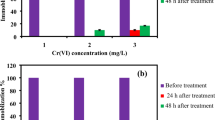
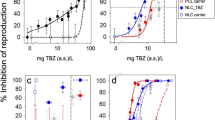
Abstract
Nanopesticides such as nanopermethrin can serve as an alternative to conventional pesticides causing eco-toxicity. The nanoformulation of this pyrethroid pesticide was carried out by solvent evaporation of pesticide-loaded microemulsion. The Z average for the nanopermethrin dispersion in paddy field water was found to be 169.2 ± 0.75 nm with a polydispersity index of 0.371 that exhibits uniform dispersion. Further, the nanopermethrin (NP) dispersion exhibited an effective stability in the paddy field water for a duration of 48 h with a Z average of 177.3 ± 1.2 nm and a zeta potential of −30.7 ± 0.9 mV. The LC50 of the nanopermethrin against Culex tritaeniorhynchus in the field condition was found to be 0.051 μg/mL. In addition to the stability assessment, the biosafety of the nanopermethrin was commenced on the beneficial bacterial isolate Enterobacter ludwigii (VITSPR1) considered as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. The toxic effect of nanopesticide was compared to its bulk counterpart, i.e. bulk permethrin (BP) at a concentration of 100 µg/mL, and the nanopesticide was found to be potentially safe. The results of biomarker enzymatic assays (lipid peroxidase, glutathione reductase, lactate dehydrogenase) displayed insignificant (p < 0.05) toxicity of NP towards the bacterial cells compared to BP. The live–dead cell staining and SEM analysis illustrated negligible toxicity of NP towards the bacteria. The non-toxic behaviour of the NP towards the non-target species was studied which displayed the eco-safe property of NP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abei H (1974) Catalase. Methods of enzymatic analysis 2, 673–684
Agnihotri A (1999) Pesticide: safety evaluation and monitoring. Indian Agricultural Research Institute, Division of Agricultural Chemicals
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Anjali C, Khan SS, Margulis-Goshen K, Magdassi S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2010) Formulation of water-dispersible nanopermethrin for larvicidal applications. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1932–1936
Balaji APB, Mishra P, Kumar RS, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2015) Nanoformulation of poly (ethylene glycol) polymerized organic insect repellent by PIT emulsification method and its application for Japanese encephalitis vector control. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 128:370–378
Banerjee B, Seth V, Bhattacharya A, Pasha S, Chakraborty A (1999) Biochemical effects of some pesticides on lipid peroxidation and free-radical scavengers. Toxicol Lett 107:33–47
Barea J-M, Pozo MJ, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2005) Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere. J Exp Bot 56:1761–1778
Barrera G, Pizzimenti S, Dianzani MU (2008) Lipid peroxidation: control of cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell death. Mol Asp Med 29:1–8
Bazzicalupo M, Fani R (1996) The use of RAPD for generating specific DNA probes for microorganisms. Species diagnostics protocols: PCR and other nucleic acid methods, 155–175
Bhatnagar V (2001) Pesticides pollution: trends and perspectives. ICMR Bull 31:87–88
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown DM, Wilson MR, MacNee W, Stone V, Donaldson K (2001) Size-dependent proinflammatory effects of ultrafine polystyrene particles: a role for surface area and oxidative stress in the enhanced activity of ultrafines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 175:191–199
Buck JD (1982) Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993
Cabiscol Català E, Tamarit Sumalla J, Ros Salvador J (2000) Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species. Int Microbiol vol. 3(núm. 1):3–8
Cajaraville MP, Bebianno MJ, Blasco J, Porte C, Sarasquete C, Viarengo A (2000) The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: a practical approach. Sci Total Environ 247:295–311
Dalai S, Pakrashi S, Kumar RS, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2012) A comparative cytotoxicity study of TiO2 nanoparticles under light and dark conditions at low exposure concentrations. Toxicology. Research 1:116–130
Derjaguin B, Landau L (1941) Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols and of the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solutions of electrolytes. Acta physicochim. URSS 14:633–662
Djènontin A, Pennetier C, Zogo B, Soukou KB, Ole-Sangba M, Akogbéto M, Chandre F, Yadav R, Corbel V (2014) Field efficacy of Vectobac GR as a mosquito larvicide for the control of Anopheline and Culicine mosquitoes in natural habitats in Benin, West Africa. PLoS One 9:e87934
Edirisinghe JP, Bambaradeniya CN (2010) Rice fields: an ecosystem rich in biodiversity. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka 34
Edwards CA, Pimentel D (1989) Impact of herbicides on soil ecosystems. Crit Rev Plant Sci 8:221–257
FAO, 2005 Proceedings of the Asia Regional Workshop, Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok
Fay JP, Farias R (1977) Inhibitory action of a non-metabolizable fatty acid on the growth of Escherichia coli: role of metabolism and outer membrane integrity. J Bacteriol 132:790–795
Freitas C, Müller RH (1998) Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN™) dispersions. Int J Pharm 168:221–229
Gopalakrishnan S, Humayun P, Kiran BK, Kannan IGK, Vidya MS, Deepthi K, Rupela O (2011) Evaluation of bacteria isolated from rice rhizosphere for biological control of charcoal rot of sorghum caused by Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1313–1321
Hoffmann H, Stindl S, Stumpf A, Mehlen A, Monget D, Heesemann J, Schleifer KH, Roggenkamp A (2005) Description of Enterobacter ludwigii sp. nov., a novel Enterobacter species of clinical relevance. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:206–212
Hong R, Kang TY, Michels CA, Gadura N (2012) Membrane lipid peroxidation in copper alloy-mediated contact killing of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1776–1784
Illmer P, Barbato A, Schinner F (1995) Solubilization of hardly-soluble AlPO 4 with P-solubilizing microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 27:265–270
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanopart Res 11:77–89
Johnen B (1977) Ecological effects of pesticides on soil microorganisms. Soil Sci 123:319–324
Johnsen K, Jacobsen CS, Torsvik V, Sørensen J (2001) Pesticide effects on bacterial diversity in agricultural soils–a review. Biol Fertil Soils 33:443–453
Kämpfer P, Ruppel S, Remus R (2005) Enterobacter radicincitans sp. nov., a plant growth promoting species of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:213–221
Kloeppe J, Rodriguez-Kabana R, Zehnder A, Murphy J, Sikora E, Fernandez C (1999) Plant root-bacterial interactions in biological control of soilborne diseases and potential extension to systemic and foliar diseases. Australas Plant Pathol 28:21–26
Kucey R, Janzen H, Leggett M (1989) Microbially mediated increases in plant-available phosphorus. Adv Agron 42:60525–60528
Kumar RS, Shiny P, Anjali C, Jerobin J, Goshen KM, Magdassi S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2013) Distinctive effects of nano-sized permethrin in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2593–2602
Kumari J, Kumar D, Mathur A, Naseer A, Kumar RR, Chandrasekaran PT, Chaudhuri G, Pulimi M, Raichur AM, Babu S (2014) Cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles towards freshwater sediment microorganisms at low exposure concentrations. Environ Res 135:333–345
Lakshmi A (1993) Pesticides in India: risk assessment to aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 134:243–253
Mac Faddin JF (1976) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria. Williams & Wilkins Co.
Margulis-Goshen K, Magdassi S (2012) Organic nanoparticles from microemulsions: formation and applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 17:290–296
Meyer S, Berrut S, Goodenough T, Rajendram V, Pinfield V, Povey M (2006) A comparative study of ultrasound and laser light diffraction techniques for particle size determination in dairy beverages. Meas Sci Technol 17:289
Naik S, Prasad R (2006) Pesticide residue in organic and conventional food-risk analysis. J Chem Health Saf 13:12–19
Oliveira C, Alves V, Marriel I, Gomes E, Scotti M, Carneiro N, Guimaraes C, Schaffert R, Sa N (2009) Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms isolated from rhizosphere of maize cultivated in an oxisol of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1782–1787
Pandey P, Kang S, Maheshwari D (2005) Isolation of endophytic plant growth promoting Burkholderia sp. MSSP from root nodules of Mimosa pudica. Curr Sci 89:177–180
Pikovskaya R (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:e370
Rai M, Ingle A (2012) Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:287–293
Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA (2011) Larvicidal activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles using Eclipta prostrata leaf extract against filariasis and malaria vectors. Acta Trop 118:196–203
Richardson AE (2001) Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Funct Plant Biol 28:897–906
Richardson A, Pankhurst C, Doube B, Gupta V, Grace P (1994) Soil microorganisms and phosphorus availability. Soil biota: management in sustainable farming systems, 50–62
Riddick T, Manual Z-M (1968) Zeta-Meter Inc. New York
Saeki M, Toyota K (2004) Effect of bensulfuron-methyl (a sulfonylurea herbicide) on the soil bacterial community of a paddy soil microcosm. Biol Fertil Soils 40:110–118
Schoonhoven L (1982) Biological aspects of antifeedants. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 31:57–69
Shoebitz M, Ribaudo CM, Pardo MA, Cantore ML, Ciampi L, Curá JA (2009) Plant growth promoting properties of a strain of Enterobacter ludwigii isolated from Lolium perenne rhizosphere. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1768–1774
Simon-Sylvestre G, Fournier J-C (1980) Effects of pesticides on the soil microflora. Adv Agron 31:1–92
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Topp E, Vallaeys T, Soulas G, van ELSAS J, Trevors J, Wellington E (1997) Pesticides: microbial degradation and effects on microorganisms. Modern Soil Microbiology:547–575
Uribe S, Ramirez J, Peña A (1985) Effects of beta-pinene on yeast membrane functions. J Bacteriol 161:1195–1200
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Nikolaeva I (2006) Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: potentials and future trends. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:137–144
Wakelin SA, Warren RA, Harvey PR, Ryder MH (2004) Phosphate solubilization by Penicillium spp. closely associated with wheat roots. Biol Fertil Soils 40:36–43
Whitelaw M, Harden T, Helyar K (1999) Phosphate solubilisation in solution culture by the soil fungus Penicillium radicum. Soil Biol Biochem 31:655–665
WHO (2005) Guidelines for laboratory and field testing of mosquito larvicides (CDS/WHOPES/GCDPP/05.13)
Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE (2008) Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc 3:163–175
Acknowledgments
We deeply acknowledge the Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India for providing the laboratory facilities. We extremely acknowledge ICMR BMS (35/10/2012-BMS) for providing the financial aid. We acknowledge Dr. Shlomo Magdassi and Dr. Katherine Margulis (Casali Center, Institute of Chemistry, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel) for their immense contribution in nanopesticide preparation. We acknowledge Dr. K. Gopalarathinam, Senior Entomologist, ZET, Vellore for his immense help in the identification of the mosquito species.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, P., Balaji, A., J.S., S. et al. Stability assessment of hydro dispersive nanometric permethrin and its biosafety study towards the beneficial bacterial isolate from paddy rhizome. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 24970–24982 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7731-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7731-9