment: correlation to sludge dewaterability. Chem Eng J 301:238–248
Funding
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Management (No. 2013ZX07201007, 2014ZX07201012), the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (No.2014DX03), and the Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Heilongjiang Province (JC201303). The authors also appreciate the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology(QA201609-02) and the Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Science Foundation (LBH-Z14093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Tian, Y. & Zhang, J. Release of phosphorus from sewage sludge during ozonation and removal by magnesium ammonium phosphate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 23794–23802 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0037-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0037-8