Abstract
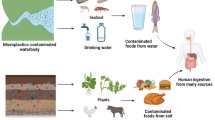
Concentration values of 24 elements (Al, As, Ba, Be, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ge, Hg, Mn, Mo, Pb, Sb, Se, Sn, Sr, Ti, Tl, U, V, and Zn) were determined in 72 honey samples produced in Italy by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Considering the recommended established heavy metal daily intakes for humans, in this perspective, an equilibrated and ordinary honey consumption should not be considered matter of concerns for human health, even if particular attention should be addressed if honey is consumed by children, due to different maximum daily heavy metal intakes. Chemometric analysis of the results obtained highlights heavy metal content differences in honey samples obtained from notoriously polluted zones, confirming then that honey can be considered a bio-indicator of environmental pollution. Finally, Pearson coefficients highlighted correlations among element contents in honey samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajibola A, Chamunorwa JP, Erlwanger KH (2012) Nutraceutical values of natural honey and its contribution to human health and wealth. Nutr Metab 9:61. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-9-61
Basile A, Sorbo S, Aprile G, et al. (2009) Heavy metal deposition in the Italian “triangle of death” determined with the moss Scorpiurum circinatum. Environ Pollut 157:2255–2260. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.04.001
Bilandžić N, Gačić M, Đokić M, Sedak M, Sîpušić DI, Končurat A, Gajger IT (2014) Major and trace elements levels in multifloral and unifloral honeys in Croatia. J Food Compos Anal 33:132–138. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2013.12.002
Bratu I, Georgescu C (2005) Chemical contamination of bee honey—identifying sensor of the environment pollution. J Cent Eur Agric 6:95–98
Caroli S (1999) Determination of essential and potentially toxic trace elements in honey by inductively coupled plasma-based techniques. Talanta 50:327–336. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00025-9
Chudzinska M, Baralkiewicz D (2011) Application of ICP-MS method of determination of 15 elements in honey with chemometric approach for the verification of their authenticity. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2741–2749. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.08.014
Codex Alimentarius (2001) CODEX STAN 12–1981
Commission Regulation (EC) (2006) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union 49:5–25
Commission Regulation (EU) (2015) 2015/1005 amending Regulation (EC) no 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of lead in certain foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union 58:9–14
Council Directive (2002) 2001/110/EC of 20 December 2001 relating to honey. Off J Eur Union 10:47–52
Council Directive (1996) 96/23/EC on measures to monitor certain substances and residues in live animal products. Off J Eur Union 39:10–33
Czipa N, Andrási D, Kovács B (2015) Determination of essential and toxic elements in Hungarian honeys. Food Chem 175:536–542. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.12.018
de Andrade CK, dos Anjos VE, Felsner ML, Torres YR, Quináia SP (2014) Relationship between geographical origin and contents of Pb, Cd, and Cr in honey samples from the state of Paraná (Brazil) with chemometric approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12372–12381. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3175-2
Di Bella G, Lo Turco V, Potortì AG, Bua GD, Fede MR, Dugo G (2015) Geographical discrimination of Italian honey by multi-element analysis with a chemometric approach. J Food Compos Anal 44:25–35
Esmaeili A, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Jaafarzadeh N, Kermani M (2014) A geochemical survey of heavy metals in agricultural and background soils of the Isfahan industrial zone, Iran. Catena 121:88–98. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2014.05.003
FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants (2010b) Seventy-second report. Technical Report Series 959. Geneva
FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants (2010a) Seventy-third report. Technical Report Series 960. Geneva
Fernandez-Torres R, Perezbernal J, Bellolopez M, Callejon-Mochon M, Jomenez-Sanchez JC, Guiraum-Perez A (2005) Mineral content and botanical origin of Spanish honeys. Talanta 65:686–691. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.07.030
Gherardi M, Pontalti F, Vianello G, Antisari LV (2009) Heavy metals in the soil-plant system: monitoring urban and extra-urban parks in the Emilia Romagna region (Italy). Agrochimica 53:196–208
González-Miret ML, Terrab A, Hernanz D, Fernández-Recamales MA, Heredia FJ (2005) Multivariate correlation between color and mineral composition of honeys and by their botanical origin. J Agric Food Chem 53:2574–2580. doi:10.1021/jf048207p
Hernández OM, Fraga JMG, Jiménez AI, Jimenez F, Arias JJ (2005) Characterization of honey from the Canary Islands: determination of the mineral content by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Food Chem 93:449–458. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.036
Ioannidou M (2004) Direct determination of toxic trace metals in honey and sugars using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 65:92–97. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.05.018
Leita L, Muhlbachova G, Cesco S, Barbattini R, Mondini C (1996) Investigation of the use of honey bees and honey bee products to assess heavy metals contamination. Environ Monit Assess 43:1–9. doi:10.1007/BF00399566
Madejczyk M, Baralkiewicz D (2008) Characterization of Polish rape and honeydew honey according to their mineral contents using ICP-MS and F-AAS/AES. Anal Chim Acta 617:11–17. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.01.038
Martin S, Griswold W (2009) Human health effects of heavy metals. Environ Sci Technol Briefs Citiz 15:1–6
Meli MA, Desideri D, Roselli C, Benedetti C, Feduzi L (2015) Essential and toxic elements in honeys from a region of Central Italy. J Toxicol Environ Health A 78:617–627. doi:10.1080/15287394.2014.1004006
Pisani A, Protano G, Riccobono F (2008) Minor and trace elements in different honey types produced in Siena County (Italy). Food Chem 107:1553–1560. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.029
Sevimli H, Bayulgen N, Varinlioglu A (1992) Determination of trace elements in honey by INAA in Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Lett 165:319–325. doi:10.1007/BF02166150
Solayman M, Islam MA, Paul S, Ali Y, Khalil MI, Nadia Alam N, Gan SH (2016) Physicochemical properties, minerals, trace elements, and heavy metals in honey of different origins: a comprehensive review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 15:219–233. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12182
Triassi M, Alfano R, Illario M, et al. (2015) Environmental pollution from illegal waste disposal and health effects: a review on the “triangle of death.”. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:1216–1236. doi:10.3390/ijerph120201216
Tuzen M, Silici S, Mendil D, Soylak M (2007) Trace element levels in honeys from different regions of Turkey. Food Chem 103:325–330. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.053
UNI EN 13805:2014 European Committee for Standardization (2014) Foodstuffs—determination of trace elements—pressure digestion
UNI EN 15763:2010 European Committee for Standardization (2010) Foodstuffs—determination of trace elements—determination of arsenic, cadmium, mercury and lead in foodstuffs by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) after pressure digestion
Vincēviča-Gaile Z (2010) Macro- and trace elements in honey. LLU-Raksti 54–66
Wang G, Su M-Y, Chen Y-H, Lin F-F, Luo D, Gao S-F (2006) Transfer characteristics of cadmium and lead from soil to the edible parts of six vegetable species in southeastern China. Environ Pollut 144:127–135. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.023
WHO Expert Committee on Exposure of Children to Chemical Hazards in Food (2009) European Environment and Health Information System
Yarsan E, Caracal F, Ibrahim IG, et al. (2007) Contents of some metals in honeys from different regions in Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol:255–258
Yücel Y, Sultanoğlu P (2013) Characterization of Hatay honeys according to their multi-element analysis using ICP-OES combined with chemometrics. Food Chem 140:231–237. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quinto, M., Miedico, O., Spadaccino, G. et al. Characterization, chemometric evaluation, and human health-related aspects of essential and toxic elements in Italian honey samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 25374–25384 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7662-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7662-5