Abstract
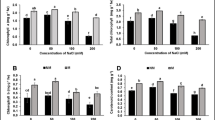
Greenhouse hydroponic experiments were carried out using three different heavy metal accumulation tobacco genotypes to evaluate how different genotypes responded to chromium (Cr) toxicity in the presence of 24-epibrassinolide (EBR; a biologically active brassinosteroid). The results showed that Cr stress caused a marked reduction in plant biomass, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and photosynthesis parameters but induced malondialdehyde accumulation and ultrastructure damage, with 2010-38 (L) less affected. Foliar application of 24-epibrassinolide (0.1 μM) on Cr-stressed plants greatly alleviated Cr-induced inhibition of growth and photosynthesis, oxidative stress and ultrastructure damage, decreased Cr accumulation in different parts of leaves and roots, with the exception of the upper and lower of leaves of genotype L, and maintained ion homeostasis. Regarding genotypes, L was more tolerant than M and H, as it absorbed less Cr and also performed better in all of the studied parameters. These findings suggest a potential role for 24-epibrassinolide in Cr stress alleviation and the utilization of elite genetic resources in future breeding programs to develop low Cr accumulation genotypes. These results advocate a positive role for 24-epibrassinolide in reducing pollutant residues from health point of view.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahammed GJ, Choudhary SP, Chen S, Xia X, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu J (2013) Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrenecadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato. J Exp Bot 64:199–213
Ali B, Tao Q, Zhou Y, Gill RA, Ali S, Rafiq MT, Xu L, Zhou W (2013) 5-Aminolevolinic acid mitigates the cadmium-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by the biochemical and ultra-structural evaluation of roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:271–280
Andre CM, Larondelle Y, Evers D (2010) Dietary antioxidants and oxidative stress from a human and plant perspective: a review. Curr Nutr Food Sci 6:2–12
Cai Y, Cao F, Cheng W, Zhang G, Wu F (2011a) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in phytochelatins and photosynthetic performance against Cd stress in the two rice genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1159–1173
Cai Y, Cao F, Wei K, Zhang G, Wu F (2011b) Genotypic dependent effect of exogenous glutathione on Cd-induced changes in proteins, ultrastructure and antioxidant defense enzymes in rice seedlings. J Hazard Mater 192:1056–1066
Cao F, Wang N, Zhang M, Dai H, Dawood M, Zhang G, Wu F (2013) Comparative study of alleviating effects of GSH, Se and Zn under combined contamination of cadmium and chromium in rice (Oryza sativa). Biometals 26:297–308
Cao F, Wang R, Cheng W, Zeng F, Ahmed I, Hu X, Zhang G, Wu F (2014a) Genotypic and environmental variation in cadmium, chromium, lead and copper in rice and approaches for reducing the accumulation. Sci Total Environ 496:275–281
Cao F, Chen F, Sun H, Zhang G, Chen Z, Wu F (2014b) Genome-wide transcriptome and functional analysis of two contrasting genotypes reveals key genes for cadmium tolerance in barley. BMC Genomics 15:611
Chary NS, Kamala CT, Raj DSS (2008) Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotox Environ Saf 69:513–524
Chen F, Wang F, Wu F, Mao WH, Zhang G, Zhou M (2010) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:663–672
Choudhary SP, Oral HV, Bhardwaj R, Yu JQ, Tran LSP (2012) Interaction of brassinosteroids and polyamines enhances copper stress tolerance in Raphanus sativus. J Exp Bot 63:5659–5675
Ci D, Jiang D, Wollenweber B, Dai T, Jing Q, Cao W (2010) Cadmium stress in wheat seedlings: growth, cadmium accumulation and photosynthesis. Acta Physiol Plant 32:365–373
Cui JX, Zhou YH, Ding JG, Xia XJ, Shi K, Chen SC, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2011) Role of nitric oxide in hydrogen peroxide-dependent induction of abiotic stress tolerance by brassinosteroids in cucumber. Plant Cell Environ 34:347–358
Dhaubhadel S, Krishna P (2008) Identification of differentially expressed genes in brassinosteroid-treated Brassica napus seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 27:297–308
Diwan H, Khan I, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2010) Induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant defence system in Brassica juncea and Vigna radiata in response to chromium treatments. Plant Growth Regul 61:97–107
Gill RA, Zang L, Ali B, Farooq MA, Cui P, Yang S, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 120:154–164
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) Brassinosteroids protect photosynthetic machinery against the cadmium induced oxidative stress in two tomato cultivars. Chemosphere 84:1446–1451
Ishida H, Makino A, Mae T (1999) Fragmentation of the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by reactive oxygen species occurs near Gly-329. J Biol Chem 274:5222–5226
Jiang YP, Cheng F, Zhou YH, Xia XJ, Shi K, Yu JQ (2012) Interactive effects of CO2 enrichment and brassinosteroid on CO2 assimilation and photosynthetic electron transport in Cucumis sativus. Environ Exp Bot 75:98–106
Kagale S, Divi U, Krochko J, Keller W, Krishna P (2007) Brassinosteroid confers tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus to a range of abiotic stresses. Planta 225:353–364
Masood A, Iqbal N, Khan NA (2012) Role of ethylene in alleviation of cadmium-induced photosynthetic capacity inhibition by sulphur in mustard. Plant Cell Environ 35:524–533
McCord JM (2000) The evolution of free radicals and oxidative stress. Am J Med 108:652–659
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Oliveira H (2012) Chromium as an environmental pollutant: insights on induced plant toxicity. J Bot 2012
Sharma I, Pati PK, Bhardwaj R (2010) Regulation of growth and antioxidant enzyme activities by 28-homobrassinolide in seedlings of Raphanus sativus L. under cadmium stress. Indian J Biochem Biophys 47:172–177
Sharma I, Pati PK, Bhardwaj R (2011) Effect of 28-homobrassinolide on antioxidant defence system in Raphanus sativus L. under chromium toxicity. Ecotoxicology 20:862–874
Shanker AK, Cervantes C, Loza-Tavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31:739–753
Skórzyńska-Polit E, Drążkiewicz M, Krupa Z (2010) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidative response in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to cadmium and copper. Acta Physiol Plant 32:169–175
Sudo E, Itouga M, Yoshida-Hatanaka K, Ono Y, Sakakibara H (2008) Gene expression and sensitivity in response to copper stress in rice leaves. J Exp Bot 59:3465–3474
Xia XJ, Zhang Y, Wu JX, Wang JT, Zhou YH, Shi K, Yu YL, Yu JQ (2009) Brassinosteroids promote metabolism of pesticides in cucumber. J Agric Food Chem 57:8406–8413
Yu JQ, Huang LF, Hu WH, Zhou YH, Mao WH, Ye SF, Nogués S (2004) A role for brassinosteroids in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. J Exp Bot 55:1135–1143
Yu XZ, Gu JD, Huang SZ (2007) Hexavalent chromium induced stress and metabolic responses in hybrid willows. Ecotoxicology 16:299–309
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Hasan S, Ahmad A (2011) Protective response of 28-homobrassinolide in cultivars of Triticum aestivum with different levels of nickel. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:68–76
Zayed A, Lytle CM, Qian JH, Terry N (1998) Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta 206:293–299
Zeng F, Qiu B, Ali S, Zhang G (2010) Genotypic differences in nutrient uptake and accumulation in rice under chromium stress. J Plant Nutr 33:518–528
Zhang M, Zhai Z, Tian X, Duan L, Li Z (2008) Brassinolide alleviated the adverse effect of water deficits on photosynthesis and the antioxidant of soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Growth Regul 56:257–264
Zhou J, Wang J, Li X, Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Shi K, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2014) H2O2 mediates the crosstalk of brassinosteroid and abscisic acid in tomato responses to heat and oxidative stresses. J Exp Bot 65:4371–4383
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501233) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (2015M570513).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Yi-ping Chen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bukhari, S.A.H., Wang, R., Wang, W. et al. Genotype-dependent effect of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on chromium-induced changes in ultrastructure and physicochemical traits in tobacco seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 18229–18238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7017-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7017-2