Abstract
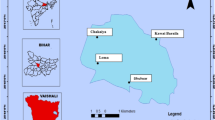
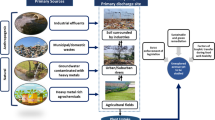
Samples of Octopus vulgaris and Sepia officinalis were collected from four areas in the Gulf of Gabes, south-eastern Tunisia, and their edible tissues (mantle and arms) were analyzed for cadmium, copper, mercury, and zinc. While the concentrations of metals showed significant differences between the sampling sites, no differences were revealed between the tissues of the two species. The spatial distribution of metals analyzed showed similar pattern for both tissues of the two species, with the highest concentrations found in the central area of Gabes Gulf, and the lowest in the northern and/or southern areas. From a human health risk point of view, the highest values of estimated daily intake, target hazard quotient, and hazard index were found in the central area of Gabes Gulf. Although the results of these indices were, in general, not alarming, the health risks posed by the consumption of cephalopods on local consumers cannot be excluded.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloulou F, EllEuch B, Kallel M (2012) Benthic foraminiferal assemblages as pollution proxies in the northern coast of Gabes gulf, Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 184:777–795
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Charbonnier L, Mesnil A, Rainbow PS, Wang WX (2008) Bioaccessibility of essential and non-essential metals in commercial shellfish from Western Europe and Asia. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2010–2022
Ayadi N, Aloulou F, Bouzid J (2014) Assessment of contaminated sediment by phosphate fertilizer industrial waste using pollution indices and statistical techniques in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Arab Journal Geosc 8:1755–1767
Ayas D, Ozogul Y (2011) The effects of season and sex in the metal levels of mature common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) in Mersin Bay, northeastern Mediterranean. J Food Sci 76:121–124
Bortey-Sam N, Nakayama SMM, Akoto O, Ikenaka Y, Fobil JN, Baidoo E, Mizukawa H, Ishizukal M (2015) Accumulation of heavy metals and metalloid in foodstuffs from agricultural soils around Tarkwa area in Ghana, and associated human health risks. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(8):8811–8827
Buchholtz Ten Brink MR, Manheim FT, Bothner MH (1996) The health of the gulf of Maine ecosystem: cumulative impacts of multiple stressors. Regional Association for Research on the Gulf of Maine (RARGOM), Dartmouth College, No. 96, 91 pp
Bustamante P, Gonzalez A, Rocha F, Miramand P, Guerra A (2008) Metal and metalloid concentrations in the giant squid Architeuthis dux from Iberian waters. Mar Environ Res 66:278–287
Bustamante P, Lahaye V, Durnez C, Churlaud C, Caurant F (2006) Total and organic Hg concentrations in cephalopods from the north eastern Atlantic waters: influence of geographical origin and feeding ecology. Sci Total Environ 368:585–596
Bustamante P, Teyssié JL, Fowler SW, Cotret O, Danis B, Miramand P, Warnau M (2002) Biokinetics of zinc and cadmium accumulation and depuration at different stages in the life cycle of the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 231:167–177
Bustamante P, Grigioni S, Boucher-Rodoni R, Caurant F, Miramand P (2000) Bioaccumulation of 12 trace elements in the tissues of the Nautilus macromphalus from New Caledonia. Mar Pollut Bull 40:688–696
Bustamante P, Cherel Y, Caurant F, Miramand P (1998) Cadmium, copper and zinc in octopuses from Kerguelen Islands, southern Indian Ocean. Polar Biol 19:264–271
De Forest D, Brix K, Adams W (2007) Assessing metal bioaccumulation in aquatic environments: the inverse relationship between bioaccumulation factors, trophic transfer factors and exposure concentration. Aquat Toxicol 84:236–246
Darmoul B (1988) Pollution dans le Golfe de Gabès (Tunisie): bilan des six années de surveillance (1976-1981). Bull Inst Nat Sci Tech Mer Salammbô 15:61–84
Darmoul B, Vitiello P (1980) Recherches expérimentales sur la toxicité aiguë des rejets de phosphogypse sur quelques organismes benthiques marins. Bull Inst Nat Sci Tech Mer Salammbô 7:63–89
Darmoul B, Hadj Ali Salem M, Vitiello P (1980) Effets des rejets industriels de la région de Gabès (Tunisie) sur le milieu récepteur. Bull Inst Nat Sci Tech Mer Salammbô 7:5–61
Duysak Ö, Ersoy B, Dural M (2013) Metal concentrations in different tissues of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) in İskenderun bay, northeastern Mediterranean. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 13:205–210
EEA (European Environment Agency) (2014) Horizon 2020 Mediterranean report, Annex 6: Tunisia, EEA Technical report, No 6/2014. 27 p
El Zrelli R, Courjault-Radé P, Rabaoui L, Castet S, Michel S, Bejaoui N (2015) Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of the coastal area surrounding the industrial complex of Gabes city, gulf of Gabes, SE Tunisia. Mar Poll Bull 101:922–929
FAO (2009) Food and Agriculture Organization. FAOSTAT. Statistical databases. Available from http://faostat.fao.org
FAO Species catalogue (1984) Cephalopods of the world An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species of interest to fisheries. Clyde F.E. Roper Michael J. Sweeney Cornelia E. Nauen 1984. FAO Fisheries Synopsis No. 125, Volume 3
JECFA (1982) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. Twenty-sixth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Technical report series 683, Genova, 52 pp
Jian L, Zhiyong YH, Yue H, Hong Y (2013) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals by consuming shellfish collected from Xiamen, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2937–2947
Jović M, Stanković S (2014) Human exposure to trace metals and possible public health risks via consumption of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Adriatic coastal area. Food Chem Toxicol 70:241–251
Kharroubi A, Gzam M, Jedoudi Y (2012) Anthropogenic and natural effects on the water and sediments qualities of costal lagoons: case of the Boughrara lagoon (Southeast Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 67:1061–1067
Koyama J, Nanamori N, Segawa S (2000) Bioaccumulation of waterborne and dietary cadmium by oval squid, Sepioteuthis lessoniana, and its distribution among organs. Mar Poll Bull 40:961–967
Lacoue-Labarthe T, Martin S, Oberhansli F, Teyssie JL, Markich S, Ross J et al (2009a) Effects of increased pCO(2) and temperature on trace element (Ag, Cd and Zn) bioaccumulation in the eggs of the common cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Biogeosciences 6:2561–2573
Lacoue-Labarthe T, Warnau M, Oberhänsli F, Teyssié J-L, Bustamante P (2009b) Bioaccumulation of inorganic Hg by the juvenile cuttlefish Sepia officinalis exposed to 203Hg radiolabelled seawater and food. Aquat Biol 6:91–98
Lahaye V, Bustamante P, Spitz J, Dabin W, Das K, Pierce GJ et al (2005) Long-term dietary segregation of common dolphins Delphinus delphis in the Bay of Biscay, determined using cadmium as an ecological tracer. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 305:275–285
Lahbib Y, Mleiki A, Marigomez I, El Menif NT (2013) Copper, zinc, and cadmium body concentrations in Hexaplex trunculus collected from the Tunisian coast. Environ Monit Assess 185:8967–8975
Larsen PF (1992) An overview of the environmental quality of the Gulf of Maine. NOAA Coastal Ocean Program Synthesis Series, No 1:25 pp
Lourenço HM, Anacleto P, Afonso C, Ferraria V, Martins MF, Carvalho ML, Lino AR, Nunes ML (2009) Elemental composition of cephalopods from Portuguese continental waters. Food Chemi 113:1146–1153
Messaoudi I, Deli T, Kessabi K, Barhoumi S, Kerkeni A, Saïd K (2009) Association of spinal deformities with heavy metal bioaccumulation in natural population of grass goby Zosterisessor ophiocephalus Pallas, 1811 from the Gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 156:551–560
Mezghani-Chaari S, Hamza A, Hamza-Chaffai A (2011) Mercury contamination in human hair and some marine species from Sfax coasts of Tunisia: levels and risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 180:477–487
Miramand P, Bentley D (1992) Concentration and distribution of heavy metals in tissues of two cephalopods, Eledone cirrhosa and Sepia officinalis, from the French coast of the English Channel. Mar Biol 114:407–414
Miramand P, Guary JC (1980) High concentrations of some heavy metals in tissues of the Mediterranean octopus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 24:783–788
Muirhead SI, Furness RW (1988) Heavy-metal concentrations in the tissues of seabirds from Gough Island, South-Atlantic Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 19:278–283
NIS (National Institute of Statistics) (2014) Tunisian census data. http://www.ins.nat.tn. Accessed 10 February 2016
Nessim RB, Riad R (2003) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Octopus vulgaris from coastal waters of Alexandria (eastern Mediterranean). Chem Ecol 19(4):275–281
Pereira P, Raimundoa J, Valea C, Kadara E (2009) Metal concentrations in digestive gland and mantle of Sepia officinalis from two coastal lagoons of Portugal. Sci Total Environ 407:1080–1088
Rabaoui L, El Zrelli R, Ben Mansour M, Balti R, Mansour L, Tlig-Zouari S, Guerfel M (2015) On the relationship between the diversity and structure of benthic macroinvertebrate communities and sediment enrichment with heavy metals in Gabes gulf Tunisia. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 95:233–245
Rabaoui L, Balti R, El Zrelli R, Tlig-Zouari S (2014) Assessment of heavy metals pollution in the gulf of Gabes (Tunisia) using four mollusk species. Med Mar Sci 15:45–58
Raimundo J, Vale C, Duarte R, Moura I (2008) Sub-cellular partitioning of Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb in the digestive gland of native Octopus vulgaris exposed to different metal concentrations (Portugal). Sci Total Environ 390:410–416
Readman JW, Kwong LLW, Grondin D, Bartocci J, Villeneuve JP et al (1993) Coastal water contamination from triazine herbicide used in antifouling paints. Environ Sci Technol 27(9):1940–1942
Rjeibi M, Metian M, Hajji T, Guyot T, Ben Chaouacha-Chekir R, Bustamante P (2015) Seasonal survey of contaminants (Cd and Hg) and micronutrients (Cu and Zn) in edible tissues of cephalopods from Tunisia: assessment of risk and nutritional benefits. J Food Sci 80(1):T199–T206
Rjeibi M, Metian M, Hajji T, Guyot T, Ben Chaouacha-Chekir R, Bustamante P (2014) Interspecific and geographical variations of trace metal concentrations in cephalopods from Tunisian waters. Environ Monit Assess 186(6):3767–3783
Ruilian Y, Xing Y, Yuanhui Z, Gongren H, Xianglin T (2008) Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci 20:664–669
Seixas S, Bustamante P, Pierce G (2005a) Interannual patterns of variation in concentrations of trace elements in arms of Octopus vulgaris. Chemosphere 59:1113–1124
Seixas S, Bustamante P, Pierce G (2005b) Accumulation of mercury in the tissues of the common octopus Octopus vulgaris (L.) in two localities on the Portuguese coast. Sci Total Environ 340:113–122
Soussi N, Ennet P, Koponen J, Sarkkula J, Ben Mustapha S, Ben Mammou A, Kokkila T (1995) Impact of the phosphogypsum waste in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment, Volume 3, pp. 1333–1346
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2005) Zinc and Compounds; CASRN 7440–66-6. Available at: http://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0426_summary.pdf. Accessed 10 February 2016
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2000) Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories, vol. 2: Risk assessment and fish consumption limits, 3rd Edition. Office of Science and Technology Office of Water, USEPA, Washington, DC
Zaghden H, Kallel M, Louati A, Elleuch B, Oudot J, Saliot A (2005) Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Sfax coastal zone (Tunisia), Mediterranean Sea. Mar Poll Bull 50:1287–1294
Zaouali J (1993) Little Syrte benthic communities, Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Results of the survey campaign of July 1990. Preliminary study: biocenosis and recent thanatocenosis. Mar Life 3:47–60
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the research group no. RG-1435-023. We are also grateful to the three referees who helped to improve the quality of the manuscript through their constructive comments and suggestions and to all those who helped in collecting samples and laboratory analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabaoui, L., El Zrelli, R., Balti, R. et al. Metal bioaccumulation in two edible cephalopods in the Gulf of Gabes, South-Eastern Tunisia: environmental and human health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 1686–1699 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7945-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7945-x