Abstract
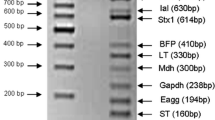
The aim of this study was the evaluation of the occurrence of pathogenic Campylobacter, Escherichia coli O157:H7, E. coli virulence genes and Salmonella spp. in different wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) using a method based on an enrichment step and PCR. This method was sensitive enough to detect low levels (∼2 CFU100 ml-1 of raw sewage) of all the investigated pathogens. In the WWTP samples, E. coli O157:H7 DNA and the eae gene were never found, but 33 % of influents and effluents exhibited amplicons corresponding to Shiga-like toxin I. Twenty-five percent of the influent and 8 % of the effluent exhibited the presence of Shiga-like toxin II. Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli DNA were identified in 50 and 25 % of the influents and in 8 and 25 % of the effluents, respectively. Salmonella spp. DNA was present in all the samples. Considering the results obtained, the method tested here offers a reliable and expeditious tool for evaluating the efficiency of the effluent treatment in order to mitigate contamination risk. Influent contamination by Salmonella spp. and Campylobacter spp. provides indirect information about their circulation; moreover, their presence in effluents underlines the role of WWTPs in the contamination of the receiving surface waters, which affects public health directly or indirectly.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berge ACB, Dueger EL, Sischo WM (2006) Comparison of Salmonella enterica serovar distribution and antibiotic resistance patterns in wastewater at municipal water treatment plants in two California cities. J Appl Microbiol 101:1309–1316. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03031.x
Bertrand R, Roig B (2007) Evaluation of enrichment-free PCR-based detection on the rfbE gene of Escherichia coli O157—application to municipal wastewater. Water Res 41:1280–1286. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.11.027
Bonetta S, Borelli E, Bonetta S, Conio O, Palumbo F, Carraro E (2011) Development of a PCR protocol for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. in surface water. Environ Monit Assess 177:493–503. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1650-x
Cataldo C, Briancesco R, Bonadonna L (2001) Water reuse: hygienic and technical aspects related to the occurrence of enteric pathogens. Rapporti ISTISAN 34:1–38
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2013) Surveillance for waterborne disease outbreaks associated with drinking water and other non recreational water—United States, 2009-2010. MMWR 62:714–720
Dumke R, Schroter-Bobsin U, Jacobs E, Roske I (2006) Detection of phages carrying the Shiga toxin 1 and 2 genes in waste water and river water samples. Lett Appl Microbiol 42:48–53. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01809.x
Espigares E, Bueno A, Espigares M, Galvez R (2006) Isolation of Salmonella serotypes in wastewater and effluent: effect of treatment and potential risk. Int J Hyg Environ Health 209:103–107. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2005.08.006
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2015) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J 13:3991
Guzman-Herrador B, Carlander A, Ethelberg S, Freiesleben de Blasio B, Kuusi M, Lund V, MacDonald E, Nichols G, Shonning C, Sudre B, Tronnberg L, Vold L, Semenza JC, Nygard K (2015) Waterborne outbreaks in the Nordic countries, 1998 to 2012. Euro Surveill 20:1–10
James CE, Stanley KN, Allison HE, Flint HJ, Stewart CS, Sharp RJ et al (2001) Lytic and lysogenic infection of diverse Escherichia coli and Shigella strains with a verocytotoxigenic bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4335–4337
Jokinen CC, Schreirer H, Mauro W, Taboada E, Isaac-Renton JL, Topp E, Edge T, Thomas JE, Gannon VPJ (2010) The occurrence and sources of Campylobacter spp., Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in the Salmon River, British Columbia, Canada. J Water Health 08(2):374–386. doi:10.2166/wh.2009.076
Kaakoush NO, Castano-Rodriguez N, Mitchell H, Man SM (2015) Global epidemiology of Campylobacter infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:687–720. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-15
Khan IUH, Gannon V, Loughborough A, Jokinen C, Kent R, Koning W, Lapen DR, Medeiros D, Miller J, Neumann N, Phillips R, Robertson W, Schereirer H, Topp E, van Bochove E, Edge TA (2009) A methods comparison for the isolation and detection of thermophilic Campylobacter in agricultural watersheds. J Microbiol Methods 79:307–313. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2009.09.024
Koivunen J, Siitonen A, Heinonen-Tanski H (2003) Elimination of enteric bacteria in biological-chemical wastewater treatment and tertiary filtration units. Water Res 37:690–698. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00305-6
Levantesi C, La Mantia R, Masciopinto C, Bockelmann U, Ayuso-Gabella MN, Salgot M, Tandoi V, Van Houtte E, Wintgens T, Grohmann E (2010) Quantification of pathogenic microorganisms and microbial indicators in three wastewater reclamation and managed aquifer recharge facilities in Europe. Sci Total Environ 408:4923–4930. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.042
Li D, Zeng S, Gu AZ, He M, Shi H (2013) Inactivation, reactivation and regrowth of indigenous bacteria in reclaimed water after chlorine disinfection of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. J Environ Sci 25:1319–1325. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60176-4
Loukiadis E, Kerouredan M, Beutin L, Oswald E, Brugere H (2006) Characterization of Shiga toxin gene (stx)-positive and intimin gene (eae)-positive Escherichia coli isolates from wastewater of slaughterhouses in France. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3245–3251. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.5.3245-3251.2006
Martinez-Castillo A, Allue-Guardia A, Dahbi G, Blanco J, Creuzburg K, Schmidt H, Muniesa M (2012) Type III effector genes and other virulence factors of Shiga toxin-encoding Escherichia coli isolated from wastewater. Environ Microbiol Rep 4:147–155. doi:10.1111/j.1758-2229.2011.00317.x
Muniesa M, Jofre J, Garcia-Aliaro C, Blanch AR (2006) Occurrence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 40:7141–7149. doi:10.1021/es060927k
Ostoich M, Aimo E, Frate R, Vazzoler M, Stradella S, Osti P (2007) Integrated approach for microbiological impact assessment of public wastewater treatment plants. Chem Ecol 23:43–62. doi:10.1080/02757540601083963
Park SH, Hanning I, Jarquin R, Moore P, Donoghue DJ, Donoghue AM, Ricke SC (2011) Multiplex PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Salmonella serotypes in water samples. FEMS Microbiol Lett 316:7–15. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02188.x
Pennington H (2010) Escherichia coli O157. Lancet 376:1428–1435. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60963-4
Pitkanen T (2013) Review of Campylobacter spp. in drinking and environmental waters. J Microbiol Methods 95:39–47. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2013.06.008
Rechenburg A, Kistemann T (2009) Sewage effluent as a source of Campylobacter spp. in a surface water catchment. Int J Environ Health Res 19:239–249. doi:10.1080/09603120802460376
Saxena T, Kaushik P, Mohan MK (2015) Prevalence of E. coli O157:H7 in water sources: an overview on associated diseases, outbreaks and detection methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 82:249–264. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.03.015
Shannon KE, Lee DY, Trevors JT, Beaudette LA (2007) Application of real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of selected bacterial pathogens during municipal wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 382:121–129. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.02.039
Strauch E, Hammerl JA, Konietzny A, Schneiker-Bekel S, Arnold W, Goesmann A et al (2008) Bacteriophage 2851 is a prototype phage for dissemination of the Shiga toxin variant gene 2c in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun 76:5466–5477
Teklehaimanot GZ, Coetzee MAA, Momba MNB (2014) Faecal pollution loads in the wastewater effluents and receiving water bodies: a potential threat to the health of Sediberg and Soshanguve communities, South Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9589–9603. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-2980-y
Teklehaimanot GZ, Genthe B, Kamika I, Momba MNB (2015) Prevalence of enteropathogenic bacteria in treated effluents and receiving water bodies and their potential health risks. Sci Total Environ 518–519:441–449. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.019
Touron A, Berthe T, Pawlak B, Petit F (2005) Detection of Salmonella in environmental water and sediment by a nested-multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay. Res Microbiol 156:541–553. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2005.01.001
Ugarte-Ruiz M, Florez-Cuadrado D, Wassenaar TM, Porrero MC, Dominguez L (2015) Method comparison for enhanced recovery, isolation and qualitative detection of C. jejuni and C. coli from wastewater effluents samples. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:2749–2764. doi:10.3390/ijerph120302749
Varela AR, Manaia CM (2013) Human health implications of clinically relevant bacteria in wastewater habitats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3550–3569. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1594-0
Wery N, Lhoutellier C, Ducray F, Delgenes J, Godon J (2008) Behaviour of pathogenic and indicator bacteria during urban wastewater treatment and sludge composting, as revealed by quantitative PCR. Water Res 42:53–62. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.048
Whiley H, van den Akker B, Giglio S, Bentham R (2013) The role of environmental reservoirs in human campylobacteriosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:5886–5907. doi:10.3390/ijerph10115886
Yang K, Pagaling E, Yan T (2014) Estimating the prevalence of potential enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and intimin gene diversity in a human community by monitoring sanitary sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:119–127. doi:10.1128/AEM.02747-13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonetta, S., Pignata, C., Lorenzi, E. et al. Detection of pathogenic Campylobacter, E. coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. in wastewater by PCR assay. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 15302–15309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6682-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6682-5