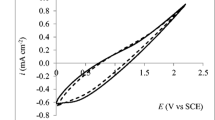
Abstract
The influence of chloride ion concentration during the photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of simulated textile effluent, using a commercial Ti/Ru0.3Ti0.7O2 anode, was evaluated. Initially, the effect of applied current and supporting electrolyte concentration on the conversion of chloride ions to form reactive chlorine species in 90 min of experiment was analyzed in order to determine the maximum production of reactive chlorine species. The optimum conditions encountered (1.5 A and 0.3 mol dm−3 NaCl) were subsequently employed for the degradation of simulated textile effluent. The efficiency of the process was determined through the analysis of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC), of the presence of organochlorine products and phytotoxicity. Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation was more efficient for COD and TOC removal than the electrochemical technique alone. With simultaneous UV irradiation, a reduced quantity of reactive chlorine was produced, indicating that photolysis of the chlorine species led to the formation of hydroxyl radicals. This fact turns a simple electrochemical process into an advanced oxidation process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari A, Desclaux S, Rouch J, Aptel P, Remigy J (2006) New UV-photografted nanofiltration membranes for the treatment of colored textile dye effluents. J Membr Sci 286:342–350
Al-Hamaiedeh HD (2013) Electrochemical-active chlorine generation by circulating the electrolyte through an electrolytic cell. Environ Eng Sci 30:82–88
Alves PA, Malpass GRP, Johansen HD, Azevedo EB, Gomes LM, Vilela WFD, Motheo AJ (2010) Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of real textile wastewater. Water Sci Technol 61:491–498
Alves PA, Johansen HD, Aquino Neto S, Andrade AR, Motheo AJ, Malpass GRP (2014) Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of textile effluent to reduce organic halide (AOX) production. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:2144–2144
Amaral FM, Kato MT, Florêncio L, Gavazza S (2014) Color, organic matter and sulfate removal from textile effluents by anaerobic and aerobic processes. Bioresour Technol 163:364–369
APHA/AWWA/WEF—American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA/AWWA/WEF, Washington
ASTM—American Society for Testing and Materials (1998) Standard guide for conducting terrestrial plant toxicity. West Conshohocken
Bilgi S, Demir C (2005) Identification of photooxidation degradation products of C.I. Reactive Orange 16 dye by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Dyes Pigments 66:69
Chen GH (2004) Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 38:11–41
Cho SH, Shim J, Moon SH (2009) Detoxification of simulated textile wastewater using a membraneless electrochemical reactor with immobilized peroxidase. J Hazard Mater 162:1014–1018
Correia VM, Stephenson T, Judd SJ (1994) Characterization of textile wastewater—a review. Environ Technol 15:917–929
Feng C, Sugiura N, Shimada S, Maekawa T (2003) Development of a high performance electrochemical wastewater treatment system. J Hazard Mater B103:65–78
Forgacs E, Cserháti T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30:953–971
Garcia JC, Oliveira JL, Silva AEC, Oliveira CC, Nozaki J, Souza NE (2007) Comparative study of the degradation of real textile effluents by photocatalytic reactions involving UV/TiO2/H2O2 and UV/Fe2+/H2O2 systems. J Hazard Mater 147:105–110
Gomes L, Miwa DW, Malpass GRP, Motheo AJ (2011) Electrochemical degradation of dye reactive Orange 16 using electrochemical flow-cell. J Braz Chem Soc 22:1299–1306
Gutowska A, Kaluzna-Czaplinska J, Jozwiak WK (2007) Degradation mechanism of Reactive Orange 113 dye by H2O2/Fe2+ and ozone in aqueous solution. Dyes Pigments 74:41
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurston RV (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Hao OJ, Kim H, Chiang PC (2000) Decolorization of wastewater. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30:449–505
Helme AJ, Ismail MN, Scarano FJ, Yang CL (2010) Bactericidal efficacy of electrochemically activated solutions and of commercially available hypochlorite. Biomed Sci 67:105–108
Huang X, Qu Y, Cid CA, Finke C, Hoffmann MR, Lim K, Jiang SC (2016) Electrochemical disinfection of toilet wastewater using wastewater electrolysis cell. Water Res 92:164–172
Jin J, El-Din MG, Bolton JR (2011) Assessment of the UV/Chlorine process as an advanced oxidation process. Water Res 45:1890–1896
Jung YJ, Baek KW, Oh BS, Kang JW (2010) An investigation of the formation of chlorate and perchlorate during electrolysis using Pt/Ti electrodes: the effects of pH and reactive oxygen species and the results of kinetic studies. Water Res 44:5345–5355
Juttner K, Galla U, Schmieder H (2000) Electrochemical approaches to environmental problems in the process industry. Electrochim Acta. doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00339X
Kuhn AT (1971) Electrolytic decomposition of cyanides, phenols and thiocyanates in effluents streams-a literature review. J Appl Chem Biotechnol 21:29–34
Kvaran Á, Konráðsson ÁE, Evans C, Geirsson JKF (2001) H NMR and UV–Vis spectroscopy of chlorine substituted stilbenes: conformational studies. J Mol Struct 553:79–90
Malpass GRP, Neves RS, Motheo AJ (2006) A comparative study of commercial and laboratory-made Ti/Ru0. 3Ti0. 7O2 ADE® electrodes. Electrochim Acta 52:936
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Miwa ACP, Machado SAS, Motheo AJ (2007a) Photo-assisted electrochemical oxidation of Atrazine on a commercial Ti/Ru0.3Ti0.7O2 DSA electrode. Environ Sci Technol 41:7120–7125
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Mortari DA, Machado SAS, Motheo AJ (2007b) Decolorisation of real textile waste using electrochemical techniques: effect of the chloride concentration. Water Res 41:2969
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Machado SAS, Motheo AJ (2010) SnO2-based materials for pesticide degradation. J Hazard Mater 180:145–151
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Santos RL, Vieira EM, Motheo AJ (2012) Unexpected toxicity decrease during photoelectrochemical degradation of atrazine with NaCl. Environ Chem Lett 10:177–182
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 87:105–145
Neodo S, Rosestolato D, Ferro S, De Battisti A (2012) On the electrolysis of dilute chloride solutions: influence of the electrode material on Faradaic efficiency for active chlorine, chlorate and perchlorate. Electrochim Acta 80:282–291
Nowell LH, Hoigné J (1992a) Photolysis of aqueous chlorine at sunlight and ultraviolet wavelengths—I. Degradation rates. Water Res 26:593–598
Nowell LH, Hoigné J (1992b) Photolysis of aqueous chlorine at sunlight and ultraviolet wavelengths—II. Hidroxyl radical production. Water Res 26:599–605
Pekakis PA, Xekoukoulotakis NP, Mantzavinos D (2006) Treatment of textile dyehouse wastewaters by TiO2 photocatalysis. Water Res 40:1276–1286
Quaratini CI, Zanoni MVB (2000) Corantes têxteis. Quim Nov. 23:71–78
Rajkumar D, Kim JG (2006) Oxidation of various reactive dyes with in situ electro-generated active chlorine for textile dyeing industry wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater B136:203–212
Rajkumar D, Kim JG, Palanivelu K (2005) Indirect electrochemical oxidation of phenol in the presence of chloride for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng Technol 28:98
Sichel C, Garcia C, Andre K (2011) Feasibility studies: UV/chlorine advanced oxidation treatment for the removal of emerging contaminants. Water Res 45:6371–6380
Silverstein RM, Webster FX, Kiemie DJ, Bryce DL (2005) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds, 7th edn. Wiley, New York
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367
Tatoulis TI, Zapantiotis S, Frontistis Z, Akratos CS, Tekerlekopoulou AG, Pavlou S, Mantzavinos D, Vayenas DV (2016) A hybrid system comprising an aerobic biological process and electrochemical oxidation for the treatment of black table olive processing wastewaters. Int Biodeter Biodegr 109:104–112
Urtiaga A, Gómez P, Arruti A, Ortiz I (2014) Electrochemical removal of tetrahydrofuran from industrial wastewaters: anode selection and process scale-up. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:1243–1250
Wang C, Zhang M, Ye M, Wang J, Li G (2014) Pilot-scale electrochemical oxidation combined with constructed wetland system for unconventional surface water treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:1599–1606
Watts MJ, Linden KG (2007) Chlorine photolysis and subsequent OH radical production during UV treatment of chlorinated water. Water Res 41:2871–2878
Ye Z, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhou D (2016) Treatment of landfill leachate using electrochemically assisted UV/chlorine process: effect of operating conditions, molecular weight distribution and fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC analysis. Chem Eng J 286:508–516
Zhang J, Liu D, Bian W, Chen X (2012) Degradation of 2,4-dichorophenol by pulsed high voltage discharge in water. Desalination 304:49–56
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CAPES, CNPq, and FAPEMIG for the financial support; AUPICOR for the donation of the dyes employed in this study. This work is a collaboration research project of members of the Rede Mineira de Química (RQ-MG) supported by FAPEMIG (Project: CEX - RED-00010-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Mello Florêncio, T., de Araújo, K.S., Antonelli, R. et al. Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of simulated textile effluent coupled with simultaneous chlorine photolysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 19292–19301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6912-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6912-x