Abstract
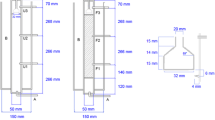
The present work evaluated the effects of (i) feeding a water contaminated with 80 mg/L PCE to bioreactors seeded with inoculum not acclimated to PCE, (ii) coupling ZVI side filters to bioreactors, and (iii) working in different biological regimes, i.e., simultaneous methanogenic aeration and simultaneous methanogenic-denitrifying regimes, on fluidized bed bioreactor performance. Simultaneous electron acceptors refer to the simultaneous presence of two compounds operating as final electron acceptors in the biological respiratory chain (e.g., use of either O2 or NO3 − in combination with a methanogenic environment) in a bioreactor or environmental niche. Four lab-scale, mesophilic, fluidized bed bioreactors (bioreactors) were implemented. Two bioreactors were operated as simultaneous methanogenic-denitrifying (MD) units, whereas the other two were operated in partially aerated methanogenic (PAM) mode. In the first period, all bioreactors received a wastewater with 1 g chemical oxygen demand of methanol per liter (COD-methanol/L). In a second period, all the bioreactors received the wastewater plus 80 mg perchloroethylene (PCE)/L; at the start of period 2, one MD and one PAM were coupled to side sand-zero valent iron filters (ZVI). All bioreactors were inoculated with a microbial consortium not acclimated to PCE. In this work, the performance of the full period 1 and the first 60 days of period 2 is reported and discussed. The COD removal efficiency and the nitrate removal efficiency of the bioreactors essentially did not change between period 1 and period 2, i.e., upon PCE addition. On the contrary, specific methanogenic activity in PAM bioreactors (both with and without coupled ZVI filter) significantly decreased. This was consistent with a sharp fall of methane productivity in those bioreactors in period 2. During period 2, PCE removals in the range 86 to 97 % were generally observed; the highest removal corresponded to PAM bioreactors along with the highest dehalogenation efficiency (94 %). Principal component analysis as well as cluster analysis confirmed the trends mentioned above, i.e., the better performance of PAM over MD, and the unexpected no effect of the ZVI side filters on PCE removal and dehalogenation efficiencies. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the combined treatment ZVI-biological of a water polluted with PCE, where the biological operation relied on simultaneous electron acceptors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DS, Li ZH (2001) Synergistic effect of cationic surfactants on perchloroethylene degradation by zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 35:3713–3717
Alther G (2004) Has “IN SITU” remediation replaced “Activated Carbon PUMP & TREAT” in the groundwater market? 18th International Activated Carbon Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, October 19–20, 2006
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 20th edn. Washington, D.C.
Aschengrau A, Rogers S, Ozonoff D (2003) Perchloroethylene-contaminated drinking water and the risk of breast cancer: additional results from Cape Cod, Massachusetts, USA. Environ Health Perspect 111:167–173
Bereded-Samuel Y, Petersen J, Skeen R (1996) Effect of perchloroethylene (PCE) on methane and acetate production by a methanogenic consortium. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 57-58:915–922
Bretón-Deval L, Rossetti S, Ríos-Leal E, Matturro B, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2016) Effect of coupling zero-valent iron side filters on performance of bioreactors fed with high concentration of perchloroethylene. J Environ Eng ASCE 142(5):9 Article 04016051
Canova J (2010) PRB expanded to full-scale operation for accelerating treatment of metals. Technol News Trends, 1–3
Camiloti PR, Mockaitis G, Rodrigues JAD, Damianovic MHRZ, Foresti E, Zaiat M (2014) Innovative anaerobic bioreactor with fixed-structured bed (ABFSB) for simultaneous sulfate reduction and organic matter removal. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:1044–1050
Capodaglio AG, Suidan M, Venosa AD, Callegari A (2010) Efficient degradation of MtBE and other gasoline-originated compounds by means of a biological reactor of novel conception: two case studies in Italy and the USA. Water Sci Technol 61:807–812
Clark CJ, Rao PSC, Annable MD (2003) Degradation of perchloroethylene in cosolvent solutions by zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 96:65–78
Chang YC, Kikuchi S, Kawauchi N, Sato T, Takamizawa K (2008) Complete dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene by use of an anaerobic Clostridium bifermentans DPH-1 and zero-valent iron. Environ Technol 29:381–391
Chen KF, Yeh TY, Kao CM, Sung WP, Lin CC (2012) Application of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nzvi) to enhance microbial reductive dechlorination of tce. A feasibility study. Curr Nanosci 8:55–59
Chen L, Jin S, Fallgren PH, Liu F, Colberg PJ (2013) Passivation of zero-valent iron by denitrifying bacteria and the impact on trichloroethene reduction in groundwater. Water Sci Technol 67:1254–1259
Cheng T, Dai YZ, Chen C, Huang ZQ (2012) Zero-valent iron supported microbial reductive dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Asian J Chem 24:2579–2584
Chu K-H, Alvarez-Cohen L (1999) Evaluation of toxic effects of aeration and trichloroethylene oxidation on methanotrophic bacteria grown with different nitrogen sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:766–772
Dolfing J, VanEckert D, Meuller J (2006) Thermodynamics of low Eh reactions, Proceedings, Fifth International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds, Monterey, CA, USA, May, 22–25
Dollhopf SL, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM (2001) Interpreting 16S rDNA T-RFLP data: application of self-organizing maps and principal component analysis to describecommunity dynamics and convergence. Microb Ecol 42:495–505
El-Fantroussi S, Naveau H, Agathos SN (1998) Anaerobic dechlorinating bacteria. Biotechnol Prog 14:167–188
EPA (1996) Pump-and-treat ground-water remediation: a guide for decision makers and practitioners. EPA/625/R-95/005, 74
EPA (2003) National Primary Drinking Water Standards. Office of Water (4606 M); EPA 816-F-03-016; www.epa.gov/safewater
Estrada-Vázquez C, Macarie H, Kato MT, Rodríguez-Vázquez R, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2001) Resistencia a la exposición al oxígeno de lodos anaerobios suspendidos. Interciencia 26:547–553
Estrada-Vázquez C, Macarie H, Kato MT, Rodríguez-Vázquez R, Esparza-García F, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2003) The effect of the supplementation with a primary carbon source on the resistance to oxygen exposure of methanogenic sludge. Water Sci Technol 48:119–124
Ferguson SJ, Richardson DJ (2004) The enzymes and bioenergetics of bacterial nitrate, nitrite, nitric oxide and nitrous oxide respiration. In: Zannoni D (ed) Respiration in archaea and bacteria: diversity of prokaryotic respiratory systems. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 169–206
Frascari D, Fraraccio S, Nocentini M, Pinelli D (2013) Aerobic/anaerobic/aerobic sequenced biodegradation of a mixture of chlorinated ethenes, ethanes and methanes in batch bioreactors. Bioresour Technol 128:479–486
Garibay-Orijel C, Rios-Leal E, Garcia-Mena J, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2005) 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol and phenol removal in methanogenic and partially-aerated methanogenic conditions in a fluidized bed bioreactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:1180–1187
Garibay-Orijel C, Ahring BK, Rinderknecht-Seijas N, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2006) A simple model for simultaneous methanogenic-denitrification systems. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:173–181
Gregory KB, Mason MG, Picken HD, Weathers LJ, Parkin GF (2000) Bioaugmentation of Fe (0) for the remediation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Environ Eng Sci 17:169–181
Harendra S, Vipulanandan C (2008) Degradation of high concentrations of PCE solubilized in SDS and biosurfactant with Fe/Ni bi-metallic particles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 322:6–13
Herrera-López D, García-Mena J, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2007) The addition of zero-valent iron to batch bioreactors with simultaneous electron acceptors: influence on removal of high concentrations of perchloroethylene. In: Gavaskar AR, Silver CF (ed) In situ and on-site bioremediation-2007. Proceedings of the Ninth International In Situ and On-Site Bioremediation Symposium, (Baltimore, Maryland; May 7–10, 2007), Baltimore
Herrera-López D, Garcia-Mena J, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2008) Coupling continuous bioreactors with zero-valent iron filters: the effect on removal of high concentrations of perchloroethylene. In: BM S (ed) Remediation of chlorinated and recalcitrant compounds—2008. Sixth international Conference Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds (Monterey, CA; May 2008). Battelle Press, Columbus, OH
HHS (2005) 11th Report on Carcinogens U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Toxicology Program
Holliger C (1995) The anaerobic microbiology and biotreatment of chlorinated ethenes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:347–351
Kocamemi BA, Çeçen F (2005) Cometabolic degradation of TCE in enriched nitrifying batch systems. J Hazard Mater 125:260–265
Kristensen GH, Jorgensen EP (1992) Characterization of functional microorganism groups and substrate in activated sludge and wastewater by AUR, NUR and OUR. Water Sci Technol 25:43–57
Lagakos SW, Wessen BJ, Zelen M (1986) An analysis of contaminated well water and health-effects in Woburn, Massachusetts. J Am Stat Assoc 81:583–596
Langwaldt JH, Puhakka JA (2000) On-site biological remediation of contaminated groundwater: a review. Environ Pollut 107:187–197
Li H, Shen TT, Wang XL, Lin KF, Liu YD, Lu SG, Gu JD, Wang P, Lu Q, Du XM (2013) Biodegradation of perchloroethylene and chlorophenol co-contamination and toxic effect on activated sludge performance. Bioresour Technol 137:286–293
Libhaber M, Orozco-Jaramillo Á (2012) Sustainable treatment and reuse of municipal wastewater for decision makers and practicing engineers. In: Libhaber M, Orozco-Jaramillo Á (ed). Iwa publishing
Ma CW, Wu YQ (2008) Dechlorination of perchloroethylene using zero-valent metal and microbial community. Environ Geol 55:47–54
Madoni P, Davoli D, Guglielmi L (1999) Response of SOUR and AUR to heavy metal contamination in activated sludge. Water Res 33:2459–2464
Matheson LJ, Tratnyek PG (1994) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 28:2045–2053
Maere T, Villez K, Marsili-Libelli S, Naessens W, Nopens I (2012) Membrane bioreactor fouling behaviour assessment through principal component analysis and fuzzy clustering. Water Res 46:6132–6142
Min JE, Kim M, Pardue JH, Park JW (2008) Reduction of trichloroethylene and nitrate by zero-valent iron with peat. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 43:144–153
Miller JN, Miller JC (2005) Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 5th edn. Prentice Hall, London
Mitra S, Gupta SK (2013) Biodegradation of tetrachloroethylene-rich synthetic wastewater in anaerobic hybrid reactor. Desalin Water Treat 51:4506–4513
OEHHA (2001) Public health goal for tetrachloroethylene in drinking water. Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment
Ohandja D-G, Stuckey DC (2010) Effect of perchloroethylene (PCE) and hydraulic shock loads on a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) biodegrading PCE. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:294–301
Ohandja DG, Stuckey DC (2007) Biodegradation of PCE in a hybrid membrane aerated biofilm reactor. J Environ Eng 133:20–27
Ouattara AS, Assih EA, Thierry S, Cayol JL, Labat M, Monroy O, Macarie H (2003) Bosea minatitlanensis sp nov., a strictly aerobic bacterium isolated from an anaerobic digester. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1247–1251
Paulu C, Aschengrau A, Ozonoff D (1999) Tetrachloroethylene-contaminated drinking water in Massachusetts and the risk of colon-rectum, lung, and other cancers. Environ Health Perspect 107:265–271
Pavlostathis S, Giraldo-Gomez E (1991) Kinetics of anaerobic treatment. Water Sci Technol 24:35–59
Peng J, Wan A (1997) Measurement of Henry’s constants of high-volatility organic compounds using a headspace autosampler. Environ Sci Technol 31:2998–3003
Poggi-Varaldo HM, Moreno-Medina CU, Galíndez-Mayer J, Ponce-Noyola MT, Esparza-García FJ, Ríos-Leal E, Juarez-Ramírez C, Rinderknecht-Seijas NF (2009) A review of zero-valent metals and biological treatment for the removal of chlorinated aliphatic compounds. New Biotechnol 25:S255–S256
Puhakka JA, Jarvinen KT, Langwaldt JH, Melin ES, Mannisto MK, Salminen JM, Sjolund MT (2000) On-site and in situ bioremediation of wood-preservative contaminated groundwater. Water Sci Technol 42:371–376
Reyna-Velarde R, Rios-Leal E, Thalasso F, Foresti E, Rinderkenecht-Seijas N, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2005) Comparison of two fluidized-bed reactors with simultaneous electron acceptors for the treatment of a perchloroethylene-contaminated effluent. In: Alleman BC, Kelley ME (eds) In situ and on-site bioremediation—2005. Proceedings of the Eighth International In Situ and on-Site Bioremediation Symposium. Batelle Press, Columbus, OH paper J04
Rivett MO, Chapman SW, Alllen-King RM, Feenstra S, Cherry JA (2006) Pump-and-treat remediation of chlorinated solvent contamination at a controlled field-experiment site. Environ Sci Technol 40:6770–6781
Rojas MDA, Netto AO, Zaiat M (2008) Specific methanogenic activity in an anaerobic-aerobic reactor applied to the treatment of domestic residual water. Interciencia 33:284–289
Rosenthal H, Adrian L, Steiof M (2004) Dechlorination of PCE in the presence of Fe-0 enhanced by a mixed culture containing two Dehalococcoides strains. Chemosphere 55:661–669
Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing K (1999) Chapter 9—adsorption by Active Carbons. In: Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing K (eds) Adsorption by powders and porous solids. Academic Press, London, pp. 237–285
Sánchez M, Mosquera-Corral A, Méndez R, Lema JM (2000) Simple methods for the determination of the denitrifying activity of sludges. Bioresour Technol 75:1–6
Sawyer C, MacCarty P, Parkin G (2003) Chemistry for environmental engineering and science. MacGraw-Hill, New York
Schmidt JE, Ahring BK (1996) Granular sludge formation in upflow anaerobic sledge blanket (UASB) reactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:229–246
Shin MC, Choi HD, Kim DH, Baek K (2008) Effect of surfactant on reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron. Desalination 223:299–307
Smidt H, de Vos WM (2004) Anaerobic microbial dehalogenation. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:43–73
Sorensen HA, Ahring BK (1993) Measurements of the specific methanogenic activity of anaerobic digestor biomas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:427–431
Sone N, Hägerhäll C, Sakamoto J (2004) Aerobic respiration in the gram-positive bacteria. In: Zannoni D (ed) Respiration in archaea and bacteria: diversity of prokaryotic respiratory systems. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp. 35–62
Sponza DT (2003) Toxicity and treatability of carbontetrachloride and tetrachloroethylene in anaerobic batch cultures. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 51:119–127
Sung Y, Ritalahti KM, Sanford RA, Urbance JW, Flynn SJ, Tiedje JM, Loffler FE (2003) Characterization of two tetrachloroethene-reducing, acetate-oxidizing anaerobic bacteria and their description as Desulfuromonas michiganensis sp nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2964–2974
Terzenbach DP, Blaut M (1994) Transformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene by homoacetogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 123:213–218
Tiehm A, Schmidt KR (2011) Sequential anaerobic/aerobic biodegradation of chloroethenes—aspects of field application. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:415–421
Van Nooten T, Lieben F, Dries J, Pirard E, Springael D, Bastiaens L (2007) Impact of microbial activities on the mineralogy and performance of column-scale permeable reactive iron barriers operated under two different redox conditions. Environ Sci Technol 41:5724–5730
Vogel TM, Criddle CS, McCarty PL (1987) ES critical reviews: transformations of halogenated aliphatic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 21:722–736
Volpe A, Del Moro G, Rossetti S, Tandoi V, Lopez A (2007) Remediation of PCE-contaminated groundwater from an industrial site in southern Italy: a laboratory-scale study. Process Biochem 42:1498–1505
Wikström P, Andersson A-C, Forsman M (1999) Biomonitoring complex microbial communities using random amplified polymorphic DNA and principal component analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 28:131–139
Worm P, Müller N, Plugge CM, Stams AJM, Schink B (2010) Syntrophy in methanogenic degradation. In: HPJ H (ed) (Endo) symbiotic methanogenic archaea. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 143–173
Yan E, LaFreniere L, Roe C (2010) Argonne National Laboratory examines an integrated carbon and ZVI source for in situ chemical reduction. Technol News Trends:1–3
Zárate-Segura PB, Rios-Leal E, Esparza-Garcia F, Garcia-Mena J, Sanz JL, Zaiat M, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2004) Perchloroethylene removal in two anaerobic continuous systems. Interciencia 29:562–567
Zolla V, Sethi R, Di Molfetta A (2007) Performance assessment and monitoring of a permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of a contaminated site. Am J Environ Sci 3:158–165
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers of ESPR for their insightful comments that improved the manuscript. The authors also gratefully acknowledge CONACYT for graduate scholarships to CUM-M and LMB-D, and Stat-Ease, Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) for a free license of Design-Expert v 8.0 to HMP-V. The excellent technical help of Mr. Rafael Hernández-Vera (GBAER, CINVESTAV del IPN) is appreciated. CONACYT granted an infrastructure Project 188281 to one of the authors (HMP-V). CINVESTAV del IPN partially funded this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 979 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno-Medina, C.U., Poggi-Varaldo, H.M., Breton-Deval, L. et al. Effect of sudden addition of PCE and bioreactor coupling to ZVI filters on performance of fluidized bed bioreactors operated in simultaneous electron acceptor modes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 25534–25549 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7275-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7275-z