Abstract
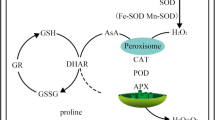
Microbe-assisted phytoremediation provides an effective approach to clean up heavy metal-contaminated soils. However, severe drought may affect the function of microbes in arid/semi-arid areas. Streptomyces pactum Act12 is a drought-tolerant soil actinomycete strain isolated from an extreme environment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. In this study, pot experiments were conducted to assess the effect of Act12 on Cd tolerance, uptake, and accumulation in amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) under water deficit. Inoculated plants had higher Cd concentrations (root 8.7–33.9 %; shoot 53.2–102.1 %) and uptake (root 19.9–95.3 %; shoot 110.6–170.1 %) than non-inoculated controls in Cd-treated soil. The translocation factor of Cd from roots to shoots was increased by 14.2–75 % in inoculated plants, while the bioconcentration factor of Cd in roots and shoots was increased by 10.2–64.4 and 53.9–114.8 %, respectively. Moreover, inoculation with Act12 increased plant height, root length, and shoot biomass of amaranth in Cd-treated soil compared to non-inoculated controls. Physiochemical analysis revealed that Act12 enhanced Cd tolerance in the plants by increasing glutathione, elevating superoxide dismutase and catalase activities, as well as reducing malondialdehyde content in the leaves. The drought-tolerant actinomycete strain Act12 can enhance the phytoremediation efficiency of amaranth for Cd-contaminated soils under water deficit, exhibiting potential for application in arid and semi-arid areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SZ, Sandhya V, Rao LV (2014) Isolation and characterization of drought-tolerant ACC deaminase and exopolysaccharide-producing fluorescent Pseudomonas sp. Ann Microbiol 64(2):493–502
Angelo D, Manel T, Federica G, Anna MT, Lello Z, Tahar G (2013) Cadmium stress responses in brassica juncea: hints from proteomics and metabolomics. J Proteome Res 12:4979–4997
Anne MR, Anna B, Barbara JG, Paul TA (2013) Urinary cadmium in the 1999–2008 U.S. National health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES). Environ Sci Technol 47:1137–1147
Bernadette LC, Divina AGN, Diana SA, Mary AB (2011) Cd tolerance and accumulation in the aquatic macrophyte, chara australis: potential use for charophytes in phytoremediation. Environ Sci Technol 45:5332–5338
Carmine G, Barbara C, Valentina S, Simona A, Rosaria S, Andrea S (2014) Proteomic analysis of eucalyptus leaves unveils putative mechanisms involved in the plant response to a real condition of soil contamination by multiple heavy metals in the presence or absence of mycorrhizal/rhizobacterial additives. Environ Sci Technol 48:11487–11496
Chen Q, Xue QH, Shen QH, Xue L, Duan CM, Wang LN, Zhao J, Mao N (2010) Effect of actinomyces seed coating agent on cotton growth and drought resistance. Acta Agric Boreali-Occiden Sin 19:84–89
Cheng SP (2003) Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:192–198
Cheng LJ, Xue QH, Lai HX (2000) Microbiology experiment technology. World Publishing Corp, Xi’an
Deng ZJ, Zhang RD, Shi Y, Hu LA, Tan HM, Cao LX (2013) Enhancement of phytoremediation of Cd- and Pb-contamination soils by self-fusion of protoplasts from endophytic fungus Mucor sp. CBRF59. Chemosphere 91:41–47
Dimkpa CO, Merten D, Svatoš A, Büchel G, Kothe E (2009) Siderophores mediate reduced and increased uptake of cadmium by Streptomyces tendae F4 and sunflower (Helianthus annuus), respectively. J Appl Microbiol 107:1687–1696
Duan CM, Xue QH, Zhao J, Hu SB, Chen Q, Wang LN, Shen GH, Xue L (2010) Effects of antimicrobial actinomyces on growth and PPO activity in cucumber. Acta Agric Bori–Occid Sin 19:48–54
Duman F, Kar M (2015) Evaluation of effects of exposure conditions on the biological responses of Gammarus pulex exposed to cadmium. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:437–444
Glick BR (2003) Phytoremediation: synergistic use of plants and bacteria to clean up the environment. Biotechnol Adv 21:383–393
Glick BR, Penrose DM, Li J (1998) A model for the lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant growth-promoting bacteria. J Theor Biol 190:63–68
Glick BR, Todorovic B, Czarny J, Cheng Z, Duan J, McConkey B (2007) Promotion of plant growth by bacterial ACC deaminase. Crit Rev Plant Sci 26(5-6):227–242
Guan X, Huang J, Guo N, Bi J, Wang G (2009) Variability of soil moisture and its relationship with surface albedo and soil thermal parameters over the Loess Plateau. Adv Atmos Sci 26:692–700
He HD, Ye ZH, Yang DJ (2013) Characterization of endophytic Rahnella sp. JN6 from Polygonum pubescens and its potential in promoting growth and Cd, Pb, Zn uptake by Brassica napus. Chemosphere 90:1960–1965
He F, Zhang ZL, Cui M, Xue QH, Wang DS (2015) Disease prevention and growth promotion effects of actinomycete strain D74 on Amorphophallus konjac. Acta Hortic Sin 42:367–376
Hu JL, Wu SC, Wu FY, Leung HM, Lin XG, Wong MH (2013) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance both absorption and stabilization of Cd by Alfred stonecrop (Sedum alfredii Hance) and perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) in a Cd-contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 93:1359–1365
Jian WH, Michael JB, Yoram K, Burt DE (1998) Phytoremediation of uranium-contaminated soils: role of organic acids in triggering uranium hyperaccumulation in plants. Environ Sci Technol 32:2004–2008
Jiang PH, Ma C, Xiang RJ, Cheng YX, Peng KJ, Liu Z (2012) Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of soil in typical function zones of Zhuzhou. Environ Sci Technol 35:379–384 (in chinese)
Kaushal M, Wani SP (2016) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria: drought stress alleviators to ameliorate crop production in drylands. Ann Microbiol 66:35–42
Lasat MM (2001) Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a review of biological mechanisms. J Environ Qual 31:109–120
Li MX, Ma ZG (2015) Soil moisture drought detection and multi-temporal variability across China. Sci China Earth Sci 58:1798–1813
Li WC, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2007) Effects of bacteria on enhanced metal uptake of the Cd/Zn-hyperaccumulating plant, Sedum alfredii. J Exp Bot 58:4173–4182
Li NY, Fu QL, Zhuang P, Guo B, Zou B, Li ZA (2012) Effect of fertilizers on Cd uptake of Amaranthus hypochondriacus, a high biomass, fast growing and easily cultivated potential Cd hyperaccumulator. Int J Phytoremediation 14:162–173
Li Y, Zhang SS, Jiang WS, Liu DH (2013) Cadmium accumulation, activities of antioxidant enzymes, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content in Pistia stratiotes L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1117–1123
Lin YF, Aarts MG (2012) The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3187–3206
Luo SL, Xu TY, Chen L, Chen JL, Rao C, Xiao X, Wan Y, Zeng GM, Long F, Liu CB, Liu YT (2012) Endophyte-assisted promotion of biomass production and metal-uptake of energy crop sweet sorghum by plant-growth-promoting endophyte Bacillus sp. SLS18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1745–1753
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Luo YM, Freitas H (2011) Inoculation of endophytic bacteria on host and non-host plants effects on plant growth and Ni uptake. J Hazard Mater 195:230–237
Mani R, Noriharu A, Prasad MNV, Helena F (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28(3):142–149
Marklund S, Marklund G (1947) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autooxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Melanie K, Markus P, Gerlinde W, Markus G, Angela S (2008) Rhizosphere bactiaria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304:35–44
Melo EEC, Costa ETS, Guilherme LRG, Faquin V, Nascimento CWA (2009) Accumulation of arsenic and nutrients by castor bean plants grown on an As-enriched nutrient solution. J Hazard Mater 168:479–483
Michel BE, Kaufmann MR (1973) The osmotic potential of polyethylene glycol 6000. Plant Physiol 51:914–916
Milone MT, Sgherri C, Clijsters H, Navari-Izzo F (2003) Antioxidative responses of wheat treated with realistic concentration of cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 3:265–276
Neidhardt FC, Bloch PL, Smith DF (1974) Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol 119:736–747
Owens WI, Belcher RV (1965) A colorimetric micro-method for the determination of glutathione. Biochem J 94:705–711
Phieler R, Merten D, Roth M, Büchel G, Kothe E (2015) Phytoremediation using microbially mediated metal accumulation in Sorghum bicolor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:19408–19416
Qu YP (2009) Effects of AM fungal on the secondary metabolites of grape under cadmium stress. J Northwest Forestry Univ 24:101–105
Schütze E, Kothe E, Schütze E, Kothe E, Schütze E, Kothe E (2012) Heavy metal-resistant streptomycetes in soil. Bio-Geo interactions in metal-contaminated soils. Springer, Berlin, pp 163–182
Schütze E, Klose M, Merten D, Nietzsche S, Senftleben D, Roth M, Kothe E (2014) Growth of streptomycetes in soil and their impact on bioremediation. J Hazard Mater 267:128–135
Udovica M, Drobneb D, Lestan D (2013) An in vivo invertebrate bioassay of Pb, Zn and Cd stabilization in contaminated soil. Chemosphere 92:1105–1110
Vurukonda SSKP, Vardharajula S, Shrivastava M, SkZ A (2016) Enhancement of drought stress tolerance in crops by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol Res 184:13–24
Wan Y, Luo SL, Chen JL, Xiao X, Chen L, Zeng GM, Liu CB, He YJ (2012) Effect of endophyte-infection on growth parameters and Cd-induced phytotoxicity of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 89:743–750
Xue QH, Cai Y, Si MR, Tu X, Chen ZQ, Yuan HL, Lai HX, Niu XL (2004) Preparation for biological prevention and cure of hot pepper epidemic disease and method for producing the same. Patent CN100334953C, Northwest A&F University and Create Microbial Engineering Institute, Yangling, China
Xue L, Xue QH, Chen Q, Lin C, Shen GH, Zhao J (2013) Isolation and evaluation of rhizosphere actinomycetes with potential application for biocontrol of Verticillium wilt of cotton. Crop Prot 43:231–240
Yang YF, Zhang S, Li HF, Jiang RF (2009) Accumulation of cadmium in the edible parts of six vegetable species grown in Cd-contaminated soils. J Environ Manag 90:1117–1122
Yuan M, He HD, Xiao L, Zhong T, Liu H, Li SB, Deng PY, Ye ZH, Jing YX (2014) Enhancement of Cd phytoextraction by two Amaranthus species with endophytic Rahnella sp. JN27. Chemosphere 103:99–104
Zaidi A, Khan M, Ahemad M, Oves M (2009) Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 56(3):263–284
Zeng XW, Qiu RL, Ying RR, Tang YT, Tang L, Fang XH (2011) The differentially-expressed proteome in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Arabis paniculata Franch. in response to Zn and Cd. Chemosphere 82:321–328
Zhang FQ, Wang YS, Lou ZP, Dong JD (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere 67:44–50
Zhang XC, Zhang SR, Xu XX, Li T, Gong GS, Jia YX, Li Y, Deng LJ (2010) Tolerance and accumulation characteristics of cadmium in Amaranthus hybridus L. J Hazard Mater 180:303–308
Zhang HY, Xue QH, Shen GH, Wang DS (2013) Effects of actinomycetes agent on ginseng growth and rhizosphere soil microflora. Chin J Appl Ecol 24:87–93
Zhao J, Xue QH, Wang LN, Duan CM, Xue L, Mao N (2011) Antagonistic effect of multifunctional actinomycete strain Act12 on soil-borne pathogenic fungi and its identification. Chin J Eco-Agric 19:394–398
Zhao FJ, Ma YB, Zhu YG, Tang Z, Steve PM (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41230314), the program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team of the Chinese Ministry of Education (No. IRT0811), the open found of Engineering Research Center of Groundwater and Eco-Environment of Shaanxi Province (No. 310829151146), and Key Laboratory of Subsurface Hydrology and Ecological Effect in Arid Region of Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, S., Wang, W., Wang, F. et al. Drought-tolerant Streptomyces pactum Act12 assist phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by Amaranthus hypochondriacus: great potential application in arid/semi-arid areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 14898–14907 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6636-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6636-y